Sidney Gulick
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Peta Imperium Britania pada tahun 1897, ditandai dengan warna merah muda. Pax Britannica (bahasa Latin untuk Perdamaian Britania, dinamakan menurut Pax Romana) adalah periode damai di Eropa dan dunia (1815-1914) selama Imperium Britania menguasai sebagian besar rute utama perdagangan maritim dan memperoleh kekuasaan lautan yang tak tertandingi. Peran ini tetap dipegang oleh Britania hingga akhir Perang Dunia I, dan kemudian mulai tumbang seiring dengan bangkitnya Jerman, Kekaisaran Jepang, Un...

Arsy WidiantoArsy pada tahun 2023LahirMuhammad Arsy Widianto26 November 1999 (umur 24)Jakarta, IndonesiaKebangsaanIndonesiaNama lainArsy Utungga WidiantoPendidikanSTIKOM The London School of Public RelationsPekerjaanPenyanyiTahun aktif2018KaryaDiskografiOrang tuaYovie Widianto (bapak)PenghargaanDaftar penghargaanKarier musikGenrePopbaladaInstrumenVokalTahun aktif2018–sekarangLabelUniversalArtis terkaitYovie WidiantoBrisia JodieTiara Andini Arsy Widianto (lahir 26 November 19...

Peta Kerajaan Italia (merah muda) yang menunjukkan wilayah yang diklaim oleh iredentis Italia (hijau, ungu, dan merah). Iredentisme Italia di Korsika adalah suatu gerakan budaya dan historis yang digalakkan oleh Italia dan Korsika yang mengidentifikasikan diri mereka sebagai bangsa Italia, bukan bangsa Prancis atau etnis Korsika saja, dan mendukung aneksasi Korsika oleh Italia. Sejarah Korsika merupakan bagian dari Republik Genova selama berabad-abad hingga tahun 1768, ketika Republik tersebu...

Hospital in Massachusetts, United StatesMassachusetts Eye and EarMEE Main CampusGeographyLocation243 Charles Street, Boston, Massachusetts, United StatesCoordinates42°21′38.39″N 71°04′12.09″W / 42.3606639°N 71.0700250°W / 42.3606639; -71.0700250OrganizationTypeSpecialistAffiliated universityHarvard Medical SchoolServicesEmergency department24-hour emergency ophthalmology and otolaryngology serviceBeds41[1]SpecialityOphthalmology, OtolaryngologyHisto...

USS Sara Thompson at anchor History German Empire NameGut Heil Operator German Empire BuilderWilliam Armstrong, Mitchell and Co., Newcastle, England Launched25 August 1888 FateSold to United States Navy 1918 United States NameUSS Sara Thompson (ID-3148) Namesakenamed Sara Thompson at request of previous owner Acquired8 August 1918 Commissioned17 September 1918 as Decommissioned21 July 1933 RenamedSarangani 1934 Reclassifiedas AO-8, 17 July 1920 Stricken12 December 1933 Honors andawardsW...

Acara Wilancha (pengorbanan) selama perayaan Willkakuti di desa Wilaqala, Bolivia Willkakuti (berarti Kembalinya Matahari), Machaq Mara (berarti Tahun Baru), Mara T'aqa, Jach'a Laymi atau Pacha Kuti[1] (dalam bahasa Spanyol disebut Año Nuevo Andino Amazónico (Tahun Baru Andes-Amazon)) adalah perayaan tahun baru suku Aymara. Festival ini dirayakan setiap tahun pada 21 Juni di Bolivia, Chili,[2] dan Peru[1] untuk memperingati titik balik matahari musim dingin di Belaha...
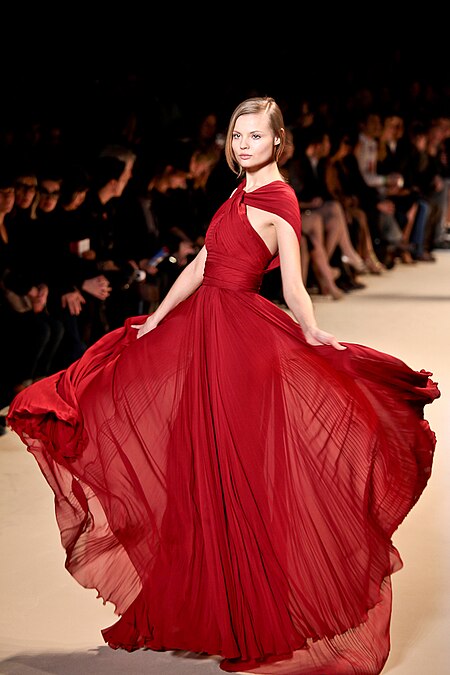

Fashion industry event in Paris, France Paris Fashion WeekMagdalena Frackowiak in Elie Saab at Paris Fashion Week F/W 2011GenreClothing and fashion exhibitionsDate(s)spring and fallFrequencysemi annualLocation(s)Paris, FranceInauguratedOctober 1–9, 1973Organised byFédération de la Haute Couture et de la ModeWebsiteOfficial website Paris Fashion Week (French: Semaine de la mode de Paris) is a series of designer presentations held semi-annually in Paris, France, with spring/summer and autum...

Walled village in Sha Tin District, Hong Kong This article is about the village in Sha Tin District. For the village in Yuen Long District, see Tai Wai Tsuen (Yuen Long District). For other uses, see Tai Wai (disambiguation). Aerial view of Tai Wai Village, surrounded by some of the modern developments of Tai Wai. Entrance gate of Tai Wai Village. Hau Wong Temple within Tai Wai Village. Wai ancestral hall within Tai Wai Village. Former Tai Wai Public School [zh] in Tai Wai Villag...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant un groupe de musique suédois. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Family Four Les Family Four en 1966, avec de gauche à droite : Berndt Öst, Inger Öst, Siw Öst et Stig Öst.Informations générales Pays d'origine Suède Genre musical Pop, schlager Années actives 1964 - 1989 Labels RCA Victor, Metronome, RCA, Polydor Composition du groupe Anciens memb...

Penghargaan HugoLogo Penghargaan HugoDeskripsiKarya fiksi ilmiah atau fantasi terbaik pada tahun sebelumnyaDipersembahkan olehWorld Science Fiction SocietyDiberikan perdana1953Situs webthehugoawards.org Penghargaan Hugo (bahasa Inggris: Hugo Awards) adalah sebuah set penghargaan sastra yang diberikan setiap tahun untuk karya-karya dan pengabdian-pengabdian fiksi ilmiah atau fantasi terbaik pada tahun sebelumnya. Penghargaan tersebut mengambil nama dari Hugo Gernsback, pendiri majalah fiks...
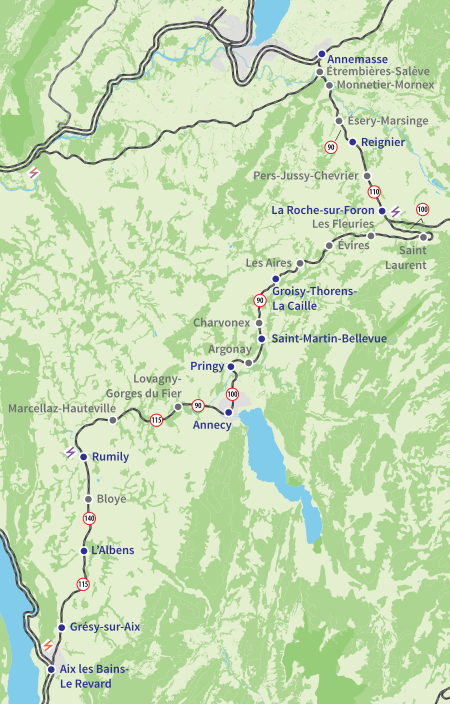
Ligned'Aix-les-Bains-Le Revard à Annemasse Carte de la ligne Un TER pour Annecy traverse le Chéran, à Rumilly. Pays France Villes desservies Aix-les-Bains, Rumilly, Annecy, La Roche-sur-Foron, Annemasse Historique Mise en service 1866 – 1884 Électrification 1950 – 1954 Concessionnaires PLM (1863 – 1937)SNCF (1938 – 1997)RFF (1997 – 2014)SNCF (depuis 2015) Caractéristiques techniques Numéro officiel 897 000 Longueur 94,646 ...

Public bath in Malmö, Sweden This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Ribersborgs open-air bath – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Ribersborg open-air bathhouse (Ribersborgs kallbadhus in Swedish, also known as Ribban by the older an...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Benavente (homonymie). Combat de Benavente Les hussards britanniques à Benavente, le 29 décembre 1808, par William Barnes Wollen. Informations générales Date 29 décembre 1808 Lieu Benavente, Espagne Issue Victoire britannique Belligérants France Royaume-Uni Commandants Charles Lefebvre-Desnouettes Henry Paget Forces en présence 550 hommes 600 hommes Pertes 30 tués 25 blessés70 prisonniers[note 1] 50 tués ou blessés[1] Guerre d'EspagneBatailles Cam...

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддій�...

SuraiyaPelafalanSu-rai-yaaLahirSuraiya Jamal Sheikh(1929-06-15)15 Juni 1929Lahore, Punjab, British India(now in Punjab, Pakistan)Meninggal31 Januari 2004(2004-01-31) (umur 74)Mumbai, Maharashtra, IndiaMakamBadakabarastan, Marine Lines, Mumbai, MaharashtraTempat tinggalKrishna Mahal, Marine Drive, Mumbai, Maharashtra, IndiaKebangsaanIndianNama lainBaby Suraiya (sebagai artis cilik)Warga negaraIndiaPekerjaanAktris dan penyanyi playback pada filmnya (dalam Bollywood)Tahun aktif19...

Scottish philosopher and ethicist (born 1987) William MacAskillMacAskill in 2015BornWilliam David Crouch (1987-03-24) 24 March 1987 (age 37)Glasgow, ScotlandEducation Jesus College, Cambridge (BA, 2008) St Edmund Hall, Oxford (BPhil, 2010) St Anne's College, Oxford (DPhil, 2014) Spouse Amanda Askell (divorced)[1]EraContemporary philosophyRegionWestern philosophyInstitutions Emmanuel College, Cambridge Lincoln College, Oxford Global Priorities Institute T...

Ernesto De Martino Ernesto De Martino (Napoli, 1º dicembre 1908 – Roma, 9 maggio 1965) è stato un antropologo, storico delle religioni e filosofo italiano. Indice 1 Biografia intellettuale 2 Il concetto di 'presenza' 2.1 Il folklore progressivo 3 Crisi della presenza e destorificazione del negativo 4 L'elaborazione del lutto ed il pianto rituale antico 5 Opere 6 Note 7 Bibliografia 8 Voci correlate 9 Altri progetti 10 Collegamenti esterni Biografia intellettuale Ernesto De Martino nacque ...

Not to be confused with Assisted suicide. This article is about the legality of euthanasia of humans. For euthanasia performed on animals, see Animal euthanasia. Current status of euthanasia around the world: Active voluntary euthanasia legal (Belgium, Canada, Colombia, Ecuador, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Portugal,[a] Spain, and the Australian states of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and Western Australia) Passi...

Статуя Давида, Микеланджело Основная статья: Периодизация мирового искусства Западное искусство, западноевропейское искусство — искусство европейских стран, а также тех регионов, которые следуют европейским культурным традициям (например, Северная Америка). Содержан�...

Dutch painter (1603 – 1655) Herman van SwaneveltSelf-portraitBorn1603WoerdenDied1655ParisKnown forPainting Herman van Swanevelt (1603 – 1655) was a Dutch painter and etcher from the Baroque era. Life Herman was born in Woerden to a family of thriving artisans whose ancestors included the famous painter Lucas van Leyden. The identity of Swanevelt’s teacher remains a mystery. A new hypothesis suggests that he was a pupil of Willem Buytewech.[1] He painted his first signed...
