Semyon Frank
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Jejak VEB Autoreparaturwerk Dresden Volkseigener Betrieb (Indonesia: Perusahaan Milik Publik, disingkat VEB) dulu adalah badan hukum utama dari industri-industri di Jerman Timur. VEB dibentuk pasca nasionalisasi massal antara tahun 1945 hingga awal dekade 1960-an, serta penyerahan kembali sekitar 33 perusahaan yang sebelumnya diambil alih oleh Uni Soviet sebagai pampasan pada tahun 1954.[butuh rujukan] Direktur utama VEB disebut sebagai Werkleiter, Werkdirektor, atau Betriebsdirektor ...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Maret 2016. MIN PadakatonInformasiJenisMadrasah ibtidaiyah negeriKepala SekolahDrs. H. Nasir, M.Pd.Rentang kelasI - VIAlamatLokasiJl. K Mimbar 6 Padakaton, Kabupaten Brebes, Jawa Tengah, IndonesiaMoto MIN Padakaton, merupakan salah satu Madrasah ibtidaiya...

Komando Distrik Militer 1316/BoalemoLambang Resmi Korem 133/Nani WartaboneDibentuk22 November 2022Negara IndonesiaAliansiKorem 133/NWBCabangTNI Angkatan DaratTipe unitKodimPeranSatuan TeritorialBagian dariKodam XIII/MerdekaMakodimTilamuta, Kabupaten BoalemoJulukanKodim 1315/BoalemoPelindungTentara Nasional IndonesiaMoto Baret H I J A U Ulang tahun22 November TokohKomandanLetkol Arm. SuryadiKepala Staf- Komando Distrik Militer 1316/Boalemo atau Kodim 1316/Boalemo merupakan satua...

الرابطة الكمبودية 2013 تفاصيل الموسم الرابطة الكمبودية البلد كمبوديا المنظم اتحاد كمبوديا لكرة القدم عدد المشاركين 10 الرابطة الكمبودية 2012 الرابطة الكمبودية 2014 تعديل مصدري - تعديل الرابطة الكمبودية 2013 هو موسم من الرابطة الكمبودية. أشرف على تنظيمه ات...

Pour l’article homonyme, voir Cornelius Becker Philip. Cornelius BeckerBiographieNaissance 24 octobre 1561LeipzigDécès 25 mai 1604 (à 42 ans)LeipzigFormation Thomasschule zu LeipzigUniversité de LeipzigActivités Théologien, psalmiste, professeur d'université, prêtreAutres informationsA travaillé pour Université de Leipzigmodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Cornelius Becker était un théologien luthérien saxon et un poète né à Leipzig le 24 octobre 1561 et d�...

Palazzo PretorioPalazzo Pretorio visto da piazza Farinata degli UbertiLocalizzazioneStato Italia RegioneToscana LocalitàEmpoli IndirizzoPiazza Farinata degli Uberti Coordinate43°43′09.59″N 10°56′46.1″E / 43.71933°N 10.94614°E43.71933; 10.94614Coordinate: 43°43′09.59″N 10°56′46.1″E / 43.71933°N 10.94614°E43.71933; 10.94614 Informazioni generaliCondizioniIn uso Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Palazzo Pretorio è l'antico pa...

Canadian television host, author and cook Mary BergMary Berg at the 2019 CFC Garden PartyBorn (1989-12-13) 13 December 1989 (age 34)Pickering, Ontario, CanadaAlma mater Wilfrid Laurier University University of Toronto Occupations Insurance broker (former) Cook TV host Author Known for Masterchef Canada Mary's Kitchen Crush Websitewww.asmallstove.com Mary Berg is a Canadian television host, author and cook, who rose to fame as the winner of the third season of MasterChef Canada....

Group command element of the Royal Air Force No. 38 Group RAFNo. 38 Group badgeActive6 November 1943 – 31 January 19511 January 1960 – 18 November 198331 October 1992 – 1 April 20001 July 2014 – 31 December 2020Country United KingdomBranch Royal Air ForceTypeRoyal Air Force groupPart ofRAF Transport CommandRAF Air Support CommandRAF Strike CommandRAF Air CommandMotto(s)Par Nobile Fratrum (Latin for 'A noble pair of brothers')[1]InsigniaGroup badge herald...

Questa voce sull'argomento registi irlandesi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. John Crowley a Dinard nel 2008 John Crowley (Cork, 19 agosto 1969) è un regista irlandese. Il regista irlandese è noto perlopiù per i suoi film Intermission (2003) e Boy A (2007). Molto attivo anche nel teatro, ha diretto numerose prime di Broadway. Indice 1 Filmografia 1.1 Cinema 1.2 Televisione 2 Premi e nomination 3 Altri progetti 4 Collegamenti esterni ...

ХуторМутилинский 49°50′59″ с. ш. 41°15′22″ в. д.HGЯO Страна Россия Субъект Федерации Ростовская область Муниципальный район Верхнедонской Сельское поселение Казанское История и география Часовой пояс UTC+3:00 Население Население →2[1] человека (2010) Название �...

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) ...

فخري عازر معلومات شخصية مواطنة مصر الحياة العملية المهنة ممثل تعديل مصدري - تعديل فخري عازر (ممثل) فخري عازر ممثل مصري [1] بدأ مشواره الفني في خمسينيات القرن العشرين وشارك في عدد كبير من الأعمال التلفزيونية وبعض الأفلام وبلغ رصيد أعماله 86 عملاً (65 مسلسل – 3 سهر�...

County in Florida, United States Consolidated city-county in FloridaDuval CountyConsolidated city-countyCity of Jacksonville and Duval CountyDuval County CourthouseLocation within the U.S. state of FloridaFlorida's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 30°20′N 81°39′W / 30.33°N 81.65°W / 30.33; -81.65Country United StatesState FloridaFoundedAugust 12, 1822[1]Named forWilliam Pope DuvalSeatJacksonvilleLargest cityJacksonvilleGovernment •&...

Se ha sugerido que esta página sea renombrada como «Universidad Harvard». Motivo: los argumentos están expuestos en la página de discusión. «Harvard» redirige aquí. Para otras acepciones, véase Harvard (desambiguación). Universidad de Harvard Harvard University Escudo de la Universidad de Harvard La Escuela de negocios Harvard (izquierda), Harvard Kennedy School (derecha) y Weeks Footbridge al atardecer.Sigla H.U.Lema Veritas«Verdad»Tipo Universidad privadaFundación 8 de septie...

29-та зенітна дивізія (Третій Рейх)29. Flak-Division Акустична станція наведення зенітних гармат на цілі.На службі 27 лютого — 8 травня 1945Країна Третій РейхНалежність ВермахтВид ЛюфтваффеРоль Війська протиповітряної оборониЧисельність зенітна дивізіяУ складі Ди�...
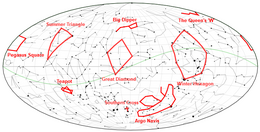
Pattern of stars recognized on Earth's night skyThis article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Asterism astronomy – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message)A picture of stars, with a group of appearingly bright blue and white stars. The bright s...

English pop rock band DexysDexys at Cambridge Corn Exchange in 2012Background informationAlso known asDexys Midnight RunnersThe Emerald ExpressOriginBirmingham, EnglandGenresPop rocknew waveblue-eyed soulCeltic folkYears active1978–1986, 2003–presentLabelsOddballEMIMercuryBMGWindsongAbsolute Dexys100% / WarnerMembersKevin RowlandJim PatersonSean ReadMichael TimothyPast membersSee members sectionWebsitedexysofficial.com Dexys Midnight Runners (currently formally Dexys, their former nicknam...

Script used to write the Greek language Greek alphabetEllinikó alfávitoGreek alphabet in the modern Greek languageScript type Alphabet Time periodc. 800 BC – present[1][2]DirectionLeft-to-right Official scriptGreeceCyprusEuropean UnionLanguagesGreekRelated scriptsParent systemsEgyptian hieroglyphsProto-Sinaitic alphabetPhoenician alphabetGreek alphabetChild systemsGothicGlagoliticCyrillicCopticArmenianOld Italic and thus Latin and RunicGeorgianAnatolianISO 15924...

إختراع الهاتفمعلومات عامةالبداية 1876 التأثيراتأحد جوانب هاتف تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات هاتف ميتوشى . فنان يرسم ألكساندر جراهام بيل يتحدث إلى هاتف نموذجي مبكر كان اختراع الهاتف تتويجا للعمل الذي قام به العديد من الأفراد، وأدى إلى مجموعة من الدعاوى القضائية الم�...
Liga del Fútbol Profesional Boliviano 1998 Competizione Liga del Fútbol Profesional Boliviano Sport Calcio Edizione 22ª Organizzatore Liga del Fútbol Profesional Boliviano Luogo Bolivia Cronologia della competizione 1997 1999 Manuale La Liga de Fútbol Profesional Boliviano 1998 è stata la 22ª edizione della massima serie calcistica della Bolivia, ed è stata vinta dal Blooming. Indice 1 Formula 2 Torneo Apertura 2.1 Classifica 3 Torneo Clausura 3.1 Fase a gironi 3.1.1 Gruppo A 3...


