Pacific Bell
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Untuk orang lain dengan nama yang sama, lihat Indra Gunawan. Indra Gunawan Wakil Bupati Rokan HuluPetahanaMulai menjabat 21 Juni 2021PresidenJoko WidodoGubernurSyamsuar Edy NasutionBupatiSukiman Informasi pribadiLahir21 Desember 1969 (umur 54) Ujung Batu, Rokan Hulu, RiauKebangsaan IndonesiaPartai politikPDI-PSuami/istriSri YulitaAnak4PekerjaanPolitikusSunting kotak info • L • B H. Indra Gunawan atau yang akrab disapa ''Ujang Lurah'' ini (lahir 21 Desember 1969) adalah ...

American football player (1940–1968) Pat TrammellNo. 12circa 1961Born:(1940-07-11)July 11, 1940Scottsboro, Alabama, U.S.Died:December 10, 1968(1968-12-10) (aged 28)Birmingham, Alabama, U.S.Career informationPosition(s)QuarterbackHeight6 ft 0 in (183 cm)Weight200 lb (91 kg)CollegeUniversity of AlabamaHigh schoolScottsboro (AL)Career highlights and awards National champion (1961) Second-team All-American (1961) SEC Player of the Year (1961) Fi...

American basketball coach Tanya HaaveHaave in 2009 while with the University of San FranciscoCurrent positionTitleHead CoachTeamMetro StateConferenceRMACBiographical detailsBorn1963 (age 60–61)Evergreen, ColoradoPlaying career1980–1984Tennessee Coaching career (HC unless noted)1999–2001Regis (assistant)2001–2005Colorado (assistant)2006Denver2006–2010San Francisco2010–presentMetro State Tanya Haave (born 1963) is an American collegiate head coach for the Metro State Roadru...

Leith bahasa Gaelik Skotlandia: Lìte Pemandangan Leith dan Firth of Forth Population 50,030 (2011) Wilayah dewan City of Edinburgh Wilayah keletnanan Edinburgh Negara konstituen Skotlandia Negara berdaulat Britania Raya Kota pos EDINBURGH Distrik kode pos EH6 Kode telepon 0131 Polisi Lothian and Borders Pemadam kebakaran Lothian and Borders Ambulans Scottish Parlemen UE Skotlandia Parlemen Britania Edinburgh North dan Leith Parlemen Skot...

Canadian Forces base 3rd Canadian Division Support Base Edmonton[1]CFB Edmonton / BFC Edmonton / Base de soutien de la 3e Division du Canada Edmonton (French)1 Canadian Mechanized Brigade Group at CFB EdmontonIATA: noneICAO: CYEDWMO: 71121SummaryAirport typeMilitaryOwnerGovernment of CanadaOperatorDepartment of National Defence (Canada) and Canadian Armed Forces[2]LocationSturgeon County, near Edmonton, AlbertaBuilt1955CommanderColonel J.G.P. Lemyre[3]Occupants3rd...

American playwright and actor Denman ThompsonBornOctober 15, 1833 (1833-10-15)Girard, Pennsylvania, USDiedApril 14, 1911 (1911-04-15) (aged 77)West Swanzey, New Hampshire, USOccupation(s)Playwright and actorKnown forThe Old HomesteadSpouseMaria BoltonSignature Denman Thompson and his residence in West Swanzey, NH Henry Denman Thompson (October 15, 1833 – April 14, 1911) was an American playwright and theatre actor. Biography Rufus Thompson, a carpenter, and his wife ...

v · m Champions du monde de poursuite professionnels 1946 : Gerrit Peters 1947 : Fausto Coppi 1948 : Gerrit Schulte 1949 : Fausto Coppi 1950 : Antonio Bevilacqua 1951 : Antonio Bevilacqua 1952 : Sydney Patterson 1953 : Sydney Patterson 1954 : Guido Messina 1955 : Guido Messina 1956 : Guido Messina 1957 : Roger Rivière 1958 : Roger Rivière 1959 : Roger Rivière 1960 : Rudi Altig 1961 : Rudi Altig 1962 ...

Daughter of Lyndon B. Johnson and Lady Bird Johnson Lynda Bird Johnson RobbJohnson Robb in January 2016First Lady of VirginiaIn roleJanuary 16, 1982 – January 18, 1986GovernorChuck RobbPreceded byEdwina P. DaltonSucceeded byJeannie BalilesSecond Lady of VirginiaIn roleJanuary 14, 1978 – January 16, 1982GovernorJohn N. DaltonPreceded byEdwina P. DaltonSucceeded byMartha Davis Personal detailsBornLynda Bird Johnson (1944-03-19) March 19, 1944 (age 80)Washington, D.C.,...

1995 single by Pulp For the social division, see Commoner. Not to be confused with Love of the Common People. Common PeopleSingle by Pulpfrom the album Different Class B-sideUnderwearReleased22 May 1995 (1995-05-22)StudioThe Town House, LondonGenre Britpop rock[1] Length5:50LabelIslandSongwriter(s) Jarvis Cocker Russell Senior Steve Mackey Nick Banks Candida Doyle Producer(s)Chris ThomasPulp singles chronology The Sisters EP (1994) Common People (1995) Mis-Shapes / Sort...
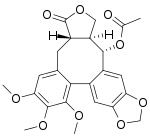
Steganacin (−)-Steganacin Names Preferred IUPAC name (3aS,14S,14aS)-6,7,8-Trimethoxy-3-oxo-1,3,3a,4,14,14a-hexahydro-11H-benzo[3,4]furo[3′,4′:6,7]cycloocta[1,2-f][1,3]benzodioxol-14-yl acetate Identifiers CAS Number (−): 41451-68-7 N[ChemSpider] 3D model (JSmol) (+): Interactive image(−): Interactive image ChEBI (−): CHEBI:9259 ChEMBL (−): ChEMBL154064 ChemSpider (+): 264758(−): 391322 KEGG (−): C10886 PubChem CID (+):&#x...

Spanish contemporary radio station in Orlando, Florida WDBO-FM redirects here. For the original WDBO-FM, see WWKA. For the AM news/talk radio station, see WDBO (AM). WOEXOrlando, FloridaBroadcast areaCentral FloridaFrequency96.5 MHz (HD Radio)BrandingÉxitos 96.5ProgrammingFormatSpanish language contemporary hitsSubchannelsHD2: News/Talk (WDBO simulcast)OwnershipOwnerCox Media Group(Cox Radio, LLC)Sister stationsWCFB, WDBO, WMMO, WWKA, part of Cox cluster with TV station WFTVHistoryFirst air ...

American composer, conductor, and violinist Alexander OlshanetskyBorn(1892-10-23)October 23, 1892OdessaDiedJune 3, 1946(1946-06-03) (aged 53)Atlantic CityCitizenshipRussian EmpireUnited StatesOccupation(s)composer, conductor, violinistYears active1911 – 1946 Alexander Olshanetsky (October 23, 1892 – June 3, 1946) was an American composer, conductor, and violinist. He was a major figure within the Yiddish theatre scene in New York City from the mid-1920s until his death in 1946.&...

لا تروبيكال أميسا بونغو 2020 تفاصيل السباقسلسلة15. لا تروبيكال أميسا بونغومنافسةطواف إفريقيا للدراجات 2020 2.1مراحل7التواريخ20 – 26 يناير 2020المسافات969٫2 كمالبلدان الغابون الكاميروننقطة البدايةبايتام [الإنجليزية]نقطة النهايةليبرفيلالفرق15عدد المتسابقين في البداية90ع�...

Questa voce sull'argomento stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: Unione Sportiva Triestina. Nuova Unione Sportiva Triestina CalcioStagione 1996-1997La formazione della Triestina, schierata prima dell'incontro con il Tolentino Sport calcio Squadra Triestina Allenatore Giorgio Roselli poi Adriano Lombardi Presidente Riccardo Del...

National Football League franchise in Detroit, Michigan Detroit Lions Current seasonEstablished July 12, 1930; 93 years ago (July 12, 1930)[1]First season: 1930Play in Ford FieldDetroit, MichiganHeadquartered in Allen Park, Michigan Detroit Lions logoDetroit Lions wordmarkLogoWordmarkLeague/conference affiliations National Football League (1930–present) Western Division (1933–1949) National Conference (1950–1952) Western Conference (1953–1969) Central Division...

Cinema of theUnited Kingdom List of British films British horror 1888–1919 1920s 1920 1921 1922 1923 19241925 1926 1927 1928 1929 1930s 1930 1931 1932 1933 19341935 1936 1937 1938 1939 1940s 1940 1941 1942 1943 19441945 1946 1947 1948 1949 1950s 1950 1951 1952 1953 19541955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960s 1960 1961 1962 1963 19641965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970s 1970 1971 1972 1973 19741975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980s 1980 1981 1982 1983 19841985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990s 1990 1991 1992 1993 19941995...

Thomas NeuwirthWurst dalam acara Dancing Stars 2014Informasi latar belakangNama lainConchita WurstLahir06 November 1988 (umur 35)Gmunden, AustriaGenrePopPekerjaanPenyanyiTahun aktif2006–sekarangArtis terkaitJetzt Anders! Thomas Tom Neuwirth (lahir 6 November 1988), lebih dikenal sebagai drag queen dengan nama Conchita Wurst, adalah seorang penyanyi Austria. Wurst mewakili Austria dan menjuarai Kontes Lagu Eurovision 2014 di Kopenhagen, Denmark. Ia menggunakan kata ganti wanita untuk me...

Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Daerah Kota JambiDewan Perwakilan RakyatKota Jambi2019-2024JenisJenisUnikameral SejarahSesi baru dimulai23 Agustus 2019PimpinanKetuaPutra Absor Hasibuan, S.H. (Gerindra) sejak 3 Oktober 2019 Wakil Ketua IIr. M.A. Fauzi (PDI-P) sejak 3 Oktober 2019 Wakil Ketua IIRoro Nully Kurniasih Kawuri, S.E. (Demokrat) sejak 15 November 2019 Wakil Ketua IIIPangeran H.K. Simanjuntak, S.E., M.Si. (NasDem) sejak 3 Oktober 2019 KomposisiAnggota45Partai & kursi &...

Państwo frankijskieRegnum Francorum 481–843 Ustrój polityczny Monarchia patrymonialna Stolica Akwizgran[1] Data powstania 481 Data likwidacji 843 Władca Karol I Wielki Waluta denar Język urzędowy łacina Religia dominująca katolicyzm Ekspansja państwa frankijskiego Położenie na mapie Multimedia w Wikimedia Commons Państwo frankijskie, in. Królestwo Franków (łac. Regnum Francorum) – początkowo plemienne państwo Franków, następnie jedno z najsilniejszych[według k...

Celtic tribe of ancient Britain This article is about an ancient British tribe. Not to be confused with Silurus. For the community in Alabama, see Siluria, Alabama. The Silures (UK: /saɪˈljʊəriːz/ sy-LURE-eez, US: /ˈsɪljəriːz/ SIL-yər-eez)[1] were a powerful and warlike tribe or tribal confederation of ancient Britain,[2] occupying what is now south east Wales and perhaps some adjoining areas. They were bordered to the north by the Ordovices; to the east by the Dobun...







