Stanisław Kiszka
| |||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Henry JohnsonNama lahirWilliam Henry JohnsonJulukanBlack DeathLahirc. (1892-07-15)15 Juli 1892[1]Winston-Salem, Carolina Utara, Amerika SerikatMeninggal1 Juli 1929(1929-07-01) (umur 36)Washington, D.C., Amerika SerikatDikebumikanArlington National CemeteryPengabdianAmerika SerikatDinas/cabangAngkatan Darat Amerika SerikatLama dinas1917–1919PangkatSersanKesatuan369th Infantry Regiment, New York National GuardPerang/pertempuranPerang Dunia I Serangan Meuse-Argonne Peng...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Culture of Akron, Ohio – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Akron street art, derived from the graffiti subculture The culture of Akron, Ohio is an amalgamation of local features of th...

Kota orang Lewi adalah 48 kota di Israel kuno yang dikhususkan untuk suku Lewi, yang mengalokasikan wilayah mereka sendiri saat bani Israel memasuki Tanah Terjanji. Kota-kota Perlindungan (ilustrasi dari sebuah gambar Alkitab terbitan tahun 1901 karya Providence Lithograph Company) Bilangan 35:1–8 menyatakan bahwa Allah memerintahkan Musa untuk mendirikan 48 kota untuk suku Lewi, dimana enam juga dijadikan sebagai kota perlindungan untuk pembunuh. Setiap pemukiman meliputi sebuah kota berte...

Đinh Bộ LĩnhKaisar Đại Cồ ViệtPatung kaisar Đinh Tiên Hoàng di Hoa LưKaisar Đại Cồ ViệtBerkuasa968–Oktober 979PendahuluĐinh Bộ Lĩnh menamai negara sebagai Đại Cồ ViệtPenerusĐinh Phế ĐếKaisar Dinasti ĐinhBerkuasa968–10/979PendahuluDinasti didirikanPenerusĐinh Phế ĐếInformasi pribadiKelahiran22 Maret 924Gia Viễn, Provinsi Ninh Bình, Giao ChâuKematianOktober 979Hoa Lư, provinsi Ninh Bình, Đại Cồ ViệtPemakamanMakam Trường Yên, Hoa...

Scottish Division One 1910-1911 Competizione Scottish Division One Sport Calcio Edizione 21ª Organizzatore SFL Date dal 15 agosto 1910al 29 aprile 1911 Luogo Scozia Partecipanti 18 Formula Girone all'italiana A/R Risultati Vincitore Rangers(6º titolo) Statistiche Miglior marcatore Willie Reid (38) Incontri disputati 306 Gol segnati 868 (2,84 per incontro) Cronologia della competizione 1909-10 1911-12 Manuale La Scottish Division One 1910-1911 è stata la 21ª edizio...

2004 song by Sakis Rouvas Shake ItSingle by Sakis Rouvasfrom the album To Hrono Stamatao (Re-release) Released20 April 2004 (2004-04-20)Recorded2004Genre Greek (syrto - syrtaki) pop dance-pop Length3:00LabelMinos EMIComposer(s)Nikos TerzisLyricist(s)Nektarios TirakisProducer(s)Nikos TerzisSakis Rouvas singles chronology Feelings (2003) Shake It (2004) Se Thelo San Trelos (2004) Music videoShake It on YouTubeAudio samplefilehelpAlternative coverScandinavian cover Eurovision Song...

Local service district / designated place in Newfoundland and Labrador, CanadaPynns BrookLocal service district / designated placePynns BrookLocation of Pynns BrookShow map of Newfoundland and LabradorPynns BrookPynns Brook (Canada)Show map of CanadaCoordinates: 49°04′55″N 57°32′56″W / 49.082°N 57.549°W / 49.082; -57.549CountryCanadaProvinceNewfoundland and LabradorRegionNewfoundlandCensus division5Census subdivisionFGovernment • TypeUnincorpor...
Оранжевый Маврикий (1847) Красный пенни (Великобритания, 1841) Церера[фр.] на марке Корриентеса (Аргентина, 1856) Церера[англ.] (Франция, 1849) Примити́вная почто́вая ма́рка (англ. «primitives» или «natives») — почтовая марка, разработанная и напечатанная с использованием заметно боле�...

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) ...

8th President of Myanmar, from 2011 to 2016 In this Burmese name, the given name is Thein Sein. There is no family name. His ExcellencyAgga Maha Thray SithuAgga Maha Thiri ThudhammaThein Seinသိန်းစိန်Thein Sein in 20138th President of MyanmarIn office30 March 2011 – 30 March 2016Vice PresidentTin Aung Myint OoSai Mauk KhamNyan TunPreceded byThan Shwe (Chairman of the State Peace and Development Council)Succeeded byHtin KyawPrime Minister of MyanmarIn office12 ...

Federalist Paper by Alexander Hamilton Federalist No. 80 Alexander Hamilton, author of Federalist No. 80AuthorAlexander HamiltonOriginal titleThe Powers of the JudiciaryCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishPublisherThe Independent Journal, New York Packet, The Daily AdvertiserPublication dateJuly 5 – August 12, 1788Media typeNewspaperPreceded byFederalist No. 79 Followed byFederalist No. 81 Federalist No. 80 is an essay by Alexander Hamilton, the eightieth...
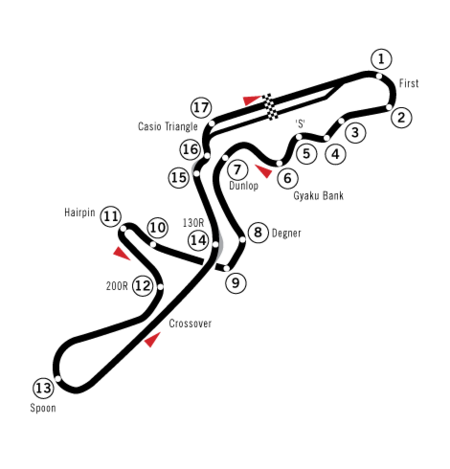
Grand Prix Jepang 1994 Lomba ke-15 dari 16 dalam Formula Satu musim 1994 Detail perlombaanTanggal 6 November 1994Nama resmi Grand Prix Jepang Televisi Fuji XXILokasi Sirkuit Suzuka, Suzuka, Mie, JepangSirkuit Fasilitas balapan permanenPanjang sirkuit 5.864 km (3.665 mi)Jarak tempuh 50 putaran, 293.200 km (183.250 mi)Rencana jarak tempuh 53 putaran, 310.792 km (194.245 mi)Cuaca Hujan berat, diikuti hujan cahayaPosisi polePembalap Michael Schumacher Benetton-FordWaktu 1’ 37,209Putaran tercepa...

Brazilian journalist and executive This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Antônio Britto – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2014) (Learn how and when to remove thi...

U.S Army Program The United States Army Art Program or U.S. Army Combat Art Program is a U.S. Army program to create artwork documenting its involvements in war and peacetime engagements. The art collection associated with the program is held by the U.S. Army Center of Military History. The United States Army Centre of Military History built the National Museum of the United States Army at Fort Belvoir that is now completed and will open when conditions allow. History War Art Unit artists Aar...
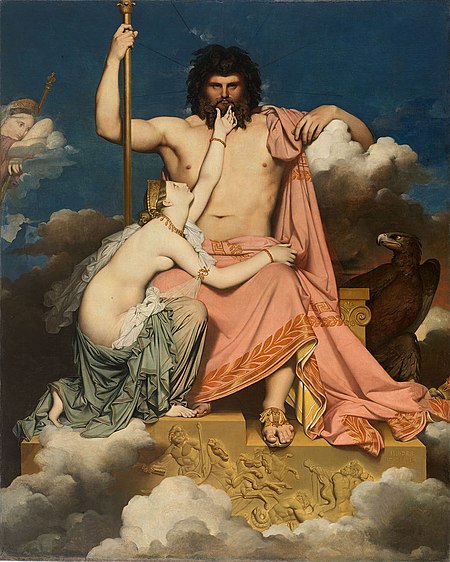

У слова «Зевс» есть и другие значения: см. Зевс (значения). Зевсдр.-греч. Ζεύς Статуя Зевса-Юпитера. I век. Эрмитаж. Санкт-Петербург. Верховный бог, повелитель неба, грома и молний Мифология Древнегреческая мифология Сфера влияния Небо, повелитель Олимпа Греческое написан...

Ritratto del decennale di TraianoAutoresconosciuto Data108 Materialemarmo Altezza56 cm UbicazioneMuseo archeologico nazionale, Venezia Il cosiddetto ritratto del decennale di Traiano è un tipo di ritratto dell'imperatore, verosimilmente prodotto in occasione del decennale della presa del potere (108), pienamente confrontabile con i conii monetali prodotti dal 108 al 111. L'opera, riprodotta in innumerevoli copie ufficiali destinate alle varie province e molto diffuso anche a Roma, ha tr...

Region of Brazil Region in BrazilNorth Region Região NorteRegionCoordinates: 3°7′45″S 60°1′17″W / 3.12917°S 60.02139°W / -3.12917; -60.02139Country BrazilLargest citiesManausBelémStatesAcre, Amapá, Amazonas, Pará, Rondônia, Roraima, and TocantinsArea • Region3,853,676.9 km2 (1,487,913.0 sq mi) • Rank1stPopulation • Region17,354,884 • Rank4th • Density4.5/km2 (12/sq mi)...
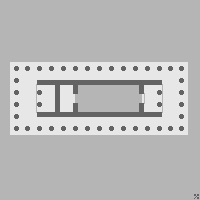
Inner chamber of Ancient Greek or Roman temples For other uses, see Cella (disambiguation). Temple layout with cella highlighted in gray In Classical architecture, a cella (from Latin 'small chamber') or naos (from Ancient Greek ναός (nāós) 'temple') is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings, of a hermit's or monk's cell, and since the 17th century, of a biological cell in plants or ani...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) ألبرتو ألفونسو معلومات شخصية الميلاد 1 مايو 1958 (66 سنة) هافانا مواطنة الولايات المتحدة الحياة العملية المدرسة الأم جامعة فلوريدا المهنة مهندس مع�...

هذه المقالة عن جهد كهربائي. لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع جهد (توضيح). جهد كهربائيمعلومات عامةالرموز الشائعة UVالتعريف الرياضي U a b = ∫ r a ( C ) r b E ⋅ d r {\displaystyle U_{\mathrm {a} \mathrm {b} }=\int \limits _{{\boldsymbol {r}}_{\mathrm {a} }({\mathsf {C}})}^{{\boldsymbol {r}}_{\mathrm {b} }}{\boldsymbol {E}}\cdot \mathrm {d} {\boldsymbol {r}}} [1][2]نظام ال...

