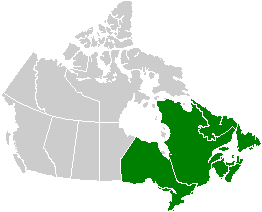
Volcanism of Eastern Canada
|
Read other articles:

Historical market district of İzmir, Turkey Hisar Mosque (1592–1598) in the Kemeraltı neighbourhood of İzmir Kemeraltı (more fully, Kemeraltı Çarşısı) is a historical market (bazaar) district of İzmir, Turkey. It remains one of the liveliest districts of İzmir. Location The district covers a vast area extending from the level of the Agora of Smyrna (the quarters of Namazgah, Mezarlıkbaşı and İkiçeşmelik), to the seashore along the Konak Square. It is bounded by the streets ...

Gereja Marais Gereja Marais adalah sebuah gereja Protestan yang terletak di arondisemen ke-4 Paris, di distrik Le Marais di 17 Rue Saint-Antoine. Awalnya dibangun sebagai biara Katolik Roma oleh Order of the Visitation of Holy Mary, yang saudara perempuannya biasa disebut Visitandines. Gereja ditutup pada Revolusi Prancis dan kemudian diberikan kepada jemaat Protestan yang melanjutkan pelayanannya hingga saat ini. Stasiun métro terdekat adalah Bastille.[1] Referensi ^ Église réform...

Dongmenying 东门营DesaGerbang desaNegaraRepublik Rakyat TiongkokMunisipalitasBeijingDistrikDistrik YanqingDaerah administrasi kota prajaZhangshanyingPopulasi • Total970 Dongmenying (Hanzi: 东门营) adalah sebuah desa berpenduduk 970 orang di Distrik Yanqing, Beijing, Tiongkok. Tahun 2018, desa ini masuk dalam daftar 44 desa di Beijing yang ditetapkan sebagai desa tradisional dan harus dilindungi.[1] Pariwisata Kuil Zhenwu. Desa ini merupakan desa terdekat dengan G...

East Village Wisma Olimpiade dan Paralimpiade London, April 2012. Dekat dengan Arena Bola Basket Ref. grid OS TQ385845 - Charing Cross 6 mi (9,7 km)* WSW Borough London Newham County seremonial Greater London Wilayah London Negara konstituen Inggris Negara berdaulat Britania Raya Kota pos LONDON Distrik kode pos E20 Kode telepon 020 Polisi Metropolitan Pemadam kebakaran London Ambulans London Parlemen&#...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (مارس 2016) القوائم التالية هي قوائم الفرق المشاركة في كأس أمم أوروبا 1964 التي أقيمت في إسبانيا، وقد لعبت ما بين تاريخ 17 ...

Peruvian football club Football clubUnión TarapotoFull nameClub Social Deportivo Unión TarapotoFounded1955GroundCarlos Vidaurre García, San MartínCapacity8,000ChairmanDaniel Escalante GómezManagerJorge CorderoLeagueCopa Perú2016Peruvian Segunda División, 16th (relegated) Home colours Away colours Unión Tarapoto is a Peruvian football club that plays in the city of Tarapoto, San Martín, Peru. Former players Fernelly Castillo Honours Regional Región II: Runner-up (1): 2007 Liga Depart...
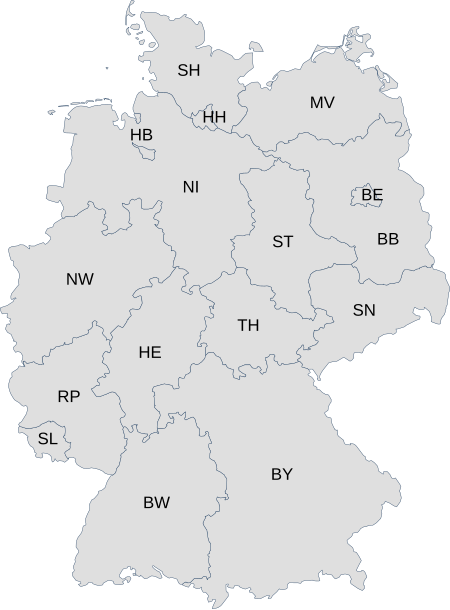
Entry for Germany in ISO 3166-2 ISO 3166-2:DE is the entry for Germany in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions (e.g., provinces or states) of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1. The current version of the standard defines codes for all 16 German states, referring to them using the German words Land (singular) and Länder (plural). Each code consists of two...

Part of a series onBritish law Acts of Parliament of the United Kingdom Year 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 1808 1809 1810 1811 1812 1813 1814 1815 1816 1817 1818 1819 1820 1821 1822 1823 1824 1825 1826 1827 1828 1829 1830 1831 1832 1833 1834 1835 1836 1837 1838 1839 1840 1841 1842 1843 1844 1845 1846 1847 1848 1849 1850 1851 1852 1853 1854 1855 1856 1857 1858 1859 1860 1861 1862 1863 1864 1865 1866 1867 1868 1869 1870 1871 1872 1873 1874 1875 1876 1877 1878 ...

Overview of television in Japan Television in Japan was introduced in 1939. However, experiments date back to the 1920s, with Kenjiro Takayanagi's pioneering experiments in electronic television.[1] Television broadcasting was halted by World War II, after which regular television broadcasting began in 1950.[2] After Japan developed the first HDTV systems in the 1960s, MUSE/Hi-Vision was introduced in the 1970s. A modified version of the NTSC system for analog signals, called ...

Mediterranean island country in the Middle East This article is about the country. For other uses, see Cyprus (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Cypress. Republic of CyprusΚυπριακή Δημοκρατία (Greek)Kıbrıs Cumhuriyeti (Turkish) Flag Coat of arms Anthem: Ὕμνος εἰς τὴν Ἐλευθερίαν[a](English: Hymn to Liberty)Location of the Republic of Cyprus in dark green, occupied territory in light greenCapitaland largest cityNicosia35...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...

恩维尔·霍查Enver Hoxha霍查官方肖像照(摄于1980年代初)阿尔巴尼亚共产党中央委员会总书记任期1943年3月—1948年11月[1]前任無(首任)继任本人(劳动党中央委员会总书记)阿尔巴尼亚劳动党中央委员会总书记任期1948年11月—1954年7月[1]前任本人(共产党中央委员会总书记)继任本人(劳动党中央委员会第一书记)阿尔巴尼亚劳动党中央委员会第一书记任期1954�...

Al-Masani' (Riyadh)PermukimanAl-Masani' (Riyadh)Location in the Kingdom of Saudi ArabiaKoordinat: 24°38′N 46°43′E / 24.633°N 46.717°E / 24.633; 46.717Koordinat: 24°38′N 46°43′E / 24.633°N 46.717°E / 24.633; 46.717Negara Arab SaudiPemerintahan • Gubernur Pangeran RiyadhFaisal bin Bandar Al Saud • Wali kotaIbraheem Mohammed Al-SultanKetinggian612 m (2,008 ft)Zona waktuUTC+3 (AST) ...

International athletics championship event19th Central American and Caribbean ChampionshipsDates4–6 JulyHost citySt. George's, Grenada VenueNational StadiumLevelSeniorEvents43[1]ParticipationAt least 318[2] athletes from 29 nations← 2001 Guatemala City 2005 Nassau → The 2003 Central American and Caribbean Championships in athletics were held in St George's, Grenada, between 4–6 July 2003. It was the first time that the country had hosted the competition.[3&...

River, tributary of the Columbia Pend OreillePend-d'Oreille, Clark ForkAlbeni Falls Dam on the Pend Oreille RiverMap of the Pend Oreille River and its main tributaries.LocationCountryUnited States, CanadaStateWashington, IdahoProvinceBritish ColumbiaCitySandpoint, IDPhysical characteristicsSourceLake Pend Oreille • locationIdaho • coordinates48°14′20″N 116°36′25″W / 48.23889°N 116.60694°W / 48.23889; -116.60694 R...

Part of a series on Ahmadiyya Beliefs and practices Tawhid Five Pillars of Islam Six articles of faith Bay'ah Distinct views Mirza Ghulam Ahmad Prophethood Jesus Jihad Evolution Days of remembrance Caliphate Day Eid al-Adha Eid al-Fitr Promised Messiah Day Promised Reformer Day Foundational texts and sciences Quran Sunnah (Hadith, Sirah) Aqidah (creed) Tafsir (exegesis) Fiqh (jurisprudence) Sharia (law) Key literature Rūhānī Khazā᾽in Malfūzāt Tafsīr-e-Kabīr Haqā'iq al-Furqān Revi...

American failed assassin (born 1930) Sara Jane MooreBornSara Jane Kahn (1930-02-15) February 15, 1930 (age 94)Charleston, West Virginia, U.S.OccupationAccountantCriminal statusParoledConviction(s)Attempted assassination of the President of the United States (18 U.S.C. § 1751)Criminal penaltyLife imprisonment Sara Jane Moore (née Kahn; born February 15, 1930) is an American criminal who attempted to assassinate U.S. President Gerald Ford in 1975.[1][2] She was given a li...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai TraXX FM. Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: Trax FM – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR TraxNama sebelumnyaMTV on Sky (2000–2002)MTV Sky (2002–2005)Trax FM (2005–2022)JenisJaringan radioSl...