Population size
|
Read other articles:

Komisi Pengawas Persaingan Usaha KPPUGambaran umumSingkatanKPPUDidirikan7 Juni 2000Dasar hukum pendirianUndang-Undang Nomor 5 tahun 1999 tentang Larangan Praktik Monopoli dan Persaingan Usaha Tidak SehatSifatIndependenStrukturKetuaDr. Ir. M. Fanshurullah Asa, S.T., M.T., IPU.Kantor pusatJl. Ir. H. Juanda No. 36 Jakarta Pusat 10120Situs webkppu.go.idSunting kotak info • L • BBantuan penggunaan templat ini Wikisumber memiliki naskah asli yang berkaitan dengan artikel ini: Per...

العلاقات البليزية الليسوتوية بليز ليسوتو بليز ليسوتو تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات البليزية الليسوتوية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين بليز وليسوتو.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة بليز ل...

Justine PasekJustine Pasek, 2002LahirYostin Lissette Pasek Patiño29 Agustus 1979 (umur 44)Kharkiv, UkrainaNama lainJustine PasekTinggi170 m (557 ft 9 in)Pemenang kontes kecantikanGelarSeñorita Panamá 2001Miss Universe 2002Warna rambutCokelatWarna mataCokelat Yostin Justine Lissette Pasek Patiño (lahir 27 Agustus 1979) adalah model yang berasal dari Panama. Ia juga dinobatkan menjadi Miss Universe 2002, setelah sebelumnya kemenangan Oxana Fedorova dibatalkan. Biog...

Agostino Lomellini BiografiKelahiran1709 Genova Kematian1791 (81/82 tahun)Genova 166 Doge of Genoa (en) 22 September 1760 – 10 September 1762 ← Matteo Franzoni – Rodolfo Emilio Brignole Sale → KegiatanPekerjaanpolitikus KeluargaKeluargaHouse of Lomellini (en) [[Berkas: |100px|alt= Lambang kebesaran Agostino Lomellini]] Agostino Lomellini adalah Doge Republik Genova. Doge sendiri adalah jabatan yang dipegang oleh pemimpin Republik Genova pada masa lampau. Se...

This is a list of spacefarers natives from Ibero-America. List Orbital Nº Image Latin American? Selection Status Agency[1] Employer[1] Spaceflights Time in space Ref. 1 Yes 1978 Inactive since1980 TSPK DAAFAR Soyuz 38 7d 20h 43m [2] Arnaldo Tamayo Méndez 2 No 19921998 Inactive since2018 ESA STS-95 Soyuz TMA-3 18d 18h 46m [3] Pedro Duque 3 Yes 1985 Inactive since1985 SCT STS-61-B 6d 21h 04m [4] Rodolfo Neri Vela 4 Yes 1998 Inactive since2019 AEB FAB S...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento calcio è priva o carente di note e riferimenti bibliografici puntuali. Sebbene vi siano una bibliografia e/o dei collegamenti esterni, manca la contestualizzazione delle fonti con note a piè di pagina o altri riferimenti precisi che indichino puntualmente la provenienza delle informazioni. Puoi migliorare questa voce citando le fonti più precisamente. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Associazione Calcio Femminile LugoCalcio Segni ...

Some of this article's listed sources may not be reliable. Please help improve this article by looking for better, more reliable sources. Unreliable citations may be challenged and removed. (May 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Sandalwood(Kannada) cinema 1930s 1940s 1950s 1960s 1960 1961 1962 1963 19641965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970s 1970 1971 1972 1973 19741975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980s 1980 1981 1982 1983 19841985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990s 1990 1991 1992 1993 19941995 1996 1...

Lighthouse on Tenerife, Spain LighthousePunta de Anaga Lighthouse LocationAnaga TenerifeCanary IslandsSpainCoordinates28°34′53″N 16°08′24″W / 28.581328°N 16.140019°W / 28.581328; -16.140019TowerConstructed1864Constructionstone towerHeight12 metres (39 ft)Shapecylindrical tower with balcony and lantern attached to 1-storey keeper's houseMarkingsunpainted tower, white lanternPower sourcesolar power LightFocal height247 metres (810 ft)Lensor...

Former Latin Catholic diocese established in Roman Carthage, now a titular see This article is about the ancient archdiocese active until the Islamic occupation (except revival 1884–1964). For its successor, see Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Tunis. Archdiocese of CarthageArchidioecesis CarthaginensisBishopric Early Christian quarter in ancient CarthageIncumbent:Cyriacus of Carthage (last residing ca. 1070)Agostino Casaroli (last titular archbishop 1979)LocationCountryRoman EmpireVandal King...

هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. إن وجهات النظر المعروضة في هذه المقالة منحازة ثقافيًا أو جغرافيًا. فضلًا، ساهم في تحسينها من خلال إزالة أي محتوى منحاز وتطوير محتواها لتعرض وجهات نظر متنوعة عرضًا حياديًا. (ن�...

Danau Kakaban, adalah air laut yang terperangkap di Pulau Kakaban, ditambah dengan air dari dalam tanah dan air hujan sejak 2 juta tahun lalu. Danau Kakaban merupakan danau prasejarah yaitu zaman peralihan Holosin. Luasnya sekitar 5 km², berdinding karang terjal setinggi 50 meter, yang mengakibatkan air laut yang terperangkap tidak lagi bisa keluar, menjadi danau. Secara administratif, Danau Kakaban termasuk wilayah Kabupaten Berau, Kalimantan Timur. Biota dalam Danau Karena perubahan dan ev...

Ongoing COVID-19 viral pandemic in Sikkim, India COVID-19 pandemic in SikkimDiseaseCOVID-19Virus strainSARS-CoV-2LocationSikkim, IndiaFirst outbreakWuhan, Hubei, ChinaArrival date23 May 2020(4 years, 2 weeks and 6 days)Confirmed cases 13,132 (23 May 2021)Active cases 3,527Recovered 9,381 (23 May 2021)Deaths 224Fatality rate1.71%TerritoriesAll 4 districtsGovernment websitewww.covid19sikkim.org The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, orig...

This article contains content that is written like an advertisement. Please help improve it by removing promotional content and inappropriate external links, and by adding encyclopedic content written from a neutral point of view. (December 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The Mowat Centre was an independent Canadian public policy think tank associated with the Munk School of Global Affairs and Public Policy at the University of Toronto. It was established in 2009 with suppor...

English actor Jack AllenBornRobert John Lea Allen(1907-10-23)23 October 1907Sandbach, Cheshire, EnglandDied25 May 1995(1995-05-25) (aged 87)London, EnglandYears active1931–1982SpouseRuth Dunning (?-1983; her death) Robert John Lea Allen (23 October 1907 – 25 May 1995) was an English film, theatre and television actor.[1][2] Career He made his stage debut in 1931 at the Liverpool Playhouse, appearing in The Swan and had a long theatrical career which lasted until ...
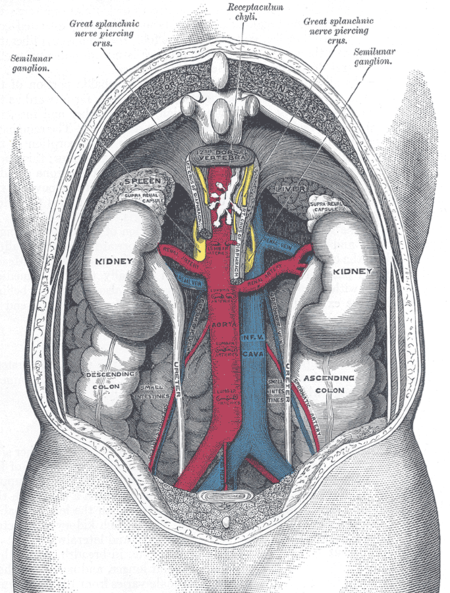
بطن الاسم العلميAbdomen بطن الإنسان والأعضاء التي يحتويها البطن بطن تفاصيل عمل العضلة حركة ودعم الجذعالمساعدة في التنفسحماية الأجزاء الداخليةالمساعدة في الوقوف يتكون من سرة، وجوف البطن، وناحية عانية، وخاصرة، ومنطقة تحت غضروفية، ومنطقة فوق معدية نوع من �...
Latvian ice hockey club For the football club, see FK Liepājas Metalurgs. Liepājas MetalurgsCityLiepājaLeagueBXL 2004-2013LHL 1997-2013 MHL B 2012-2013Founded1997Folded2013Home arenaOlimpiskā ledus halle(capacity: 1,200)Colours Websitehttp://www.skliepajasmetalurgs.lv/Franchise historyHK Liepājas Metalurgs HK Liepājas Metalurgs was a professional hockey club based in Liepāja, Latvia that fielded multiple teams over the years competing in the Belarusian Extraliga (BXL...

Chemical compound Not to be confused with Danabol. DanazolClinical dataTrade namesDanatrol, Danocrine, Danol, Danoval, othersOther namesWIN-17757; 2,3-Isoxazolethisterone; 2,3-Isoxazol-17α-ethynyltestosterone; 17α-Ethynyl-17β-hydroxyandrost-4-en-[2,3-d]isoxazoleAHFS/Drugs.comMonographMedlinePlusa682599Pregnancycategory AU: D Routes ofadministrationBy mouthDrug classAndrogen; Anabolic steroid; Progestogen; Progestin; Antigonadotropin; Steroidogenesis inhibitor; AntiestrogenATC codeG03X...

Voce principale: Associazione Sportiva Martina Franca 1947. Associazione Sportiva Martina Franca 1947Stagione 2014-2015Sport calcio Squadra Martina Allenatore Salvatore Ciullo(fino al 30 marzo 2015) Eduardo Imbimbo(dal 30 marzo 2015)[1] Presidente Antonio Donato Muschio Schiavone Lega Pro14° Coppa Italia Lega ProFase eliminatoria a gironi Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Bleve (37)Totale: Bleve (38) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Montalto (11)Totale: Montalto (11) StadioGiuseppe Dome...

Tournoi Clausura2017 Généralités Sport Football Organisateur(s) FEDEFUTBOL Édition 20e Lieu(x) Costa Rica Date du 7 janvier 2017 au 21 mai 2017 Participants 12 équipes Matchs joués 72 Hiérarchie Hiérarchie 1er échelon Niveau inférieur Segunda División (es) Palmarès Tenant du titre Deportivo Saprissa Vainqueur CS Herediano Deuxième Deportivo Saprissa Relégué(s) AD San Carlos Navigation Saison précédente Saison suivante modifier Le Tournoi Clausura 2017 est le vingti...

أديداس تيليستاركرة كأس العالم 1974 - أديداس تيليستارمعلومات عامةالنوع كرةالاستعمالات كأس العالم 1970 — بطولة أمم أوروبا 1968 البداية 1968؛ منذ 56 سنوات (1968)المصنع أديداس آخر إنتاج 2018الموديلات Telstar Elast Telstar Telstar Durlastأديداس تلستار 18تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات كرة ال�...