Remi
|
Read other articles:

Lokasi Distrik Shiwa di Prefektur Iwate. Lokasi munisipalitas yang ada di Distrik Shiwa, Prefektur Iwate1. – Shiwa 2. – Yahabawarna hijau - cakupan wilayah distrik saat iniwarna kuning - bekas wilayah distrik pada awal zaman Meiji Distrik Shiwa (紫波郡code: ja is deprecated , Shiwa-gun) adalah sebuah distrik yang terletak di Prefektur Iwate, Jepang. Per 1 Oktober 2015, distrik ini memiliki estimasi jumlah penduduk sebesar 60.203 jiwa dan kepadatan penduduk sebesar 196,55 orang per km²...

Golfo Aranci FìgariKomuneComune di Golfo AranciLokasi Golfo Aranci di Provinsi SassariNegara ItaliaWilayah SardiniaProvinsiSassari (SS)Pemerintahan • Wali kotaMario MulasLuas • Total37,43 km2 (14,45 sq mi)Ketinggian19 m (62 ft)Populasi (2016) • Total2,452[1]Zona waktuUTC+1 (CET) • Musim panas (DST)UTC+2 (CEST)Kode pos07020Kode area telepon0789Situs webhttp://www.comune.golfoaranci.ot.it Golfo Aranci (b...

Process in winemaking A winemaker running a paper chromatography test to determine whether a wine has completed malolactic fermentation Malolactic conversion (also known as malolactic fermentation or MLF) is a process in winemaking in which tart-tasting malic acid, naturally present in grape must, is converted to softer-tasting lactic acid. Malolactic fermentation is most often performed as a secondary fermentation shortly after the end of the primary fermentation, but can sometimes run concu...

SMP Negeri 23 SemarangInformasiJenisNegeriAkreditasiA[1]Nomor Pokok Sekolah Nasional20328816Kepala SekolahDrs. Suwarno Agung Nugroho, Mm.NIP. 196810111993031005Rentang kelasVII sampai IXAlamatLokasiJl. Rm Hadi Subeno Mijen, Semarang, Jawa Tengah, IndonesiaTel./Faks.(024) 7711053Koordinat7°3'26S 110°18'47ESitus webhttp://smp23smg.sch.idMoto SMP Negeri (SMPN) 23 Semarang, merupakan salah satu Sekolah Menengah Pertama Negeri yang ada di Jl. Rm Hadi Subeno Mijen, Semarang Prov...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Nessebar. Nessebar НесебърΜεσημβρία Héraldique Administration Pays Bulgarie District Municipalité de Nessebar Oblast Bourgas (oblast) Code postal 8230 Démographie Population 12 036 hab. (2022) Géographie Coordonnées 42° 39′ 33″ nord, 27° 43′ 42″ est Altitude 5 m Divers https://www.nesebar.bg/ Localisation Géolocalisation sur la carte : Bulgarie Nessebar modifier Nessebar ...

Thierry Henry Henry pada 2021Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Thierry Daniel Henry[1]Tanggal lahir 17 Agustus 1977 (umur 46)[1]Tempat lahir Les Ulis, Essonne, PrancisTinggi 188 cm (6 ft 2 in)Posisi bermain PenyerangKarier junior1983–1989 CO Les Ulis1989–1990 US Palaiseau1990–1992 Viry-Châtillon1992 Clairefontaine1992–1994 MonacoKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1994–1999 Monaco 105 (20)1999 Juventus 16 (3)1999–2007 Arsenal 376 (228)2007–2010 ...

Questa voce sull'argomento squadre di hockey su ghiaccio è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. MHC MartinHockey su ghiaccio Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali bianco-blu Dati societari Città Martin Paese Slovacchia Confederazione IIHF Federazione SZL'H Campionato Extraliga Fondazione 1932 Presidente Jaroslav Zigo Allenatore Ladislav Spišiak e Marian Brúsil Impianto di gioco Zimný Štadión Martin(4.200 ...

Koordinat: 31°35′33″N 74°18′34″E / 31.5925°N 74.3095°E / 31.5925; 74.3095 Minar-e-Pakistan مینارِ پاکستانLokasi di LahoreInformasi umumStatusMenara Nasional PakistanJenisMonumen publikLokasiLahore, Punjab PakistanMulai dibangun23 Maret 1960Rampung21 Oktober 1968TinggiAtap62 meter (203 ft)Desain dan konstruksiArsitekNasreddin Murat-KhanTeknisi strukturA Rehman NiaziKontraktor utamaMian Abdul Khaliq Company Minar-e-Pakistan (bahasa Urdu...

Military campaign of the Spanish–American War Puerto Rico campaignPart of the Spanish–American WarMap of the Puerto Rico campaign illustrating operations July 25 – August 12, 1898, and showing municipality borders in 1898. Blue are US Naval forces, red are US land forces, and green are Spanish ground forces.Map of Puerto Rico under the US and Spanish flags from August 14 til September 19, 1898. The 23 blue-colored municipalities were under the US flag and the 55 yellow-colored municipal...

Romanesque church in Milan See also: Sant'Ambrogio, Florence Basilica of Sant'Ambrogio(Basilica di Sant'Ambrogio)Exterior view of the basilica.ReligionAffiliationCatholicProvinceMilanEcclesiastical or organizational statusMinor basilicaYear consecrated379StatusActiveLocationLocationMilan, ItalyGeographic coordinates45°27′44.73″N 9°10′32.90″E / 45.4624250°N 9.1758056°E / 45.4624250; 9.1758056ArchitectureTypeChurchStyleRomanesqueCompleted1099 The Basilica of ...

«I.R.S.» redirige aquí. Para la canción de Guns N' Roses con ese título, véase I.R.S. (canción). Servicio de Impuestos Internos Internal Revenue Service Logo del Servicio de Impuestos Internos Internal Revenue Service Building, sede del Servicio de Impuestos Internos.LocalizaciónPaís Estados UnidosInformación generalSigla IRSJurisdicción Estados UnidosTipo Agencias independientes del gobierno de Estados UnidosSede Internal Revenue Service Building, Washington D. C., Estados U...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с такой фамилией, см. Кондратьев; Кондратьев, Александр. Александр Васильевич Кондратьев Дата рождения 14 ноября 1901(1901-11-14) Место рождения город Санкт-Петербург Дата смерти 5 сентября 1981(1981-09-05) (79 лет) Место смерти город Ленинград �...

Civil service examination system in Imperial China For the Indonesian and Malay word for cheese, see cheese. Imperial examination科舉Candidates gathering around the wall where the results are posted. This announcement was known as releasing the roll (放榜). (c. 1540, by Qiu Ying) Imperial examinationImperial examinations in Traditional (top) and Simplified (bottom) Chinese charactersChinese nameTraditional Chinese科舉Simplified Chinese科举Hanyu Pinyinkējǔ TranscriptionsStandard...
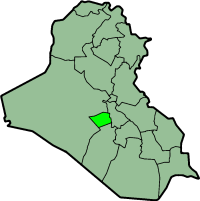
2008 Karbala bombingLocation of KarbalaLocationKarbala, IraqDate17 March 2008 (UTC+3)Attack typesuicide bombDeathsAt least 22Injured58PerpetratorsUnknown vteList of bombings during the Iraq War‡ indicates attacks resulting in over 100 deaths § indicates the deadliest attack in the Iraq WarThis list only includes major attacks. 2003 1st Baghdad 2nd Baghdad Najaf 3rd Baghdad 1st Nasiriyah 1st Karbala 2004 ‡ 1st Erbil ‡ Ashoura 1st Basra 1st Mosul 4th Baghdad 5th Baghdad Karbala & Naj...

Versorgungshaus Alberschwende Eingangsbereich Das Versorgungsheim Alberschwende, auch Sozialzentrum Alberschwende ist ein Altenheim und Zentrum für Betreutes Wohnen im Ortszentrum der Bregenzerwälder Gemeinde Alberschwende im Bezirk Bregenz in Vorarlberg. Die an der Adresse Hof 23 gelegenen Gebäude werden von der Gesellschaft „Benevit“ betrieben. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Geschichte und Architektur 1.1 Kapelle 2 Weblinks 3 Literatur Geschichte und Architektur Der dreigeschossige Bau wurde i...

Якопо Робусти Портрет прокуратора Якопо Соранцо. Ок. 1550 итал. Ritratto del procuratore Jacopo Soranzo Холст, масло. 106 × 90 см Галерея Академии, Венеция Медиафайлы на Викискладе «Портрет прокуратора Якопо Соранцо» (итал. Ritratto del procuratore Jacopo Soranzo) — картина итальянского жив...
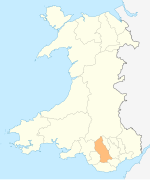
Human settlement in WalesTynewyddTynewyddLocation within Rhondda Cynon TafOS grid referenceSS 9307 9905Principal areaRhondda Cynon TafPreserved countyMid GlamorganCountryWalesSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townTreorchyPostcode districtCF42Dialling code01443PoliceSouth WalesFireSouth WalesAmbulanceWelsh UK ParliamentRhonddaSenedd Cymru – Welsh ParliamentRhondda List of places UK Wales Rhondda Cynon Taf 51°40′48″N 3°32′53″W / þ...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с фамилиями Белый и Бугаев. Андрей Белый Белый в 1912 году Имя при рождении Борис Николаевич Бугаев Псевдонимы Андрей Белый Дата рождения 14 (26) октября 1880[1][2][…] Место рождения Москва, Российская империя Дата смерти 8 января 1934(19...

Australian academic Black in 2019 Rufus Edward Ries Black (born 20 May 1969) is the vice-chancellor of the University of Tasmania.[1] Early life and education Black was educated at Wesley College and the University of Melbourne, where he resided at Ormond College and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts in politics and economics and a Bachelor of Laws with honours in 1994. He won a Rhodes Scholarship in 1992,[2] and obtained a Diploma of Theology and Master of Philosophy in Ethic...

Úrvalsdeild2003 Généralités Sport Football Édition 92e Date du 18 mai 2003 au 20 septembre 2003 Participants 10 Palmarès Tenant du titre KR Reykjavik Promu(s) þrottur ReykjavikValur Reykjavik Meilleur(s) buteur(s) Björgólfur Hideaki Takefusa (10) Navigation Saison précédente Saison suivante modifier La saison 2003 du Championnat d'Islande de football était la 92e édition de la première division islandaise. Les 10 clubs jouent les uns contre les autres lors de rencontres di...





