The Shul of New York
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Infeksi oportunistikGambaran sinar-X seseorang yang pada awalnya menderita influenza dan kemudian berkembang menjadi pneumonia akibat infeksi Haemophilus influenzae, yang diduga bersifat oportunistikInformasi umumSpesialisasiPenyakit infeksi Infeksi oportunistik adalah infeksi yang disebabkan oleh organisme (seperti bakteri, jamur, parasit, atau virus) yang memanfaatkan kesempatan yang biasanya tidak tersedia. Kesempatan ini dapat berupa sistem imun yang melemah (misalnya akibat AIDS at...

Bagian dari seri mengenai Sejarah Indonesia Prasejarah Manusia Jawa 1.000.000 BP Manusia Flores 94.000–12.000 BP Bencana alam Toba 75.000 BP Kebudayaan Buni 400 SM Kerajaan Hindu-Buddha Kerajaan Kutai 400–1635 Kerajaan Tarumanagara 450–900 Kerajaan Kalingga 594–782 Kerajaan Melayu 671–1347 Kerajaan Sriwijaya 671–1028 Kerajaan Sunda 662–1579 Kerajaan Galuh 669–1482 Kerajaan Mataram 716–1016 Kerajaan Bali 914–1908 Kerajaan Kahuripan 1019&#...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Diah Kumorowati Marsidi (lahir dan meninggal di Jakarta, 20 April 1957 – 6 Mei 2021) merupakan jurnalis senior Kompas. Ia dikenal sebagai seorang wartawan poliglot yang menguasai beberapa bahasa asing, yaitu bahasa Prancis, Inggris, Italia, Spanyol, ...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Keajaiban Cinta – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Keajaiban CintaAlbum studio karya HelenaDirilis2 Oktober 2005GenrePopLabelPro SoundKronologi Helena Keajaiban Cinta (2005) Helena(2...

KeplerplatzLokasiFavoritenWinaAustriaJalurOperasi layanan Stasiun sebelumnya U-Bahn Wina Stasiun berikutnya Reumannplatzmenuju Oberlaa Jalur U1Südtiroler Platz-Hauptbahnhofmenuju Leopoldau Sunting kotak info • L • BBantuan penggunaan templat ini Keplerplatz adalah stasiun metro yang terletak di Jalur U1 pada U-Bahn Wina.[1] Stasiun ini terletak di distrik Favoriten dan dibuka secara resmi pada 25 Februari 1978. Referensi ^ Line U1 Leopoldau - Oberlaa. The ...

العلاقات الفرنسية المنغولية فرنسا منغوليا فرنسا منغوليا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الفرنسية المنغولية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين فرنسا ومنغوليا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة ف�...

Флаг гордости бисексуалов Бисексуальность Сексуальные ориентации Бисексуальность Пансексуальность Полисексуальность Моносексуальность Сексуальные идентичности Би-любопытство Гетерогибкость и гомогибкость Сексуальная текучесть Исследования Шк...

Clarkson performing in 2018 American singer-songwriter Kelly Clarkson has written tracks on all ten of her albums, greatest hits album, for other artists, and as well as several unreleased songs. She rose to fame after winning the inaugural season of American Idol in 2002, in which she received a recording contract with RCA Records. Clarkson began writing songs as a teenager, and one of those songs, Because of You, which she wrote at age 16 ended up on her sophomore studio album Breakaway. B...

Austrian ski area Silvretta MontafonLocationVorarlberg, AustriaNearest major citySchruns, BludenzCoordinates46°58′51″N 9°57′57″E / 46.9809°N 9.9658°E / 46.9809; 9.9658Top elevation2430 mBase elevation700 mSkiable area141 kmLift system10 cable cars18 chairlifts5 drag liftsWebsitehttps://www.silvretta-montafon.at/enThe Silvretta Montafon ski area is located in the Montafon valley in Vorarlberg (Austria). It is one of Austria's ten largest ski areas.[...

Unincorporated community in Mohave County, Arizona, US Census-designated place in Arizona, United StatesMeadview, ArizonaCensus-designated placeMeadview looking east to Grand Wash CliffsMotto(s): In Hardship, Always UnitedLocation in Mohave County, ArizonaMeadviewShow map of ArizonaMeadviewShow map of the United StatesCoordinates: 36°0′8″N 114°4′6″W / 36.00222°N 114.06833°W / 36.00222; -114.06833CountryUnited StatesStateArizonaCountyMohaveArea[1 ...

British advocate The Right HonourableThe Lord Mackay of ClashfernKT PC FRSEOfficial portrait, 2018Lord Clerk RegisterIn office27 April 2007 – November 2022MonarchsElizabeth IICharles IIIPreceded byThe Earl of WemyssSucceeded byLady Elish AngioliniShadow Lord ChancellorIn office2 May 1997 – 11 June 1997LeaderJohn MajorPreceded byThe Lord Irvine of LairgSucceeded byThe Lord KingslandLord ChancellorIn office28 October 1987 – 2 May 1997Prime MinisterMargar...

British politician Sir Charles LemonBtEarly photograph showing people, including Sir Charles Lemon, bottom left, at Carclew. Taken in August 1841 by Henry Fox Talbot, Charles' nephewBorn3 September 1784Died13 February 1868(1868-02-13) (aged 83)NationalityBritishOccupationPoliticianSpouseLady Charlotte Ann FoxstrangwaysChildrenCharles William(died aged 13 months)Charles William (died aged 12) Charlotte Augusta Caroline (died aged 10)Parent(s)William LemonJane Buller Sir Charles Lemon, 2nd...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Brownie (homonymie). Cet article est une ébauche concernant une légende. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Brownies Un brownie (scots : broonie ou brunie; gaélique écossais : brùnaidh, parfois confondu avec le gruagach) est un personnage du folklore écossais. Génie domestique sympathique et travailleur, il effectue les tâches ménagères de la fam...
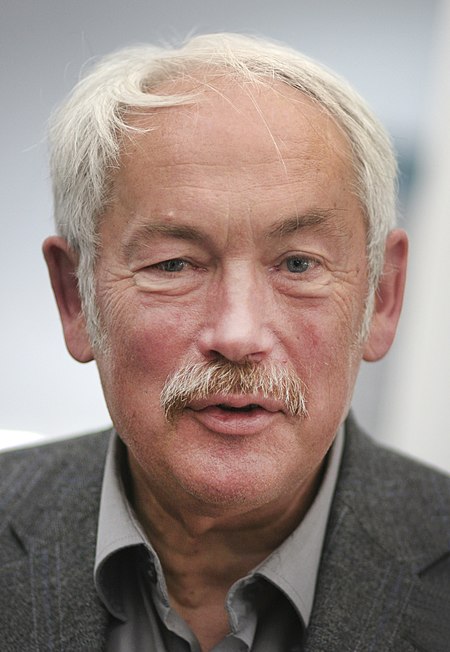
Peter GrünbergGrünberg pada tahun 2009LahirPeter Andreas Grünberg(1939-05-18)18 Mei 1939Plzeň, Protektorat Bohemia dan MoraviaMeninggal7 April 2018(2018-04-07) (umur 78)Jülich, JermanKebangsaanJermanAlmamaterUniversitas Teknologi DarmstadtDikenal atasMagnetoresistansi raksasaPenghargaanHadiah James C. McGroddy untuk Materi Baru (1994)Persatuan Fisika Murni dan Terapan Internasional Penghargaan Magnetisme(1994)Hadiah Masa Depan Jerman (1998)Medali Stern–Gerlach (2006)Penghargaan P...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Museum Gunung Kelud adalah museum khusus yang memberikan informasi tentang Gunung Kelud. Di dalam museum, pengunjung diberi tontonan berupa film dokumenter yang menampilkan keindahan Gunung Kelud dan bencana letusannya. Bangunan museum bersebelahan den...

Josh GadGad di Annie Awards ke-41 pada 2014LahirJoshua Ilan Gad23 Februari 1981 (umur 43)Hollywood, Florida, ASAlmamaterCarnegie Mellon College of Fine ArtsPekerjaanPemeran, pengisi suara, komedian, penyanyiTahun aktif2002–sekarangDikenal atasFrozenThe Book of MormonBeauty and the BeastSuami/istriIda Darvish (m. 2008)Anak2 Joshua Ilan Gad[1] (lahir 23 Februari 1981[2]) adalah seorang pemeran, pengisi suara, komedian dan penyanyi Amer...

Кубок Хопмана — ежегодный традиционный выставочный теннисный турнир, задуманный, организованный и впервые проведённый Полом Макнами и Чарли Фанкаттом, проходивший в Перте, Западная Австралия, на рубеже декабря и января. Содержание 1 Формат 2 Место проведения 3 Гарри Х...

Indice 1 Storia dell'urbanistica di Siracusa 1.1 Età antica 1.2 Età medievale 1.3 Età moderna 1.3.1 La nuova urbanizzazione di Siracusa 1.4 Suddivisioni storiche 1.4.1 Arenella 1.4.2 Canalicchio e Tremilia 1.4.3 Carrozzieri 1.4.4 Fanusa e Punta Milocca 1.4.5 Fontane Bianche e Ognina 1.4.6 Isola 1.4.7 Plemmirio e Terrauzza 1.4.8 Santa Teresa Longarini Scalo 1.4.9 Targia 1.4.10 Tivoli 1.4.11 Villaggio Santa Lucia 1.5 Suddivisioni amministrative 1.6 Suddivisioni cittadine 1.6.1 Bosco Minniti ...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Урал (значения). Урал Обложка осенних номеров журнала с 2011 г. Специализация литературно-художественный и публицистический журнал Периодичность ежемесячно Язык русский Адрес редакции 620014, Екатеринбург, ул. Малышева, �...

Desideri in un timbro postale Ippolito Desideri (Pistoia, 21 dicembre 1684 – Roma, 14 aprile 1733) è stato un gesuita e missionario italiano in Tibet, e il primo europeo esperto della cultura e lingua tibetana. Nel 1623 la prima missione cattolica in Tibet era stata fondata dal gesuita portoghese P. António de Andrade nella città di Tsaparang nel regno di Guge, Tibet Occidentale. Questo regno fu rovesciato dal vicino Re di Ladakh nel 1630, ed anche la piccola ma vigorosa missione guidata...