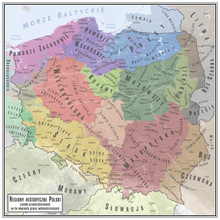
Subcarpathian Voivodeship
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Перуанский анчоус Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеГруппа:Костные рыбыКласс:Лучепёрые рыбыПодкласс:Новопёрые �...

Museum UGMBangunan Museum UGMDidirikan2013; 11 tahun lalu (2013)LokasiKompleks Perumahan Dosen UGM D6-D7, Kecamatan Depok, Kabupaten Sleman, Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta, IndonesiaJenisMuseum sejarah universitasSitus webmuseum.ugm.ac.id Museum UGM atau Museum Universitas Gadjah Mada adalah sebuah museum yang terletak di Kompleks Bulaksumur, Sleman, Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Terletak di dalam kawasan kampus UGM, museum ini didirikan oleh UGM sebagai jendela dari jati diri UGM y...

Kontes Lagu Eurovision 1989 adalah Kontes Lagu Eurovision tahunan ke-34. Acara tersebut diadakan pada 6 Mei 1989 di Lausanne, Swiss, setelah kemenangan Celine Dion di Dublin setahun sebelumnya. Acara tersebut dipandu oleh Lolita Morena dan Jacques Deschenaux. Riva, mewakili Yugoslavia, menang dengan lagu Rock Me. Ini adalah satu-satunya kemenangan untuk Yugoslavia sebagai negara bersatu.[1] Referensi ^ Eurovision Song Contest 1989. Eurovision.tv. Diakses tanggal 8 July 2013. Pra...

第三十二届夏季奥林匹克运动会柔道比賽比賽場館日本武道館日期2021年7月24日至31日項目數15参赛选手393(含未上场5人)位選手,來自128(含未上场4队)個國家和地區← 20162024 → 2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会柔道比赛个人男子女子60公斤级48公斤级66公斤级52公斤级73公斤级57公斤级81公斤级63公斤级90公斤级70公斤级100公斤级78公斤级100公斤以上级78公斤以上级团体混...
Type of video gameplay scenario that tests a player's response time Twitch game redirects here. Not to be confused with Twitch (service). This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Twitc...

American basketball player and coach (born 1948) Dave CowensCowens in 2005Boston CelticsPositionConsultantLeagueNBAPersonal informationBorn (1948-10-25) October 25, 1948 (age 75)Newport, Kentucky, U.S.Listed height6 ft 9 in (2.06 m)Listed weight230 lb (104 kg)Career informationHigh schoolNewport Catholic(Newport, Kentucky)CollegeFlorida State (1967–1970)NBA draft1970: 1st round, 4th overall pickSelected by the Boston CelticsPlaying career1970–1980, 1982–198...
提示:此条目页的主题不是中國—瑞士關係。 關於中華民國與「瑞」字國家的外交關係,詳見中瑞關係 (消歧義)。 中華民國—瑞士關係 中華民國 瑞士 代表機構駐瑞士台北文化經濟代表團瑞士商務辦事處代表代表 黃偉峰 大使[註 1][4]處長 陶方婭[5]Mrs. Claudia Fontana Tobiassen 中華民國—瑞士關係(德語:Schweizerische–republik china Beziehungen、法�...

Part of a plant producing and containing male gametes General structure of antheridia. Antheridia consist of a thin cellular layer that holds many sperm inside. Here, the diagram of a liverwort antheridium is shown. An antheridium is a haploid structure or organ producing and containing male gametes (called antherozoids or sperm). The plural form is antheridia, and a structure containing one or more antheridia is called an androecium.[1] Androecium is also the collective term for the ...

此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2022年3月11日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而被移除。 政治主題的一部分選舉/投票制度 多數/複數制 多數制 領先者當選 不可轉移單票制 有限投票制 全票制 總選票 多輪選舉制 两轮选举制 多輪絕對多數制 排序投票制 排序複選制 權變投票制(英语:Conti...

City in California, United States City in California, United StatesTrinidad, CaliforniaCityA view of Trinidad from a trail on nearby Trinidad Head on May 27, 2006.Location in Humboldt County and the state of CaliforniaA 2007 view of the coastline south of Trinidad overlooking Trinidad Bay with offshore rocks; part of the California Coastal National Monument.TrinidadLocation in the United StatesShow map of Northern CaliforniaTrinidadTrinidad (California)Show map of CaliforniaTrinidad...
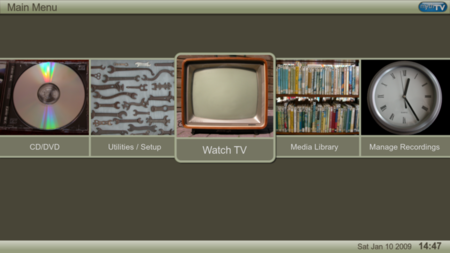
Free and open source home entertainment application MythTVA screenshot of MythTV's main menu in the default theme, TerraDeveloper(s)Isaac RichardsInitial releaseApril 10, 2002; 22 years ago (2002-04-10)Stable release34 / 10 February 2024; 5 months ago (2024-02-10) Repositorygithub.com/MythTV/mythtv Written inC, C++Operating systemLinux, FreeBSD, macOS, Windows (playback only)TypeDigital video recorderLicenseGNU GPLWebsitewww.mythtv.org MythTV is a free and ...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с такой фамилией, см. Салтыков; Салтыков, Алексей.Алексей Салтыков Имя при рождении Алексей Александрович Салтыков Дата рождения 13 мая 1934(1934-05-13)[1] Место рождения Москва, СССР[1] Дата смерти 8 апреля 1993(1993-04-08) (58 лет) Мест...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (فبراير 2016) الدوري الكويتي 1964–65معلومات عامةالرياضة كرة القدم البطولة الدوري الكويتي الفئة كرة القدم للرجال الفترة ...

Reconstructed culture of Proto-Indo-Europeans This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (January 2022) This article should specify the language of its non-English content, using {{lang}}, {{transliteration}} for transliterated languages, and {{IPA}} for phonetic transcriptions, with ...
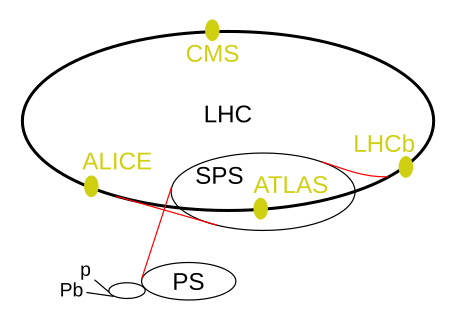
CERN LHC experiment This article is about the LHC detector at CERN. For other experiments, see Atlas (disambiguation). Large Hadron Collider(LHC)Plan of the LHC experiments and the preaccelerators.LHC experimentsATLASA Toroidal LHC ApparatusCMSCompact Muon SolenoidLHCbLHC-beautyALICEA Large Ion Collider ExperimentTOTEMTotal Cross Section, Elastic Scattering and Diffraction DissociationLHCfLHC-forwardMoEDALMonopole and Exotics Detector At the LHCFASERForwArd Search ExpeRimentSNDScattering and ...

Cavalry regiment in the British Army 8th (King's Royal Irish) HussarsCrest of the 8th King's Royal Irish HussarsActive1693–17141715–17161719–1958Country Kingdom of Ireland (1693–1800) United Kingdom (1801–1958)Branch British ArmyTypeCavalry of the Line/Royal Armoured CorpsRoleLight cavalrySize550 menRegimental HeadquartersLondonNickname(s)The CrossbeltsMotto(s)Pristinae virtutis memoresMarchQuick: The Galloping 8th HussarSlow: The Scottish ArchersAnniversariesBalaklav...

Cinema ofSpain pre-1930 1930s 1940s 1950s 1950 1951 1952 1953 19541955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960s 1960 1961 1962 1963 19641965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970s 1970 1971 1972 1973 19741975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980s 1980 1981 1982 1983 19841985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990s 1990 1991 1992 1993 19941995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000s 2000 2001 2002 2003 20042005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010s 2010 2011 2012 2013 20142015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020s 2020 2021 2022 2023 20242025 vte A list of Spanish-produced and co-pr...

United States Army general (1883–1946) For his son, the United States Army general, see Joseph Warren Stilwell Jr. General Stilwell redirects here. For other uses, see General Stilwell (disambiguation). Joseph StilwellNickname(s)Vinegar Joe, Uncle JoeBorn(1883-03-19)March 19, 1883Palatka, Florida, USDiedOctober 12, 1946(1946-10-12) (aged 63)San Francisco, California, USAllegianceUnited StatesService/branchUnited States ArmyYears of service1904–1946RankGeneralService number0-1912...

Physautotype attribué à Nicéphore Niépce (1832). Le physautotype est un procédé photographique mis au point par Nicéphore Niépce et peut-être Louis Daguerre vers 1832, avant l'invention du daguerréotype qui en est inspirée. La substance photosensible est obtenue en chauffant un peu de l'essence de lavande. Après évaporation partielle est obtenu un résidu brun. Ce goudron est dissous dans de l'alcool pour obtenir une solution jaune pâle, qui est versée sur une plaque d'argent o...

Vous lisez un « article de qualité » labellisé en 2014. Trajan Empereur romain Buste de Trajan portant la couronne civique, une courroie d'épée et l'égide (attribut de Jupiter et symbole de la toute-puissance divine). Glyptothèque de Munich. Règne 28 janvier 98 – 8/9 août 117 (19 ans, 6 mois et 12 jours) Période Antonins Précédé par Nerva Suivi de Hadrien Biographie Nom de naissance Marcus Ulpius Traianus Naissance 18 septembre 53[N 1] Italica (Bétiq...