St Matthew's Anglican Church, Drayton
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Pertempuran BailénBagian dari Perang Peninsular The Surrender at Bailén oleh José Casado del Alisal.Tanggal18 Juli - 22 Juli 1808LokasiBailén, SpanyolHasil Kemenangan SpanyolPihak terlibat Kekaisaran Prancis Pertama Kerajaan SpanyolTokoh dan pemimpin Pierre Dupont Francisco CastañosKekuatan 24.000 orang 33.000 orang dan milisiKorban 2.200 tewas,400 terluka,17.600 ditangkap 240 tewas,730 terluka Pertempuran Bailén adalah pertempuran yang terjadi antara Spanyol yang dipimpin oleh Jendral ...

Экономика КНДР Валюта Вона КНДР (KPW, ₩) $1 ≈ 900₩ Фискальный год календарный год Статистика ВВП $48,3 млрд (номинал, 2023)[1][note 1] ~$350-400 млрд (ППС, 2023)[2][note 2] Рост ВВП ▼-0,2%(2022) ▼-0,1%(2021) ▼-4,5%(2020) ▲0,4%(2019) ▼-4,1%(2018) ▼-3,5%(2017) ▲3,9%(2016) ▼-1,1%(2015) ▲1%(2014) ВВП на душу населения 1700 долл.&...

Untuk penyair, lihat Kim Ok (penyair). Dalam nama Korea ini, nama keluarganya adalah Kim. Kim OkNama asal김옥Lahir28 Agustus 1964 (umur 59)PasanganKim Jong-il (2004–2011)Nama KoreaJosŏn-gŭl김옥 Hanja金玉 Alih AksaraGim OkMcCune–ReischauerKim Ok Kim Ok (김옥; lahir 28 Agustus 1964) adalah seorang mantan karyawati pemerintahan Korea Utara yang menjabat sebagai sekretaris pribadi Kim Jong-il dari 1980an sampai kematiannya.[1] Setelah kematian Ko Yong-hui pada Agus...

East German rower Uwe HeppnerHeppner in 1985Personal informationBorn (1962-06-26) 26 June 1962 (age 61)Merseburg, East GermanyHeight196 cm (6 ft 5 in)Weight91 kg (201 lb)SportSportRowingClubSV Halle, Halle an der Saale Medal record Representing East Germany Olympic Games 1980 Moscow Quadruple sculls World Rowing Championships 1981 Munich Quadruple sculls 1982 Lucerne Quadruple sculls 1983 Duisburg Double sculls 1985 Hazewinkel Double sculls 1979 Bled Double...

Wall and crown knotNamesWall and crown knot, Manrope knotCategoryDecorativeRelatedTurk's head knot, Underwriter's knotABoK#672, #847Instructions[1] A wall and crown knot is a decorative kind of rope button. The original use of the knot was to put at the end of the ropes on either side of a gangway leading onto a ship as stoppers. A wall and crown knot consists of a wall knot and a crown knot with doubled strands.[1].The strands of the wall knot go over, under twice, and over, while th...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori sudcoreani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Lee Yong Nazionalità Corea del Sud Altezza 180 cm Calcio Ruolo Difensore Squadra Suwon CarrieraGiovanili 1993-1998 Seul Wooi ES1999-2001 Kyungshin MS S2002-2005 Yeongdeungpo HS2006-2009 Università di Chung-AngSquadre di club1 2010-2014 Ulsan Hyundai104 (1)[1]2014-2016→ Sang...
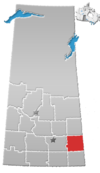
Indian reserve in Saskatchewan, Canada Indian reserve in Canada, OchapowaceOchapowace 71-70Indian reserveOchapowace Indian Reserve No. 71-70Location in SaskatchewanFirst NationOchapowaceCountryCanadaProvinceSaskatchewanArea[1] • Total64 ha (158 acres)Population (2016)[2] • Total0 • Density0.0/km2 (0.0/sq mi) Ochapowace 71-70 is an Indian reserve of the Ochapowace Nation in Saskatchewan.[1][3] It is about 1...

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддій�...
本表是動態列表,或許永遠不會完結。歡迎您參考可靠來源來查漏補缺。 潛伏於中華民國國軍中的中共間諜列表收錄根據公開資料來源,曾潛伏於中華民國國軍、被中國共產黨聲稱或承認,或者遭中華民國政府調查審判,為中華人民共和國和中國人民解放軍進行間諜行為的人物。以下列表以現今可查知時間為準,正確的間諜活動或洩漏機密時間可能早於或晚於以下所歸�...

تحتاج النصوص المترجمة في هذه المقالة إلى مراجعة لضمان معلوماتها وإسنادها وأسلوبها ومصطلحاتها ووضوحها للقارئ، لأنها تشمل ترجمة اقتراضية أو غير سليمة. فضلاً ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة بمراجعة النصوص وإعادة صياغتها بما يتناسب مع دليل الأسلوب في ويكيبيديا. This article is about the flatfish...

Group of ancient Mesopotamian deities Four copper-alloy foundation figures depicting ancient Mesopotamian gods wearing characteristic horned crowns (c. 2130 BC) The Anunnaki (Sumerian: 𒀭𒀀𒉣𒈾, also transcribed as Anunaki, Annunaki, Anunna, Ananaki and other variations) are a group of deities of the ancient Sumerians, Akkadians, Assyrians and Babylonians. In the earliest Sumerian writings about them, which come from the Post-Akkadian period, the Anunnaki are deities in the pant...

Underground coal gasificationProcess typechemicalIndustrial sector(s)oil and gas industrycoal industryFeedstockcoalProduct(s)coal gasLeading companiesAfricaryLinc EnergyCarbon EnergyMain facilitiesAngren Power Station (Uzbekistan)Majuba Power Station (South Africa)Chinchilla Demonstration Facility (Australia)InventorCarl Wilhelm SiemensYear of invention1868Developer(s)African Carbon EnergyErgo Exergy TechnologiesSkochinsky Institute of Mining Underground coal gasification (UCG) is an industr...
For women's edition, see List of current women boxing rankings. This is a list of current men's professional boxing rankings, which includes the latest rankings by each one of the sport's four major sanctioning bodies, as well as other well-regarded sites and entities. Overview As professional boxing has four major sanctioning bodies (WBA, WBC, IBF, WBO) each with their own champions, the sport doesn't have a centralized ranking system. The rankings published by these organizations share the...
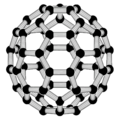
Zero-dimensional, nano-scale semiconductor particles with novel optical and electronic properties Colloidal quantum dots irradiated with a UV light. Differently sized quantum dots emit different colors of light due to quantum confinement. Part of a series of articles onNanomaterials Carbon nanotubes Synthesis Chemistry Mechanical properties Optical properties Applications Timeline Fullerenes Buckminsterfullerene C70 fullerene Chemistry Health impact Carbon allotropes Other nanoparticles Carbo...

خورفكان الاسم الكامل نادي خورفكان الرياضي الثقافي اللقب المونديالي تأسس عام 1980 الملعب ملعب صقر بن محمد(السعة: 3,000) البلد الإمارات العربية المتحدة الدوري الدوري الإماراتي للمحترفين الإدارة المدير عبد العزيز العنبري المدرب نيبويشا يوفوفيتش الموقع الرسمي موقع النادي ال...

American politician George D. O'BrienO'Brien, c. 1943Member of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Michigan's 13th districtIn officeJanuary 3, 1937 – January 3, 1939Preceded byClarence J. McLeodSucceeded byClarence J. McLeodIn officeJanuary 3, 1941 – January 3, 1947Preceded byClarence J. McLeodSucceeded byHoward A. CoffinIn officeJanuary 3, 1949 – January 3, 1955Preceded byHoward A. CoffinSucceeded byCharles Diggs Personal detailsBorn(1900-...

Voce principale: Associazione Calcio Meda 1913. Associazione Calcio Meda 1913Stagione 1999-2000Sport calcio Squadra Meda Allenatore Marco Roberto Falsettini Presidente Umberto Cassina Serie C25º posto nel girone A. Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Palumbieri (34) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Galimberti (7) 1998-1999 2000-2001 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti l'Associazione Calcio Meda 1913 nelle competizioni ufficiali della stagione 1...

Midwestern United States flooding Great Flood of 1993 Flood waters inundated parts of Jefferson City, Missouri, and limited access to the Missouri State Capitol during the Great Flood of 1993.Meteorological historyDurationApril – October 1993Overall effectsFatalities38[1] – 50[2]Damage$12–16 billion[1][2] The Great Flood of 1993 (or Great Mississippi and Missouri Rivers Flood of 1993) was a flood that occurred in the Midwestern United States, along the Mi...

Este artículo trata sobre la división administrativa británica. Para el archipiélago de las Georgias del Sur, véase Islas Georgias del Sur. Para el archipiélago de las Sandwich del Sur, véase Islas Sandwich del Sur. Islas Georgias del Sur y Sandwich del SurSouth Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (inglés) Territorio británico de ultramar BanderaEscudo Lema: Leo Terram Propriam Protegat(latín: 'Que el león defienda su propia tierra') Himno: Oh, God Hail to the South G...

1976 Venezuelan book Del buen salvaje al buen revolucionario Cover of the bookAuthorCarlos RangelPublication date1976Publication place VenezuelaPages397ISBN8437700493Followed byEl tercermundismo From the Noble Savage to the Noble Revolutionary (Spanish: Del buen salvaje al buen revolucionario) is a book published in 1976 by Venezuelan writer Carlos Rangel that seeks to explore a new interpretation of the reality of Latin America far from and opposed to, what the author conside...



