Religionen in Ungarn
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
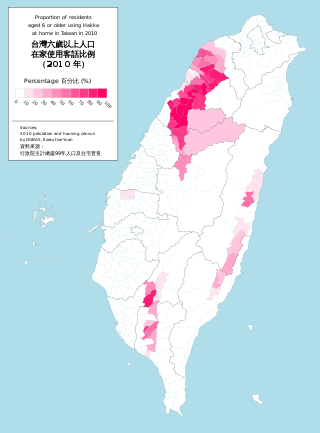
Cari artikel bahasa Cari berdasarkan kode ISO 639 (Uji coba) Kolom pencarian ini hanya didukung oleh beberapa antarmuka Halaman bahasa acak Bahasa Hakka Taiwan toiˇ vanˇ hagˋ gaˊ ngiˊ / toiˇ vanˇ hagˋ faThòi-vàn Hak-kâ-ngî / Thòi-vàn Hak-fa PengucapanSixian: [tʰoi˩ van˩ hak̚˨ fa˥]Hailu: [tʰoi˥ van˥ hak̚˨ fa˩]Dapu: [tʰoi˧ van˩˩˧ kʰak̚˨˩ fa˥˧]Raoping: [tʰoi˧ van˥ kʰak̚˥ fa˨˦]Zhao'an: [tʰai˧ ban˥˧ kʰa˥ su˥]D...

Ashish NandaDirector Indian Institute of Management, AhmedabadIn officeSeptember 2013 – April 2017 Personal detailsNationalityAmericanAlma materIndian Institute of Technology DelhiIndian Institute of Management AhmedabadHarvard UniversityOccupationProfessor Ashish Nanda is a business economist and professor who is the former Director of the Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad (IIMA).[1] Nanda joined IIMA as Director on 2 Sept 2013.[2] Upon taking charge, Nanda...

1842 work of fly tying literature by William Blacker Blacker's Art of Fly Making Frontispiece - Blacker Fly-fishing (1855)AuthorWilliam BlackerCountryGreat BritainLanguageEnglishSubjectFly fishing, Fly tyingPublisherGeorge Nichols, LondonPublication date1842Pages259 (1855 edition) Blacker's Art of Fly Making - comprising angling and dyeing of colours with engravings of Salmon and Trout flies shewing the process of the gentle craft as taught in the pages with descriptions of flies for the seas...
Le feu blanc clignotant, aussi appelé manœuvre réduite, est un signal ferroviaire de type SNCF. Définition Le feu blanc clignotant commande la marche en manœuvre sur un parcours de faible longueur. Il interdit dans tous les cas le départ en ligne d'un train. Liens externes Signalisation Ferroviaire SNCF Serveur Européen des Signalisations Ferroviaires v · mSignalisation ferroviaire en Europe Allemagne Signalisation ferroviaire allemande LZB PZB / Indusi Belgique Signalisation fer...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Ilario Preti (II) Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Attaccante Carriera Squadre di club1 1919-1925 SPAL65+ (24+) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il simbolo → indica un trasferimento in prestito. Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manua...

Town in Texas, United StatesNavarro, TexasTownLocation of Navarro, TexasCoordinates: 31°59′56″N 96°22′45″W / 31.99889°N 96.37917°W / 31.99889; -96.37917CountryUnited StatesStateTexasCountyNavarroArea[1] • Total0.67 sq mi (1.73 km2) • Land0.67 sq mi (1.73 km2) • Water0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2)Elevation417 ft (127 m)Population (2010) • Total210 ...

Berikut ini adalah daftar Presiden federal Austria (Jerman: Bundespräsident der Republik Österreichcode: de is deprecated ) sejak dibentuk tahun 1919 setelah runtuhnya Kekaisaran Austria Hungaria Kediaman utama dan tempat kerja Presiden Federal Austria adalah di Bagian Sayap Leopoldine Istana Kekaisaran Hofburg, Wina, Austria Daftar Presiden Austria (1919-Sekarang) Presiden Federal Republik Austria Pertama (1918-1938) No. Potret Nama Lahir-Wafat Periode Jabatan Partai 1 Karl Seitz (Presiden...

سوبر ماريو 3دي لاند Super Mario 3D Land (باليابانية: スーパーマリオ 3Dランド) غلاف اللعبة المطور نينتندو إنترتينمنت إي آيه دي طوكيو الناشر نينتندو الموزع نينتندو إي شوب المنتج يوشياكي كويزومي سلسلة اللعبة سوبر ماريو النظام نينتندو 3دي إس تاریخ الإصدار نينتندو 3دي إس 3 نوفمبر 20...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع قورت تبة (توضيح). قورت تبة تقسيم إداري البلد إيران إحداثيات 37°28′05″N 45°12′42″E / 37.46805556°N 45.21166667°E / 37.46805556; 45.21166667 تعديل مصدري - تعديل قورت تبة هي قرية في مقاطعة أرومية، إيران. عدد سكان هذه القرية هو 316 في سنة 2006.[1] مراجع ^ تعد�...

For other Mexico City Metro stations with Aragón in their names, see Aragon (disambiguation). Mexico City metro station Bosque de AragónSTC rapid transitStation and sign, 2012General informationLocationMexico CityMexicoCoordinates19°27′29″N 99°04′09″W / 19.458115°N 99.069192°W / 19.458115; -99.069192Line(s) (Ciudad Azteca - Buenavista)Platforms1 island platformTracks2ConstructionStructure typeAt gradeHistoryOpened15 December 1999Passengers20231,794,969 ...

Association football club in Spain Football clubCaspeFull nameClub Deportivo CaspeFounded13 March 1923; 101 years ago (1923-03-13)[1]GroundLos Rosales, Caspe,Aragon, SpainCapacity1,000[2]PresidentManuel Piazuelo Callao[3]Head coachCarlos Gil[4]LeagueTercera Federación – Group 172022–23Tercera Federación – Group 17, 12th of 16WebsiteClub website Home colours Away colours Club Deportivo Caspe is a Spanish football team based in Caspe, in...

Extinct language group of Colombia MalibuGeographicdistributionDepartment of Magdalena, ColombiaLinguistic classificationunclassifiedSubdivisions Malibú Mocana Glottolog(not evaluated)mali1242 (Malibu proper)Pre-contact distribution of the Malibu languages The Malibu languages are a poorly attested group of dead languages once spoken along the Magdalena River in Colombia. Material exists only for two of the numerous languages mentioned in the literature: Malibú and Mocana. Classificat...

1986 musicalPearls Before SwineOriginal cast recordingMusicChris HarriottLyricsDennis WatkinsBookDennis WatkinsPremiere13 May 1986: Belvoir St Theatre, SydneyProductions1986 Sydney/Melbourne 1988 Penrith Pearls Before Swine is an Australian musical with book and lyrics by Dennis Watkins and music by Chris Harriott. Billed as in the tradition of South Pacific and Apocalypse Now, it is a satirical take on Australia's involvement in the Vietnam War, suggesting that one of the world's worst caba...
Professional association football club based in Kyiv, Ukraine Football clubDynamo KyivFull nameФутбольний клуб «Динамо» КиївFootball Club Dynamo KyivNickname(s)Біло-сині (The Blue & Whites)Founded13 May 1927; 97 years ago (1927-05-13)GroundNSC OlimpiyskiyCapacity70,050OwnerIhor Surkis (63.71%)[1]Investment Fund Sports Capital (23%)[1]Alutsiana Commercial Ltd (Cyprus) (11.26%)[1]Dynamo (.66%)[1]Leonid Kravc...

Term from medieval scholastic philosophy Part of a series onJohn Duns Scotus ScotismScholasticism Univocity Haecceity Immaculate Conception Beatific vision Formal distinction Hylomorphism Scotistic realism Substance theory (ousia) Accident Substantial form Quiddity (essence / nature) Individuation Existence of God Christology Platonic realism Categories (Aristotle) Problem of universals Metaphysics Christianity and slavery WorksOpus Oxoniense Tractatus de Primo Principio Quaestiones Quodlibet...

本多 逸郎 基本情報国籍 日本出身地 愛知県犬山市生年月日 1931年5月3日没年月日 (2005-01-02) 2005年1月2日(73歳没)身長体重 175 cm67 kg選手情報投球・打席 左投左打ポジション 投手、外野手プロ入り 1950年初出場 1950年11月1日最終出場 1965年経歴(括弧内はプロチーム在籍年度) 選手歴 愛知県立犬山高等学校 中日ドラゴンズ名古屋ドラゴンズ中日ドラゴンズ (1950 - 1961、1964 - 1...

Political and economic ideology integrating libertarianism with Georgism This article is part of a series onLibertarianismin the United States Schools Agorism Anarcho-capitalism Austro Autarchism Bleeding-heart Christian Consequentialist Feminist Fusionism Geo Green Market anarchism Minarchism Natural-rights Neo Paleo Panarchism Paternalist Propertarianism Techno Transhumanist Voluntaryism Principles Anti-imperialism Civil libertarianism Constitutionalism Counter-economics Decentralization De...

Act of the Parliament of Australia that granted autonomy to the Australian Capital Territory Australian Capital Territory (Self-Government) Act 1988Parliament of Australia Long title An Act to provide for the Government of the Australian Capital Territory, and for related purposes CitationAustralian Capital Territory (Self-Government) Act 1988 (Cth)Assented to6 December 1988Introduced byAllan Holding MPStatus: Amended The Australian Capital Territory (Self-Government) Act 1988 is an Act ...

1975 book by Michel Foucault Discipline and Punish Cover of the French editionAuthorMichel FoucaultOriginal titleSurveiller et punirTranslatorAlan SheridanLanguageFrenchSubjectsPrisonsPrison disciplinePunishmentPublished 1975 (Gallimard, in French) 1977 (Pantheon Books, in English) Publication placeFranceMedia typePrint (Hardback & Paperback)Pages318ISBN0-394-49942-5 (First English edition)OCLC3328401Dewey Decimal365LC ClassHV8666 .F6813 1977 Discipline and Punish: The Birt...

13th-century trouvère The song Je vous pri, dame Maroie in the Chansonnier d'Arras Dame Margot (fl. 13th century) was a trouvère from Arras, in Picardy, France. One extant work of hers is jeu parti, a debate song, in which she debates Dame Maroie. This song, Je vous pri, dame Maroie, survives in two manuscripts,[1] which each give separate and unrelated melodies.[2] In another jeu parti she is a judge, opposing Jehan le Cuvelier d'Arras and Jehan Bretel.[3] She is li...



