Paeonia mascula
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento aziende è priva o carente di note e riferimenti bibliografici puntuali. Sebbene vi siano una bibliografia e/o dei collegamenti esterni, manca la contestualizzazione delle fonti con note a piè di pagina o altri riferimenti precisi che indichino puntualmente la provenienza delle informazioni. Puoi migliorare questa voce citando le fonti più precisamente. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Cisco SystemsLogo Il Building 10, sede della C...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Anton ArsenyevInformasi pribadiNama lengkap Anton Vladimirovich ArsenyevTanggal lahir 22 Maret 1985 (umur 38)Tinggi 1,84 m (6 ft 1⁄2 in)Posisi bermain Penjaga gawangInformasi klubKlub saat ini FC Petrotrest Saint PetersburgNo...

Arti Semestinya CintaAlbum mini karya Arsy Widianto dan Tiara AndiniDirilis8 Maret 2024 (2024-03-08)Direkam2023GenrePopDurasi20:59LabelUniversal Music IndonesiaProduser Yovie Widianto Adrian Kitut Ari Renaldi (trek 3) Kronologi Arsy Widianto Puisi(2023) Arti Semestinya Cinta(2024) Kronologi Tiara Andini Tiara Andini(2021) Arti Semestinya Cinta(2024) Arti Semestinya Cinta (digayakan ArTi) adalah album mini kolaboratif kedua antara Arsy Widianto dan Tiara Andini setelah Arti untuk Cint...

American singer and songwriter (born 1994) Not to be confused with Danni Leigh. DaniLeighDaniLeigh in 2018BornDanielle Leigh Curiel (1994-12-20) December 20, 1994 (age 29)Miami, Florida, U.S.OccupationsSingersongwriterrapperdancerchoreographerYears active2013–presentChildren1Musical careerGenresR&BInstrument(s)VocalsLabelsDef Jam Musical artistWebsiteiamdanileigh.com Danielle Leigh Curiel (born December 20, 1994), known professionally as DaniLeigh, is an American singer and so...

American Hockey League team in Abbotsford, British Columbia Abbotsford CanucksCityAbbotsford, British Columbia, CanadaLeagueAmerican Hockey LeagueConferenceWesternDivisionPacificFounded1932Home arenaAbbotsford CentreColoursField green, Pacific blue, Fraser blue, valley fog grey, mountain white[1] Owner(s)Canucks Sports & EntertainmentGeneral managerRyan Johnson[2]Head coachJeremy CollitonCaptainChase WoutersAffiliatesVancouver Canucks ...

County in Texas, United States Not to be confused with Coke County, Texas. Cooke County redirects here. Not to be confused with Cook County. County in TexasCooke CountyCountyThe Cooke County Courthouse in Gainesville FlagLocation within the U.S. state of TexasTexas's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 33°38′00″N 97°13′00″W / 33.633333333333°N 97.216666666667°W / 33.633333333333; -97.216666666667Country United StatesState TexasFounded1849SeatGain...

Sedia 412 Cabprodotto di disegno industrialeUno dei prodotti icona di Mario BelliniDati generaliAnno di progettazione1977 ProgettistaMario Bellini Profilo prodottoTipo di oggettoSedia IdeaIspirato al rapporto fra scheletro e pelle ConcettiSimbiosi, lusso e originalità ProduttoreCassina S.p.a. Prodotto dal1977 MaterialiCuoio e Acciaio Tecnica di lavorazioneScarnitura Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale La Sedia 412 Cab è una sedia disegnata nel 1977 dal designer Mario Bellini e commerc...

English footballer Brandon Hanlan Personal informationFull name Brandon Alex Graham Hanlan[1]Date of birth (1997-05-31) 31 May 1997 (age 26)[2]Place of birth Chelsea, EnglandHeight 6 ft 0 in (1.82 m)[3]Position(s) ForwardTeam informationCurrent team Wycombe WanderersNumber 18Youth career2012–2015 Charlton AthleticSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2015–2018 Charlton Athletic 9 (0)2017 → Bromley (loan) 8 (4)2017–2018 → Colchester United (lo...

Association football tournament in India Football tournamentSantosh TrophyOrganising bodyAIFFFIFAFounded1941; 83 years ago (1941)RegionIndiaNumber of teamsGroup stage: 36Final round: 10+2Related competitionsNational GamesInternational cup(s)Asian Champion Club Tournament (1967–70)Current championsServices (7th title)Most successful team(s)West Bengal (32 titles)Television broadcastersFIFA+WebsiteSenior NFC 2023–24 Santosh Trophy The National Football Championship for San...
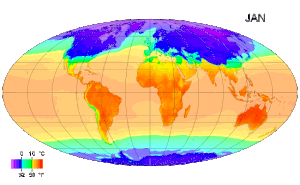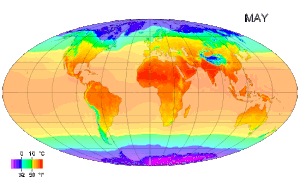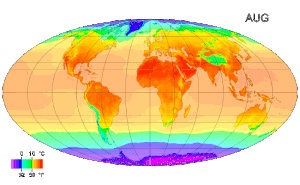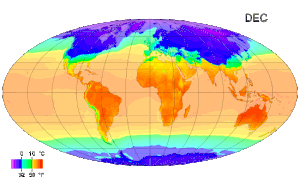
Air akan mulai membeku pada suhu 0° Celsius (di gambar ini suhu udara -17° C). Suhu atau temperatur adalah alat yang menunjukkan derajat atau ukuran panas suatu benda. Mudahnya, semakin tinggi suhu suatu benda, semakin panas benda tersebut. Secara mikroskopis, suhu menunjukkan energi yang dimiliki oleh suatu benda. Setiap atom dalam suatu benda masing-masing bergerak, baik itu dalam bentuk perpindahan maupun gerakan di tempat, getaran. Semakin tinggi energi atom-atom penyusun benda, makin t...

Une cité[1] en Colombie-Britannique est une classification des municipalités utilisée dans la province canadienne de la Colombie-Britannique. Une communauté peut être incorporée en tant que cité par lettres patentes du lieutenant-gouverneur en conseil sous la recommandation du ministre des Communautés, des Sports et du Développement culturel si sa population dépasse 5 000 habitants et si plus de 50 % des résidents touchés votent en faveur de l'incorporation proposé...

2019 single by Dan ShayAll to MyselfSingle by Dan + Shayfrom the album Dan + Shay ReleasedFebruary 11, 2019 (2019-02-11)GenreCountry popLength2:49LabelWarner NashvilleSongwriter(s)Dan SmyersShay MooneyJordan ReynoldsNicolle GalyonProducer(s)Dan SmyersScott HendricksDan + Shay singles chronology Speechless (2018) All to Myself (2019) 10,000 Hours (2019) All to Myself is a song recorded by American country music duo Dan + Shay. It is the third single from their 2018 self-titled a...
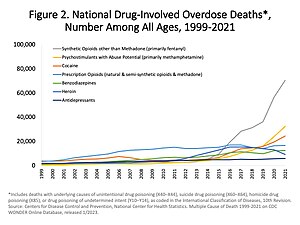
Detroit police inspecting equipment found in a clandestine brewery during the Prohibition era US yearly overdose deaths, and the drugs involved. Among the more than 70,200 deaths estimated in 2017, the sharpest increase occurred among deaths related to fentanyl and synthetic opioids (28,466 deaths).[1] In the United States, the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act defined the word drug as an article intended for use in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disea...

WWII American fighter pilot (1921–1947) Duane Willard BeesonDuane W. BeesonNickname(s)BeeBorn(1921-07-16)July 16, 1921Boise, Idaho, USDiedFebruary 13, 1947(1947-02-13) (aged 25)Walter Reed General HospitalWashington, D.C., USBuriedArlington National CemeteryAllegianceCanadaUnited StatesService/branchRoyal Canadian Air Force (1941–42)United States Army Air Forces (1942–47)Years of service1941–1947RankLieutenant ColonelUnitNo 71 Eagle Squadron4th Fighter GroupCommands held334t...

English footballer and manager (1943–2019) Martin PetersMBE Peters in 1970Personal informationFull name Martin Stanford PetersDate of birth (1943-11-08)8 November 1943Place of birth Plaistow, Essex, EnglandDate of death 21 December 2019(2019-12-21) (aged 76)Place of death Brentwood, England[1]Height 6 ft 0 in (1.83 m)[2]Position(s) MidfielderSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1959–1970 West Ham United 302 (81)1970–1975 Tottenham Hotspur 189 (46)1975�...

الحزب الشيوعي الكوبي البلد كوبا تاريخ التأسيس 3 أكتوبر 1965 المؤسسون فيدل كاسترو الحزب الاشتراكي الشعبي، وحركة 26 يوليو، ودليل الطالب الثوري [لغات أخرى] قائد الحزب ميغيل دياز كانيل (19 أبريل 2021–) الأمين العام ميغيل دياز كانيل عدد الأعضا�...

1982 single by Grandmaster Flash The MessageSide A of the US 12-inch singleSingle by Grandmaster Flash and the Furious Fivefrom the album The Message B-sideThe Message (instrumental)ReleasedJuly 1, 1982Recorded1982StudioSweet Mountain (Englewood, New Jersey)GenreOld-school hip hopconscious hip hopelectro[1]progressive rap[2]Length7:10LabelSugar HillSongwriter(s)Edward G. FletcherMelle MelClifton Jiggs ChaseSylvia RobinsonProducer(s)Edward G. FletcherSylvia RobinsonGrandmaster ...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Fiksasi target adalah sebuah fenomena berkaitan dengan perhatian manusia di mana individu menjadi begitu fokus pada objek yang diamati (baik itu target atau bahaya) sehingga mereka secara tidak sengaja meningkatkan risiko bertabrakan dengan objek terse...

Nord LB Open ATP Challenger Tour Nama turnamenBraunschweigLokasiBraunschweig, JermanTempatBraunschweiger Tennisund Hockey ClubKategoriATP Challenger TourPermukaanTanah liat merahJumlah peserta32T/16K/16GHadiah uang€106,500+HSitus webwww.nordlb-open.org Juara saat ini, Nicolas Devilder (FRA), mengalahkan Sergio Roitman (ARG) di final tahun 2008Óscar Hernández (ESP) mencapai 2 kali final kategori tunggal, juara tahun 2005 dan 2007, dan final ganda dua kali, menjadi juara kedua tahun ...

Australian celebrity talent show For the upcoming season, see Dancing with the Stars (Australian TV series) season 21. This article may contain excessive or irrelevant examples. Please help improve the article by adding descriptive text and removing less pertinent examples. (August 2023) This article may overuse or misuse color, making it hard to understand for color-blind users. Please remove or fix instances of distracting or hard-to-read colors or remove colored links that may impede user ...







