Richard H. Jackson
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

DB class 624 / 634A class 624 at Oldenburg main stationType and originPower typeDiesel-hydraulicBuilderMAN AG, Waggonfabrik UerdingenBuild date1961 (prototypes)1964-1968 (regular)SpecificationsConfiguration: • AARB'2' + 2'2' + 2'B' (standard configuration)Gauge1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in)Axle load12 t (12 long tons; 13 short tons)Prime moverMANEngine typeDiesel enginePerformance figuresMaximum speed120 km/h (75 mph) (class 624)140 ...

God video game This article is about the 2001 video game. For the Pokémon games, see Pokémon Black and White. For other uses, see Black and white (disambiguation). 2001 video gameBlack & WhitePC black coverDeveloper(s)Lionhead StudiosPublisher(s)Electronic ArtsFeral Interactive (Mac)Director(s)Steve JacksonDesigner(s)Peter MolyneuxProgrammer(s)Peter MolyneuxMark WebleyJonty BarnesArtist(s)Paul McLaughlinMark HealeyAndy BassChristian BraveryWriter(s)James LeachComposer(s)Russell ShawPlat...

Political subdivision in Malaysia This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Kijal state constituency – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2020) Kijal Terengganu constituencyState constituencyLegislatureTerengganu State Legislative AssemblyMLA Razali Idri...

Institut équin d’YpäjäPrésentationType Institution de formationPatrimonialité Site culturel construit d'intérêt national en Finlande (d)Bâtiment protégé dans le Registre du patrimoine bâti (d)LocalisationLocalisation Agricultural Research Centre (d) Ypäjä FinlandeCoordonnées 60° 48′ 14″ N, 23° 17′ 52″ Emodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata L’ institut équin d’Ypäjä est un établissement finlandais d’éducation agr...

Ash, come compare su un sigillo del faraone Peribsen (ca. 2740 a.C.) Ash (anche Sha) è una divinità egizia appartenente alla religione dell'antico Egitto. Dio delle oasi[1] e dei vigneti della zona occidentale del Delta del Nilo[1], era venerato come una divinità benefica. Nella sua spedizione del 1923 a Saqqara, l'egittologo inglese Flinders Petrie individuò diversi riferimenti ad Ash su etichette di giare di vino dell'Antico Regno: Io sono rinfrescato da questo Ash, era ...

وزارة الإعلام والشتات تفاصيل الوكالة الحكومية البلد إسرائيل تأسست 1967 الإدارة منصب المدير وزارة الإعلام والشتات [لغات أخرى] موقع الويب الموقع الرسمي تعديل مصدري - تعديل وزارة الإعلام والشتات (بالعبرية: משרד ההסברה והתפוצות) هي وزارة في الحكومة ال...
Pandurii Târgu JiuCalcio Minerii (Minatori) Segni distintiviUniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Terza divisa Colori sociali Azzurro, bianco Dati societariCittà Târgu Jiu Nazione Romania ConfederazioneUEFA Federazione FRF Fondazione1962 Scioglimento2022StadioStadionul Tudor Vladimirescu(9.200 posti) Sito webwww.pandurii-tg-jiu.ro PalmarèsSi invita a seguire il modello di voce Il Clubul Sportiv Pandurii Lignitul Târgu Jiu, noto come Pandurii Târgu Jiu o semplicemente Pandurii, è stata u...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Горностай (значения). Горностай Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:Челюстнороты...

Book by E.V. Timms The Big Country First editionAuthorE. V. TimmsAlma TimmsCountryAustraliaLanguageEnglishSeriesGreat South Land SagaPublisherAngus and RobertsonPublication date1962Preceded byRobina Followed byTime and Chance The Big Country is an 1962 Australian novel by E. V. Timms and Alma Timms. It was the eleventh in the Great South Land Saga of novels. E. V. Timms died in 1960, before the novel was finished so his wife Alma completed it.[1][2] He die...

KikiPoster rilis teatrikalSutradaraSam TaylorProduserJoseph M. SchenckSkenarioSam TaylorBerdasarkanSandiwara:David Belasco André PicardPemeranMary PickfordReginald DennyPenata musikAlfred NewmanSinematograferKarl StrussPerusahaanproduksiArt CinemaDistributorUnited ArtistsTanggal rilis 14 Maret 1931 (1931-03-14) Durasi84 menitNegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaInggrisPendapatankotor$400.000[1] Kiki adalah sebuah film komedi romansa Pre-Code Amerika Serikat tahun 1931, yang menampil...

خبز طابونمعلومات عامةالمنشأ الأردن،لبنان،سوريا العراق، وفلسطينو معظم الوطن العربيالنوع خبز مفرودتعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات خبز الطابون أو خبر التنور أو الخبز البلدي أو اللفة،[1] هو خبز مفرود يستخدم في الشرق الأوسط لفَّة ويستخدم في بعض الطبخات التراثية أي�...

Public university in Abington, Pennsylvania, U.S. This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: Penn State Abington – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2018) (Learn how and when to r...

Hindu temple in Andhra Pradesh, India Kotasattemma TempleReligionAffiliationHinduismDistrictEast GodavariDeityKotasattemmaLocationLocationNidadavolu, East Godavari districtStateAndhra PradeshCountryIndiaLocation in Andhra PradeshGeographic coordinates16°58′16″N 81°46′23″E / 16.971°N 81.773°E / 16.971; 81.773ArchitectureTypeVengi ChalukyanWebsitesrikotasattemmaammavaridevasthanam.com/inde1.php Kotasattemma Temple is a Hindu pilgrimage center in Nidadavolu o...

Women's sporting event International sporting eventWomen's slalom C-1 at the 2015 Pan American GamesVenueMinden Wild Water PreserveDatesJuly 18–19Competitors6 from 6 nationsWinning time113.01Medalists Ana Sátila Brazil Colleen Hickey United States Haley Daniels Canada2019» Canoeing at the2015 Pan American GamesQualificationSlalomC-1menwomenC-2menK-1menwomenSprintC-1 200 mmenwomenC-1 1000 mmenC-2 1000 mmenK-1 200 mmenwomenK-1 5...

「團隊精神」重定向至此。團隊精神也可以指團隊合作。 此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2022年3月22日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而被移除。 管理層與工廠雇員的培訓會議,培訓是凝聚雇員士氣的其中一個良方。 士氣也稱為團隊精神,是指一個團隊的工作氣勢和氛圍,它用來�...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع شاهد (توضيح). شاهد النوع منصة رقمية، تلفزة عبر الإنترنت تاريخ التأسيس 2011 المقر الرئيسي الرياض البلد السعودية مناطق الخدمة العالم العربي، والشرق الأوسط، وشمال أفريقيا الصناعة إعلام، وسائل ترفيه، منصة بث فيديو رقمية، تلفزة رقمية الخدمات و�...

Ship of the line of the French Navy For other ships with the same name, see French ship Orient, French ship Dauphin Royal, and French ship Sans Culotte. Battle of the Nile, August 1st 1798 at 10 pm, by Thomas Luny. Orient is depicted aflame at the centre left. History France NameDauphin-Royal BuilderToulon Arsenal Laid downMay 1790 Launched20 July 1791 CommissionedAugust 1793 Out of serviceAugust 1798 Renamed Sans-Culotte September 1792 Orient May 1795 FateDestroyed by explosion at the Battle...

Haredi neighborhood in Jerusalem Western entrance to Kiryat Mattersdorf. Kiryat Mattersdorf (Hebrew: קרית מטרסדורף) is a Haredi neighborhood in Jerusalem. It is located on the northern edge of the mountain plateau on which central Jerusalem lies. It is named after Mattersburg (formerly Mattersdorf), a town in Austria with a long Jewish history. It borders Kiryat Itri and Romema. The main thoroughfare is Panim Meirot Street, which segues into Sorotzkin Street at the neighborhood's ...
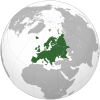
Daftar keuskupan di Austria adalah sebuah daftar yang memuat dan menjabarkan pembagian terhadap wilayah administratif Gereja Katolik Roma yang dipimpin oleh seorang uskup ataupun ordinaris di Austria. Para uskup di wilayah Austria bergabung dalam Konferensi Waligereja Austria. Saat ini terdapat 12 buah yurisdiksi, di mana 2 merupakan keuskupan agung, 7 merupakan keuskupan sufragan, 1 merupakan keabasan teritorial, 1 merupakan ordinariat, dan 1 merupakan ordinariat militer. Daftar keuskupan Pr...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant une localité suisse. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Lichtensteig Rue principale et hôtel de ville. Armoiries Drapeau Administration Pays Suisse Canton Saint-Gall Circonscription électorale Toggenburg Communes limitrophes Oberhelfenschwil, Bütschwil, Wattwil NPA 9620 No OFS 3374 Démographie Population permanente 1 980 hab. (31 décembre ...




