Silvery lutung
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Merpati Nusantara Airlines Penerbangan 9760Pesawat yang mirip dengan yang mengalami kecelakaanRingkasan kecelakaanTanggal2 Agustus 2009RingkasanPenerbangan terkontrol menuju daratan (menabrak gunung)LokasiPapua, IndonesiaPenumpang13Awak3Tewas16Selamat0Jenis pesawatde Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter 300OperatorMerpati Nusantara AirlinesRegistrasiPK-NVCAsalBandar Udara Sentani, Jayapura (WAJJ)TujuanBandar Udara Oksibil (WAJO) Merpati Nusantara Airlines Penerbangan 9760 adalah penerbangan...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

Comacchio commune di Italia Tempat categoria:Articles mancats de coordenades Negara berdaulatItaliaRegion di ItaliaEmilia-RomagnaProvinsi di ItaliaProvinsi Ferrara NegaraItalia Ibu kotaComacchio PendudukTotal22.017 (2023 )GeografiLuas wilayah284,13 km² [convert: unit tak dikenal]Ketinggian1 m Berbatasan denganArgenta, Italia Codigoro Lagosanto Ostellato Portomaggiore Ravenna SejarahSanto pelindungCassian of Imola (en) Informasi tambahanKode pos44022 Zona waktuUTC+1 UTC+2 Kode tele...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Sebastian CastroCastro pada Agustus 2011LahirBenjamin Brian Castro22 Desember 1989 (umur 34)Oceanside, New York, ASNama lainSeb Castro, Brian CastroPekerjaanAktor, penyanyi, seniman, selebritas internetTahun aktif2009–sekarang Benjami...

John MachinLahirc. 1686InggrisMeninggal9 Juni 1751 – 1680; umur -72–-71 tahunLondon, InggrisKebangsaanInggrisDikenal atasRumus MachinKarier ilmiahBidangMatematika dan astronomiInstitusiKampus GreshamMahasiswa ternamaBrook Taylor John Machin (bapt. c. 1686 – 9 Juni 1751),[1] seorang profesor astronomi di Kampus Gresham, London Sejarah John Machin menjabat sebagai sekretaris Royal Society dari 1718 sampai 1747. Referensi ^ Anita McConnell, ‘Machin, John (bap. 1686?...

Voce principale: Eccellenza 2012-2013. Eccellenza Toscana 2012-2013 Competizione Eccellenza Toscana Sport Calcio Edizione 22ª Organizzatore FIGC - LNDComitato Regionale Toscana Date dal 9 settembre 2012al 5 maggio 2013 Luogo Italia Partecipanti 32 Formula 2 gironi Cronologia della competizione 2011-2012 2013-2014 Manuale Il campionato italiano di calcio di Eccellenza regionale 2012-2013 è stato il ventiduesimo organizzato in Italia. Rappresenta il sesto livello del calcio ita...

Parliamentary elections 1994 European Parliament election in Belgium ← 1989 12 June 1994 1999 → 25 seats to the European Parliament First party Second party Leader Leo Tindemans José Happart Party CVP PS Alliance EPP PES Last election 4 seats, 21.14% 5 seats, 14.48% Seats won 4 3 Seat change 2 Popular vote 1,013,266 680,142 Percentage 16.98% 11.40% Swing 4.16% 3.08% Third party Fourth party Leader Willy De Clercq Freddy Wi...

Lick–Carnegie Exoplanet SurveyAlternative namesLCESWebsitewww.exoplanets.org/cps.html[edit on Wikidata] The Lick–Carnegie Exoplanet Survey (LCES) is a search for exoplanets using the Keck I optical telescope of the W. M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii. The survey is sponsored by NASA and the National Science Foundation. The survey comprises a decade of observations. The survey is led by Steven Vogt, professor of astronomy and astrophysics at University of California at Santa Cruz, an...

For the state constituency represented in the Negeri Sembilan State Legislative Assembly, see Nilai (state constituency). This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (September 2022) (Learn how ...

STANAG è l'abbreviazione NATO di Standardization Agreement (in lingua inglese: «accordo sulle norme»): una convenzione che stabilisce processi, termini e condizioni per equipaggiamenti o procedure tecniche in ambito militare tra i paesi membri dell'alleanza. Indice 1 Caratteristiche 2 Contenuto 3 Lista (parziale) 4 Note 5 Voci correlate 6 Collegamenti esterni Caratteristiche Ciascuno stato aderente al Patto Atlantico ratifica ogni STANAG e lo rende operativo nelle proprie strutture e comun...

Dog breedPembroke Welsh CorgiCommon nicknamesCorgi, Welsh Corgi, PembrokeOriginWalesTraitsHeight Males 10–12 in (25–30 cm) Females 10–12 in (25–30 cm)Weight Males 24–31 lb (11–14 kg) Females 24–28 lb (11–13 kg)Coat Medium length, thick, weather-resist double coatColor Fawn, Black & Tan, Black & White, Red, SableLife span 12 – 15 yearsKennel club standardsThe Kennel Club standardFédération Cynologique Internationale stand...

Sân bay VeronaAeroporto di Verona-Villafranca Mã IATAVRN Mã ICAOLIPX VRNVị trí sân bay ở Ý Thông tin chungKiểu sân bayDân dụng/quân sựCơ quan quản lýGardaAeroportiThành phốVerona, ÝVị tríVillafranca di VeronaPhục vụ bay thẳng cho Meridiana Neos Độ cao240 ft / 73 mTọa độ45°23′47″B 010°53′17″Đ / 45,39639°B 10,88806°Đ / 45.39639; 10.88806 (Verona Airport)Trang mạngwww.aeroportoverona.itĐườn...

Rihanna at the Cannes Film Festival in 2017 Rihanna has released four video albums and appeared in 62 music videos, 12 films, 13 television programs, and several television commercials. In 2005, Rihanna signed a recording contract with Def Jam Recordings and released her debut single Pon de Replay, taken from her first studio album Music of the Sun (2005).[1] Like its lyrical theme, the music video for the song was inspired by disco and dance;[2] it was directed by Little X.&...

This list of bridges in the Republic of Ireland lists bridges of particular historical, scenic, architectural or engineering interest. Road and railway bridges, viaducts, aqueducts and footbridges are included. Historical and architectural interest bridges Name Irish Distinction Length Type CarriesCrosses Opened Location County Ref. 1 King John's Bridge Droichead Eoin Shasana Reputed to be Ireland's oldest surviving bridge Masonry1 semi-circular arch Griffeen River 1199 to 1216 Griffeen Vall...

Žan CelarNazionalità Slovenia Altezza187 cm Peso80 kg Calcio RuoloAttaccante Squadra Lugano CarrieraGiovanili 2012-2014 Triglav2014-2017 Maribor2017-2019 Roma Squadre di club1 2016-2017 Maribor1 (0)2018-2019 Roma1 (0)2019-2020→ Cittadella10 (1)2020-2021→ Cremonese38 (4)2021- Lugano95 (40) Nazionale 2015-2016 Slovenia U-176 (2)2016-2017 Slovenia U-186 (3)2017 Slovenia U-193 (3)2019-2021 Slovenia U-2110 (1)2021- Slovenia11 (0) 1 I due nu...

Fashion in Russia and the Soviet Union This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (March 2015) ”Two Russian Beauties” by Filipp Malyavin (c.1905) Russian fashion is diverse and reflects contemporary fashion norms and the historical evolution of clothing across the Russian Federation. Russian fashion is thought to be influenced by the state's socialist ideology, the various cultures within Russia, and the cultu...

جزء من سلسلة مقالات حولبوابة المجتمع إرشادات الركائز الخمس إمكان التحقق ويكيبيديا ليست وجهة النظر المحايدة حقوق التأليف والنشر لا أبحاث غير منشورة السير الذاتية قواعد النقاش افترض حسن النية تصويت مساعدة مبتدئون تحرير الصفحات بداية مقالة تسمية المقالات روابط تصنيف تسمية...

Mathematics of change in size and age This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (January 2024) Population dynamics is the type of mathematics used to model and study the size and age composition of populations as dynamical systems. History Population dynamics has traditionally been the dominant branch of mathematical biology, which has a hist...
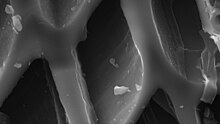
Lightweight black residue, made of carbon and ashes, after pyrolysis of biomass This article is about charcoal which goes into soil. For more general information, see Charcoal. This article may require copy editing for cohesion. You can assist by editing it. (May 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) A pile of biochar Biochar mixture ready for soil application Biochar is the lightweight black residue, consisting of carbon and ashes, remaining after the pyrolysis of biomass, and is...

Illustration de la valeur-p. X désigne la loi de probabilité de la statistique de test et z la valeur calculée de la statistique de test. Dans un test statistique, la valeur-p (en anglais p-value pour probability value), parfois aussi appelée p-valeur ou probabilité critique, est la probabilité pour un modèle statistique donné sous l'hypothèse nulle d'obtenir une valeur au moins aussi extrême que celle observée. L'usage de la valeur-p est courant dans de nombreux domaines de recher...




