Étienne Gilson
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel atau bagian artikel ini diterjemahkan secara buruk. Kualitas terjemahannya masih kurang bagus. Bagian-bagian yang mungkin diterjemahkan dari bahasa lain masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Anda dapat mempertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menulis ulang artikel atau bagian artikel ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pula: panduan penerjemahan artikel) ...
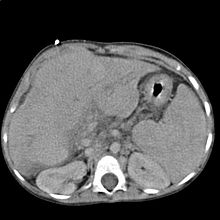
متلازمة كبدية كلوية ينتمي الكبد إلى علم الأمراض، ولكن يتم التبديل في متلازمة هتش أر أس لأن الكلى تتبع علم الأنسجة. الصورة في الأعلى ثلاثية الألوان لحالة تليف الكبد في الكبد.صورة مجهرية لقسم من الكبد مرسومة بالأحمر والأزرق والأرجواني. تظهر كميات كبيرة من التليف وبالأزرق ال...

Bola jaringMalawi (merah) melawan Fiji (biru) pada Pekan Olahraga Persemakmuran 2006.Induk organisasiInternational Federation of Netball AssociationsPertama dimainkanPertengahan hingga akhir 1890-an, InggrisKarakteristikKontak fisikTerbatasAnggota timTujuh pemain lapangan per timGender campuranKompetisi lokalKategoriDalam atau luarPeralatanBola jaringKeberadaanOlimpiadeTidak (diakui IOC, 1995) Bola jaring adalah sebuah olahraga bola besar yang dimainkan antara dua tim yang mana setiap tim ber...

Questa voce sull'argomento vescovi italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Pietro Corsettovescovo della Chiesa cattolica Incarichi ricopertiVescovo di Cefalù (1638-1643) Natoa Palermo Nominato vescovo21 giugno 1638 da papa Urbano VIII Consacrato vescovo24 giugno 1638 dall'arcivescovo metropolita Biagio Proto de Rubeis Deceduto23 ottobre 1643 a Palermo Manuale Pietro...

Sporting event delegationAustria at the2004 Summer OlympicsIOC codeAUTNOCAustrian Olympic CommitteeWebsitewww.oeoc.at (in German)in AthensCompetitors74 in 18 sportsFlag bearer Roman Hagara[1]MedalsRanked 27th Gold 2 Silver 4 Bronze 1 Total 7 Summer Olympics appearances (overview)189619001904190819121920192419281932193619481952195619601964196819721976198019841988199219962000200420082012201620202024Other related appearances1906 Intercalated Games Austria competed at the 2004 S...

Peristiwa Petrus memotong telinga Malkhus saat Yesus ditangkap di Taman Getsemane (circa 1520, Musée des Beaux-Arts de Dijon). Malkhus adalah nama seorang yang dicatat dalam Perjanjian Baru di Alkitab Kristen sebagai hamba imam kepala, bagian dari orang-orang yang menangkap Yesus Kristus di taman Getsemani beberapa jam sebelum Yesus disalibkan.[1] Dalam peristiwa itu, Petrus marah karena Yesus akan ditangkap oleh kelompok bersenjata.[1][2] Petrus mengayunkan pedangnya...

Fran Kirby Fran Kirby (2019)Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Francesca Kirby[1]Tanggal lahir 29 Juni 1993 (umur 30)Tempat lahir Reading, InggrisTinggi 157 cm (5 ft 2 in)[1]Posisi bermain PenyerangInformasi klubKlub saat ini ChelseaNomor 14Karier junior2001–2010 ReadingKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2012–2015 Reading 42 (67)2015– Chelsea 12 (9)Tim nasional‡2013– Inggris-U23 4 (1)2014– Inggris 18 (5) * Penampilan dan gol di klub senior hanya di...

Kite festival Shakrain FestivalFire work during the festivalAlso calledPoush SangkrantiTypeTraditionalDateJanuary 14 or 15 Shakrain Festival (Bengali: সাকরাইন; also known as Kite Festival and Ghuri Utsob) is an annual Bengali celebration in Dhaka, Bangladesh, observed with the flying of kites.[1] The celebration is uniquely celebrated by the Bengali Muslim Dhakaiya community based on Old Dhaka.[2] It occurs at the end of Poush, the ninth month of the Bengali cale...

American artist and illustrator (1907–1994) Picture of Stevan Dohanos while shooting Lord Calvert Whiskey ad in 1951 Stevan Dohanos (May 18, 1907 – July 4, 1994) was an American artist and illustrator of the social realism school, best known for his Saturday Evening Post covers, and responsible for several of the Don't Talk set of World War II propaganda posters.[1] He named Grant Wood and Edward Hopper as the greatest influences on his painting. Life Christmas Toys – set of fou...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: AH14 – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Asian Highway 14 (AH14) adalah sebuah bagian dari Jaringan Jalan Asia membentang sejauh 2.004 kilometer (1.245 mi) dari Hai Phong, Vietnam ke...
لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع القرار (توضيح). هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (يوليو 2021) القرار (بالإنجليزية: Decision) المؤلف أ...

Neighborhood in Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, BrazilDeodoroNeighborhoodDeodoroLocation in Rio de JaneiroShow map of Rio de JaneiroDeodoroDeodoro (Brazil)Show map of BrazilCoordinates: 22°51′18″S 43°23′07″W / 22.85500°S 43.38528°W / -22.85500; -43.38528Country BrazilStateRio de Janeiro (RJ)Municipality/CityRio de JaneiroZoneWest ZoneArea • Total46,405 ha (114,669 acres)Population (2010) • Total10 842 Deodoro is a...

Federally recognized Native American tribe Ethnic group Kaw NationTotal population3,559[2]Regions with significant populationsUnited States (OklahomaKansas)LanguagesEnglish, historically KansaReligionNative American Church, Christianity, traditional tribal religionRelated ethnic groupsother Siouan and Dhegihan peoples Water tower of the Kaw nation, along I-35 in Oklahoma KnoShr, Kansa Chief, 1853 The Kaw Nation (or Kanza or Kansa) is a federally recognized Native American tribe in Okl...

Soviet Academy of Agricultural Sciences This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Russian. (December 2012) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the Russian article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting ...

HeadshotPoster filmSutradaraTimo Tjahjanto, Kimo StamboelProduserShinjiro Nishimura, Mike Wiluan, Wicky V. Olindo, Sukhdev SinghDitulis olehTimo TjahjantoPemeran Iko Uwais Chelsea Islan Julie Estelle Zack Lee PerusahaanproduksiScreenplay Infinite FilmsTanggal rilis 8 Desember 2016 (2016-12-08) (Indonesia) Durasi117 menitNegaraIndonesiaBahasaBahasa IndonesiaPendapatankotorRp 25.646.705.000,00 Penghargaan Festival Film Indonesia 2016 Efek Visual Terbaik: Andi Novianto Headshot adalah s...

Association football club in Scotland This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Carluke Rovers F.C. – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Football clubCarluke RoversFull nameCarluke Rovers Football ClubNickname(s)The RoversFounded1887G...

Chinese polearm Gē with engraved decoration of a tiger, Warring States period (475–221 BC) Eastern Zhou bronze dagger-axe Two dagger-axes (left), alongside four jis The dagger-axe (Chinese: 戈; pinyin: gē; Wade–Giles: ko) is a type of polearm that was in use from the Longshan culture until the Han dynasty in China.[1] It consists of a dagger-shaped blade, mounted by its tang to a perpendicular wooden shaft. The earliest dagger-axe blades were made of stone. Later ve...

American grocery store chain operator No Frills Supermarkets redirects here. Not to be confused with the Canadian supermarket chain by the same name, No Frills (grocery store). Martin's Super Markets redirects here. Not to be confused with Martin's Foods, a subsidiary of The Giant Company. SpartanNash CompanyTrade nameSpartanNashCompany typePublicTraded asNasdaq: SPTNS&P 600 ComponentIndustryRetailerDistributionPredecessorsNash Finch CompanySpartan StoresGrand Rapids Wholesale Grocer...

The Quiet AmericanPoster film The Quiet AmericanSutradaraPhillip NoyceProduserStaffan AhrenbergWilliam HorbergDitulis olehChristopher HamptonRobert SchenkkanBerdasarkanThe Quiet Americanoleh Graham GreenePemeranMichael CaineBrendan FraserPenata musikCraig ArmstrongSinematograferChristopher DoylePenyuntingJohn ScottPerusahaanproduksiMiramax FilmsIntermedia FilmsDistributorMiramax FilmsTanggal rilis 9 September 2002 (2002-09-09) (Festival Film Internasional Toronto) 22 November 2...

Place in West Pomeranian Voivodeship, PolandŚwidwinŚwidwin Castle Coat of armsŚwidwinCoordinates: 53°47′N 15°46′E / 53.783°N 15.767°E / 53.783; 15.767Country PolandVoivodeshipWest PomeranianCountyŚwidwinGminaŚwidwin (urban gmina)Government • MayorPiotr FelińskiArea • Total22.38 km2 (8.64 sq mi)Elevation99 m (325 ft)Population (2018[1]) • Total15,725 • Density702/km2...