Regime theory
|
Read other articles:

JemberlorKelurahanKantor Lurah JemberlorNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TimurKabupatenJemberKecamatanPatrangKodepos68118Kode Kemendagri35.09.20.1006 Kode BPS3509730002 Luas2,98 km²Jumlah penduduk19.897 jiwaKepadatan... jiwa/km² Jemberlor adalah kelurahan di kecamatan Patrang, Jember, Jawa Timur, Indonesia. Pembagian wilayah Kelurahan Jemberlor terdiri dari lingkungan: Krajan Kreyongan Atas Kreyongan Bawah Pagah Tegalrejo Wetan Kantor Pendidikan Lembaga pendidikan formal yang terdapat di K...

Ziarah keTempat-tempat suciagama Buddha Empat Tempat Utama Bodh Gaya Kushinagar Lumbini Sarnath Empat Tempat Tambahan Rajgir Sankassa Shravasti Vaishali Tempat lainnya Amaravathi Chandavaram Devadaha Gaya Kapilavastu Kesaria Kosambi Nalanda Pataliputra Pava Varanasi Tempat yang ditambahkan kemudian Gua Ajanta Gua Barabar Bharhut Gua Ellora Lalitgiri Mathura Gua Pandavleni Piprahwa Ratnagiri Sanchi Udayagiri Vikramashila lbs Ziarah Buddhis adalah kunjungan ke tempat-tempat suci agama Buddha. T...

بالرغم من ضخامة وتعقيد الأسلحة النووية البدائية، فإنها وفرت القواعد الأساسية لتصميم القنابل النووية الاحقة. يظهر في الصورة الجهاز الأول الذي استعمل في أول اختبارات الإنفجارات النووية المسماة: ترينيتي. هذه المقالة هي جزء من سلسلة مقالات حولالأسلحة النووية خلفية التاريخ ا...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Горностай (значения). Горностай Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:Челюстнороты...

For people with the name, see Haighton (surname). Human settlement in EnglandHaightonHaighton ManorHaightonShown within the City of Preston districtShow map of the City of Preston districtHaightonLocation within LancashireShow map of LancashirePopulation202 (2011)OS grid referenceSD566349Civil parishHaightonDistrictPrestonShire countyLancashireRegionNorth WestCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townPRESTONPostcode districtPR2Dialling code01772Pol...

Kuaitiao khua kaiKuaitiao khua kai served with a poached egg and deep-fried doughsticksNama lainKhua kaiJenisRice noodlesTempat asalThailandSuhu penyajianHotBahan utamarice noodles, chicken, eggs, squid, lettuceSunting kotak info • L • BBantuan penggunaan templat ini Kuaitiao khua kai (Thai: ก๋วยเตี๋ยวคั่วไก่code: th is deprecated , pengucapan [kǔa̯j.tǐa̯w kʰûa̯ kàj]) adalah hidangan populer Thailand yang dipengaruhi oleh pengaruh T...

Gaetano Belloni Nazionalità Italia Ciclismo Specialità Strada, pista Termine carriera 1932 CarrieraSquadre di club 1916-1922 Bianchi1923-1924 Legnano1925Wolsit1926-1927Opel1928Wolsit1929-1931 Bianchi1932 OlympiaCarriera da allenatore 1956-1958 Leo-Chlorodont Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Gaetano Belloni (Pizzighettone, 26 agosto 1892 – Milano, 9 gennaio 1980) è stato un ciclista su strada e pistard italiano. Professionista dal 1916 al 19...
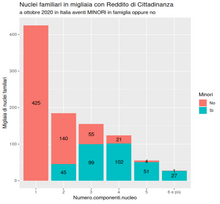
Il Reddito di cittadinanza fu un sussidio in vigore in Italia dal gennaio 2019 al gennaio 2024.[1][2] A dispetto del nome, era in realtà totalmente privo delle caratteristiche di un reddito di base, trattandosi piuttosto di una forma condizionata e non individuale di reddito minimo garantito.[3] Indice 1 Storia legislativa 1.1 Introduzione 1.2 Superamento 2 Descrizione 2.1 Condizionalità 3 Effetti 4 Illeciti 5 Note 6 Voci correlate 7 Altri progetti Storia legislativa...

Open cluster in the constellation Tucana NGC 346James Webb Space Telescope image of NGC 346Observation data (J2000 epoch)Right ascension00h 59m 05.090s[1]Declination−72° 10′ 33.24″[1]Distance210,000 light-yearsPhysical characteristicsH II regionOther designationsESO 51-10,[2] N66AssociationsConstellationTucana[3]See also: Open cluster, List of open clusters NGC 346 is a young[4] open cluster of stars with associated neb...

This template does not require a rating on Wikipedia's content assessment scale.It is of interest to the following WikiProjects:Internet Internet portalThis template is within the scope of WikiProject Internet, a collaborative effort to improve the coverage of the Internet on Wikipedia. If you would like to participate, please visit the project page, where you can join the discussion and see a list of open tasks.InternetWikipedia:WikiProject InternetTemplate:WikiProject InternetInternet artic...

國立光復高級商工職業學校地址花蓮縣光復鄉林森路100號邮政编码976其它名称National Guanfu Senior Commercial and Industrial Vocational High School类型技術型高級中等學校创办日期1996年学区 臺灣,花蓮縣,光復鄉教育部學校代碼150411校長李秋嫺学生人数不到200人 (109/5)電話號碼+886-3-870-0245学校网址https://www.kfcivs.hlc.edu.tw 國立光復高級商工職業學校(National Kuangfu Commercial and Industrial Vocational...

County in Texas, United States County in TexasKerr CountyCountyKerr County Courthouse, southside viewLocation within the U.S. state of TexasTexas's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 30°04′N 99°21′W / 30.06°N 99.35°W / 30.06; -99.35Country United StatesState TexasFounded1856Named forJames KerrSeatKerrvilleLargest cityKerrvilleArea • Total1,107 sq mi (2,870 km2) • Land1,103 sq mi (2,860 km2) ...

Theatre ballistic missile R-5 R-5 on display at the Zhytomyr Korolyov MuseumTypeTheatre ballistic missileMedium-range ballistic missilePlace of originUSSRService historyIn service1956 – 1967Production historyManufacturerYuzhmashSpecificationsMass29,100 kgLength20.75 mDiameter1.65 mWarhead80 kt, 1 Mt thermonuclear warheadEngineRD-103M, 8D52[1]PropellantLiquid (92% Ethanol/water solution & LOX)Operationalrange1,200 km (750 mi)Guidancesysteminertial guidanc...

Impatiens sylvicola Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae (tanpa takson): Tracheophyta (tanpa takson): Angiospermae (tanpa takson): Eudikotil (tanpa takson): Asterid Ordo: Ericales Famili: Balsaminaceae Genus: Impatiens Spesies: Impatiens sylvicola Nama binomial Impatiens sylvicolaBurtt Davy & Greenway Impatiens sylvicola adalah spesies tumbuhan yang tergolong ke dalam famili Balsaminaceae. Spesies ini juga merupakan bagian dari ordo Ericales. Spesies Impatiens sylvicola sendiri merupakan...

Ini adalah nama Minahasa, marganya adalah Limpele. Flandy LimpeleInformasi pribadiNama lahirFlandy LimpeleKebangsaan IndonesiaLahir9 Februari 1974 (umur 50)ManadoTinggi181 cm (5 ft 11 in)Berat74 kg (163 pon)PeganganKiriPelatihRichard MainakyRekor bertandingGanda Putra dan Ganda Campuran Flandy Limpele Rekam medali Bulu tangkis Putra Olimpiade Athena 2004 Ganda Putra Flandy Limpele (lahir 9 Februari 1974) adalah seorang pemain bulu tangkis berdarah Minahasa d...

Football match1876 FA Cup finalAn illustration of the FA Cup trophy awarded in 1876Event1875–76 FA Cup Wanderers Old Etonians Final Wanderers Old Etonians 1 1 Date11 March 1876 (1876-03-11)VenueKennington Oval, LondonRefereeW. S. Buchanan (Clapham Rovers)Attendance3,500Replay Wanderers Old Etonians 3 0 Date18 March 1876 (1876-03-18)VenueKennington Oval, LondonRefereeWilliam Rawson (Oxford University)Attendance3,500← 1875 1877 → The 1876 FA Cup fina...

محطة واتس بار النووية محطة واتس بار النووية توربينات محطة واتس بار النووية محطة واتس بار النووية هي عبارة عن مفاعلين نوويين تابعة لمقاطعة ريا (تينيسي) تستخدم لتوليد الطاقة الكهربائية وتم انشائها في عام 1973.[1] الموقع تقع في موقع مساحته 1770 فدان (7,2 كيلومتر مربع) في مقاطعة ر�...

Chess player For other people named Joseph Gallagher, see Joseph Gallagher (disambiguation). This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Joseph Gallagher – news · newspapers · books · scholar ...

This article is about the 1744 raid. For the 1776 raid, see Raid on Canso (1776). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Raid on Canso – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Raid on CansoPart of King George's WarFort William Augustus,...

ガイウス・アンティスティウス・ウェトゥスC. Antistius C. f. -. n. Vetus出生 不明死没 不明出身階級 プレブス氏族 アンティスティウス氏族官職 財務官(紀元前61年)護民官(紀元前56年)前法務官?(紀元前45年-44年、紀元前35年-33年)軍団副司令官(紀元前43年-42年)補充執政官(紀元前30年)総督代理(紀元前26年-25年)担当属州 シリア属州(紀元前45年-41年)ガリア・ナ�...