Alec Bangham
|
Read other articles:

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) الضحي الجرايح السفلى - مديرية - تقسيم إداري البلد اليمن المحافظة محافظة الحديدة المديرية �...

Part of a series onAnimal rights Overview Animal welfare Around the world History Timeline Animal cruelty Veganism Vegetarianism Primate rights in research Movement Advocates Vegans Vegetarians Groups Animal abuse Animal–industrial complex Killing Mutilation Wild animals Consumption Dogs Horses Cats Cattle Bloodsports Bullfighting Hunting Fishing Animal testing Cosmetic Captivity Zoos Circuses Oceanariums Companion animals Puppy mills Abandonment Ideas Abolitionism Animal protectionism Car...

The Wolf of Wall StreetPoster filmSutradaraMartin ScorseseProduserMartin ScorseseLeonardo DiCaprioRiza AzizJoey McFarlandEmma Tillinger KoskoffDitulis olehTerence WinterBerdasarkanThe Wolf of Wall Streetoleh Jordan BelfortPemeranLeonardo DiCaprioJonah HillMargot RobbieMatthew McConaugheyKyle ChandlerRob ReinerJon BernthalJon FavreauJean DujardinSinematograferRodrigo PrietoPenyuntingThelma SchoonmakerPerusahaanproduksiRed Granite PicturesAppian Way ProductionsSikelia ProductionsEMJAG Productio...
American freestyle skier Lane SpinaPersonal informationBorn (1962-01-03) 3 January 1962 (age 62)[1]Reno, Nevada, U.S.[2]SportCountry United StatesSportMen's freestyle skiing Medal record FIS Freestyle World Ski Championships 1991 Lake Placid Acro Skiing 1986 Tignes Acro Skiing 1989 Oberjoch Acro Skiing 1993 Altenmarkt Acro Skiing Lane Spina (born 3 January 1962)[1] is an American freestyle skier who won two medals in demonstration events of the Olympic Games;...
Cet article est une ébauche concernant le cyclisme. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Circuit du WesthoekOmloop van de Westhoek (nl) Logo de la courseGénéralités Sport cyclisme sur route Création 1955 Éditions 55 (en 2021) Catégorie UCI 1.1 Type / Format course d'un jour Périodicité annuel (mars) Lieu(x) Belgique Flandre-Occidentale Palmarès Tenant du titre Christine Majerus Plus titré(s...

ロバート・デ・ニーロRobert De Niro 2011年のデ・ニーロ生年月日 (1943-08-17) 1943年8月17日(80歳)出生地 アメリカ合衆国・ニューヨーク州ニューヨーク市身長 177 cm職業 俳優、映画監督、映画プロデューサージャンル 映画、テレビドラマ活動期間 1963年 -配偶者 ダイアン・アボット(1976年 - 1988年)グレイス・ハイタワー(1997年 - )主な作品 『ミーン・ストリート』(1973年)...

Neodymium(III) bromide Names IUPAC name Tribromoneodymium Identifiers CAS Number 13536-80-6 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ChemSpider 75394 ECHA InfoCard 100.033.528 EC Number 236-897-2 PubChem CID 83564 CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID4065527 InChI InChI=1S/3BrH.Nd/h3*1H;/q;;;+3/p-3Key: LBWLQVSRPJHLEY-UHFFFAOYSA-K SMILES Br[Nd](Br)Br Properties Chemical formula NdBr3 Molar mass 383.95g (anhydrate) 492.05 (hexahydrate) Appearance Off-white to pale green powder Densi...

Irish League 1905-1906 Competizione Irish League Sport Calcio Edizione 16ª Luogo Irlanda Formula Girone all'italiana Cronologia della competizione 1904-05 1906-07 Manuale Il campionato era formato da otto squadre e il Cliftonville e il Distillery vinsero entrambe il titolo dopo un doppio spareggio. Non vi furono retrocessioni. Classifica finale Pos. Squadra G V N P GF GS Punti 1 Cliftonville 14 7 5 2 19 8 19 1 Distillery 14 8 3 3 20 13 19 3 Linfield 14 7 3 4 21 14 17 4 Belfast Celtic 14 6 3...

Palais du parlement hellénique devant la place Syntagma à Athènes. La crise de la dette publique grecque est une crise financière ayant débuté en 2008, affectant la Grèce et menaçant de s'étendre à l'Union européenne, due à l'emballement de la dette publique de la Grèce. Cette dette pèse sur l'économie du pays de deux manières : par les craintes qu'elle fait naître chez les investisseurs sur la capacité de la Grèce à rembourser sa dette publique et par le poids du pai...

密西西比州 哥伦布城市綽號:Possum Town哥伦布位于密西西比州的位置坐标:33°30′06″N 88°24′54″W / 33.501666666667°N 88.415°W / 33.501666666667; -88.415国家 美國州密西西比州县朗兹县始建于1821年政府 • 市长罗伯特·史密斯 (民主党)面积 • 总计22.3 平方英里(57.8 平方公里) • 陸地21.4 平方英里(55.5 平方公里) • ...

Questa voce sugli argomenti porte cittadine e architetture dei Paesi Bassi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Altra immagine della Waterpoort di Sneek La Waterpoort (Porta sull'acqua) è un'antica fortificazione della cittadina di Sneek, in Frisia (Paesi Bassi), costruita all'incirca tra il 1492 e il 1613[1][2]. Serviva per limitare l'afflusso dell'acqua in città.[1][2] Sneek (Frisia, Paesi Bassi): panoram...

Para teknisi di ruang manufaktur Boeing Space and Intelligence Systems, California, tengah mempersiapkan satelit komunikasi MEASAT-3. MEASAT (disebut juga MEASAT Satellite Systems), singkatan dari Malaysia East Asia Satellite adalah operator satelit telekomunikasi milik Malaysia yang dibuat oleh Measat Satellite System Sdn Bhd.[1] Perusahaan ini pertama kali meluncurkan satelitnya yang bernama Measat pada tahun 1996 dengan dua versi sekaligus MEASAT-1 dan MEASAT-2 di bandara angkasa E...

جزء من سلسلة مقالات حولالله في الإسلام مصطلحاتالتسبيح: سبحان الله التكبير: الله أكبر الحمد: الحمد لله التشهّد: لا إله إلّا الله تعابير مرتبطة جلَّ جلاله سبحانه وتعالى عزَّ وجلّ أخرى إنَّا لله بسم الله إن شاء الله ما شاء الله استغفر الله لا حول ولا قوة إلا بالله جزاك الله أعو�...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助�...

Deva KattaShri Deva Katta, at the presentation of the film (Prasthanam) 2010LahirAndhra Pradesh, IndiaAlmamaterUniversitas Negara Bagian WaynePekerjaanSutradara, produser dan penulis Deva Kaushik Katta adalah seorang pembuat film India Amerika, yang dikenal karena karya-karyanya dalam sinema Telugu. Pada 2010, ia menyutradarai Prasthanam, yang ditayangkan di sesi Panorama India di Festival Film Internasional India.[1] Film tersebut juga memenangkan Penghargaan Kritikus Filmfare Selat...

Polish chess grandmaster (born 1989) Tomasz WarakomskiTomasz Warakomski in 2022CountryPolandBorn (1989-06-22) 22 June 1989 (age 34)Suwałki, PolandTitleGrandmaster (2017)FIDE rating2545 (May 2024)Peak rating2549 (February 2024) Tomasz Warakomski (born 22 June 1989) is a Polish chess Grandmaster (GM) (2017). Biography Tomasz Warakomski is a three-time Polish Junior Chess Championship winner in various age groups: U12 (Kołobrzeg, 2001),[1] U14 (Brody, 2003)[2] an...

2017 Georgia's 6th congressional district special election ← 2016 June 20, 2017 2018 → Georgia's 6th congressional districtTurnout58.16% Nominee Karen Handel Jon Ossoff Party Republican Democratic Popular vote 134,799 125,517 Percentage 51.78% 48.22% U.S. Representative before election Tom Price Republican Elected U.S. Representative Karen Handel Republican Elections in Georgia Federal government Presidential elections 1788–89 1792 1796 1800 1804 1808 1812...

Electoral district of New South Wales (1894–1904) Australian electorate AlmaNew South Wales—Legislative AssemblyStateNew South WalesCreated1894Abolished1904NamesakeAlma Alma was an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales from 1894 to 1904,[1][2][3] named after Alma, a locality in southern Broken Hill, now known as South Broken Hill.[4] Members for Alma Josiah Thomas easily won the seat for Labor at the 1894 ...
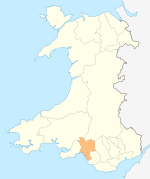
For other uses, see Seven Sisters (disambiguation). Human settlement in WalesSeven SistersWelsh: BlaendulaisSeven SistersLocation within Neath Port TalbotPopulation2,123 (2011)[1]OS grid referenceSN820088Principal areaNeath Port TalbotPreserved countyWest GlamorganCountryWalesSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townNEATHPostcode districtSA10Dialling code01639PoliceSouth WalesFireMid and West WalesAmbulanceWelsh UK ParliamentNeathSenedd Cymru ...

Febbre di vivereIl bello ma ottuso protagonista Massimo Serato in una scena del filmLingua originaleitaliano Paese di produzioneItalia Anno1953 Durata91 min Dati tecniciB/N Generedrammatico RegiaClaudio Gora SoggettoLeopoldo Trieste SceneggiaturaSuso Cecchi d'Amico, Luigi Filippo D'Amico, Claudio Gora, Lamberto Santilli, Leopoldo Trieste ProduttorePAC Film Distribuzione in italianoAtlantis Film FotografiaEnzo Serafin, Oberdan Troiani MontaggioMario Arditi MusicheValentino Bucchi ScenografiaSa...