J. T. Gulick
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Kedaung (disambiguasi). Kedaung Parkia timoriana Status konservasiRisiko rendahIUCN153891751 TaksonomiDivisiTracheophytaSubdivisiSpermatophytesKladAngiospermaeKladmesangiospermsKladeudicotsKladcore eudicotsKladSuperrosidaeKladrosidsKladfabidsOrdoFabalesFamiliFabaceaeSubfamiliMimosoideaeTribusMimoseaeGenusParkiaSpesiesParkia timoriana Merr., 1910 Tata namaBasionimInga timoriana (en) lbs Kedaung[1][a] atau kedawung (Parkia timoriana) adalah pohon kayu ...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Ki Empu Sungkowo Harumbrodjo merupakan keturunan ke-17 dari salah satu empu majapahit yang bernama Empu Tumenggung Supodriyo. Ia merupakan seorang pembuat keris. Kerahliannya membuat keris terasah sejak ia membatu ayahnya, Epu Djeno Harumbrodjo pada 19...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Republik Kongo. Republik Demokratik KongoRépublique démocratique du Congo (Prancis)Repubilika ya Kôngo ya Dimokalasi (Kongo)Republíki ya Kongó Demokratíki (Lingala)Jamhuri ya Kidemokrasia ya Kongo (Swahili)Ditunga dia Kongu wa Mungalaata (Tshiluba) Bendera Lambang Semboyan: Justice, Paix, Travail (Prancis: Keadilan, Perdamaian, Pekerjaan)Lagu kebangsaan: Debout Congolais (Indonesia: Bangkitlah Bangsa Kongo) Perlihatkan BumiPerlihatkan peta AfrikaPer...

Artikel ini perlu diterjemahkan ke bahasa Indonesia. Artikel ini ditulis atau diterjemahkan secara buruk dari Wikipedia bahasa selain Indonesia. Jika halaman ini ditujukan untuk komunitas berbahasa tersebut, halaman itu harus dikontribusikan ke Wikipedia bahasa tersebut. Lihat daftar bahasa Wikipedia. Artikel yang tidak diterjemahkan dapat dihapus secara cepat sesuai kriteria A2. Jika Anda ingin memeriksa artikel ini, Anda boleh menggunakan mesin penerjemah. Namun ingat, mohon tidak menyalin ...

Acute sense of self-awareness, a preoccupation with oneself Not to be confused with Self-awareness, Self-concept, Self-image, or Self-perception theory. Part of a series onThe Self Constructs Self-knowledge (psychology) Self-image Self-concept Self-schema Theories Neural basis of self Self-categorization theory Processes Self-perception theory Self-awareness Self-reflection Self-consciousness Value judgment Self-esteem True self and false self As applied to activities Self-assessment Self-eff...

Part of a series onBritish law Acts of Parliament of the United Kingdom Year 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 1808 1809 1810 1811 1812 1813 1814 1815 1816 1817 1818 1819 1820 1821 1822 1823 1824 1825 1826 1827 1828 1829 1830 1831 1832 1833 1834 1835 1836 1837 1838 1839 1840 1841 1842 1843 1844 1845 1846 1847 1848 1849 1850 1851 1852 1853 1854 1855 1856 1857 1858 1859 1860 1861 1862 1863 1864 1865 1866 1867 1868 1869 1870 1871 1872 1873 1874 1875 1876 1877 1878 ...

Les prix du Gouverneur général sont une collection de prix annuels présentés par le gouverneur général du Canada, reconnaissant la distinction dans de nombreux domaines littéraires, artistiques et sociaux. Prix littéraires du Gouverneur général Article principal : Prix littéraire du Gouverneur général. Les prix littéraires du Gouverneur général récompensent les meilleures œuvres de littérature canadienne de l'année[1]. Régis par le Conseil des arts du Canada, ils son...

Dux ArabiaeLa diocesi d'Oriente nel 400, ai tempi della Notitia dignitatum. Descrizione generaleAttivafine IV secolo - V secolo NazioneImpero romano Tipocomandante del limes arabicus Voci su unità militari presenti su Wikipedia Il Dux Arabiae era il comandante di truppe limitanee di un settore del limes romano orientale, nella diocesi d'Oriente della provincia d'Arabia. Suo diretto superiore era al tempo della Notitia dignitatum (nel 400 circa), il magister militum per Orientem. Indice 1 Ele...

This article's tone or style may not reflect the encyclopedic tone used on Wikipedia. See Wikipedia's guide to writing better articles for suggestions. (October 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Type of formal dining The historical form of service à la russe (French: [sɛʁvis a la ʁys]; 'service in the Russian style') is a manner of dining with courses brought to the table sequentially, and the food portioned on individual plates by the waiter (typically from a side...

Jeremiah WrightLahirJeremiah Alvesta Wright, Jr.22 September 1941 (umur 82)Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Jeremiah Alvesta Wright, Jr., (kelahiran 22 September 1941) adalah seorang pastur dan guru spiritual dari Barack Obama yang merupakan anak dari seorang pendeta. Ayahnya, Jeremiah Alvesta Wright adalah seorang pastur di gereja Grace Baptist pada tahun 1938 sampai dengan 1980. Ibunya dalah seorang guru yang menjadi orang hitam pertama yang mengajar Germantown High dan Philadelphia High Sc...

FornacifrazioneLocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Lombardia Provincia Brescia Comune Brescia Flero Castel Mella TerritorioCoordinate45°30′02″N 10°10′04″E / 45.500556°N 10.167778°E45.500556; 10.167778 (Fornaci)Coordinate: 45°30′02″N 10°10′04″E / 45.500556°N 10.167778°E45.500556; 10.167778 (Fornaci) Altitudine140 m s.l.m. Abitanti2 651[1] (2018) Altre informazioniCod. postale25131 P...

Fourth Division 1962-1963 Competizione Fourth Division Sport Calcio Edizione 5ª Organizzatore Football League Date dal 18 agosto 1962al 23 maggio 1963 Luogo Inghilterra Galles Partecipanti 24 Formula girone all'italiana A/R Risultati Vincitore Brentford(1º titolo) Altre promozioni Crewe AlexandraMansfield TownOldham Athletic Statistiche Miglior marcatore Ken Wagstaff (34) Incontri disputati 552 Gol segnati 1 755 (3,18 per incontro) Cronologia della competi...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助�...

Israeli communications satellite operator For other uses, see Spacecom (disambiguation). Space Communication Ltd.Company typePublicTraded asTASE: SCCIndustryCommunicationsFounded1993; 31 years ago (1993)HeadquartersRamat Gan , Israel RevenueNIS 513.226 million (2017) [1]Operating incomeNIS 46.7 million (2017) [1]Net incomeNIS 94.2 million (2017) [1]Total equityNIS 826.9 million (2017) [1]ParentEurocom GroupWebsitehttps://www.amo...
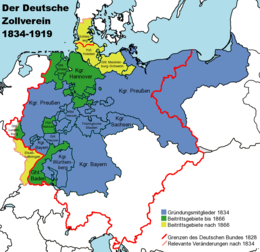
Німецький митний союз 1834–1919 рр.синій = на момент створеннязелений = розширення до 1866 рокужовтий = розширення після 1866 рокучервоний = кордони Німецького союзу станом на 1828 рікрожевий = зміни кордону після 1834 року. Німецький митний союз (нім. Deutsche Zollverein) був створений де�...

Monte CarloTheatrical release posterSutradaraThomas BezuchaProduserNicole KidmanDenise Di NoviArnon MilchanAlison GreenspanSkenarioThomas BezuchaApril BlairMaria MaggentiCeritaKelly BoweBerdasarkanHeadhunters (novel)oleh Jules BassPemeranSelena GomezLeighton MeesterKatie CassidyJuliette DumouchelPierre BoulangerAndie MacDowellCory MonteithPenata musikMichael GiacchinoSinematograferJonathan BrownPenyuntingJeffrey FordPerusahaanproduksiRegency EnterprisesDi Novi PicturesBlossom FilmsDistr...

Conca del NaviglioLa Conca di Viarenna in Via Conca del Naviglio Stato Italia Regione Lombardia Provincia Milano Città Milano CircoscrizioneMunicipio 1 Altri quartieriCentro storico · Brera · Porta Tenaglia · Guastalla · Conca del Naviglio · Bottonuto Conca del NaviglioConca del Naviglio (Milano) La Conca del Naviglio è un quartiere in centro Milano, facente parte del municipio 1. Conserva i resti della conca e alcuni resti dell'anfiteatro romano...

Daftar keuskupan di Haiti adalah sebuah daftar yang memuat dan menjabarkan pembagian terhadap wilayah administratif Gereja Katolik Roma yang dipimpin oleh seorang uskup ataupun ordinaris di Haiti. Konferensi para uskup Haiti bergabung dalam Konferensi Waligereja Haiti. Per Juni 2020, terdapat 10 buah yurisdiksi, di mana 2 merupakan keuskupan agung dan 8 lainnya merupakan keuskupan sufragan. Daftar keuskupan Provinsi Gerejawi Cap-Haïtien Keuskupan Agung Cap-Haïtien: Launay Saturné Keuskupan...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: 獅子坪駅 – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2019年3月) 獅子坪駅 ししへい shiziping ◄唐家院子 重慶北...

Institut Agama Islam Negeri TakengonIAIN Takengon Tampilkan peta yang diperbesarTampilkan peta yang diperkecil InformasiNama sebelumnyaSTAIN Gajah Putih TakengonMotoHighland Islamic CampusJenisPerguruan Tinggi Islam NegeriDidirikan18 September 2007AfiliasiKementerian Agama RIAfiliasi keagamaanIslamRektorDr. Zulkarnain, M.Ag [1]Staf akademik132 [2]Jumlah mahasiswa1.212AlamatJl. Aman Dimot No.10, Lut Tawar, Takengon, Aceh, Indonesia4°37′22.3″N 96°50′43.2″...
