Ottokar Czernin
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada September 2016. Michael Doughty Pelatihan adonan dengan Queens Park Rangers pada tahun 2016Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Michael Edward Doughty[1]Tanggal lahir 20 November 1992 (umur 31)Tempat lahir Westminster, InggrisTinggi 6 ft 1 in (1,85&#...

Wiebes pada 2015 Eric Derk Wiebes (lahir 12 Maret 1963) adalah seorang politikus Belanda yang menjabat sebagai Menteri Urusan Ekonomi dan Kebijakan Iklim dalma kabinet Rutte ketiga dari 26 Oktober 2017 sampai 15 Januari 2021. Ia adalah anggota Partai Rakyat untuk Kebebasan dan Demokrasi (VVD).[1] Referensi ^ VVD'er Eric Wiebes moet economische groei gaan combineren met Parijsdoelen (dalam bahasa Belanda). NOS. 23 October 2017. Diarsipkan dari versi asli tanggal 25 October 2017. ...

Universal Robina CorporationLogo yang digunakan sejak tahun 2016JenisPublikKode emitenPSE: URCIndustriManufakturDidirikan1954; 70 tahun lalu (1954)PendiriJohn Gokongwei Jr.Kantorpusat6/F Tera Tower, Bridgetowne, E.Rodriguez, Jr., Avenue, Ugong Norte, Kota QuezonWilayah operasiAsia Tenggara dan Oseania[1]Tokohkunci John L. Gokongwei, Jr.(Pendiri dan Ketua Emeritus) James L. Go(Ketua Emeritus) Lance Y. Gokongwei(Ketua) Irwin C. Lee(Presiden dan CEO)[2] ProdukMakanan manis, ...

Madoera Stoomtram Maatschappij, N.V.Stasiun KamalIkhtisarKantor pusatMadura, Hindia BelandaDen Haag, BelandaLokalMaduraPenerusKereta Api Indonesia (lintas Madura)TeknisLebar sepur1.067 mm (3 ft 6 in)Panjang jalur225 km (140 mi) Peta jaringan MSM pada tahun 1915. Madoera Stoomtram Maatschappij, N.V. (disingkat MdrSM) adalah salah satu perusahaan kereta api di Hindia Belanda yang beroperasi di Madura. Perusahaan ini menyelenggarakan angkutan trem uap yang melayani ...

This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (August 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Overview of the role of science and technology in the Soviet Union Politics of the Soviet Union Leadership Leaders President list Vice President Collective leadership State Council Presidential Council Communist Party Congress Central Commi...

Édouard GrindaFonctionsMinistre du Travail (en)Gouvernement Théodore Steeg13 décembre 1930 - 27 janvier 1931Conseiller général des Alpes-Maritimes1923-1931Député des Alpes-Maritimes16 novembre 1919 - 31 mai 1932BiographieNaissance 20 décembre 1866Nice (France)Décès 28 mars 1959 (à 92 ans)Nice (France)Sépulture Cimetière du ChâteauNationalité FrançaiseFormation Lycée MassénaActivité Homme politiqueAutres informationsParti politique Alliance démocratiqueVue de la sépul...

Genus of carnivores This article is about the genus of canines. For other uses, see Canis (disambiguation). CanisTemporal range: 5.332–0 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Miocene to present[1] 1st row: wolf (C. lupus),dog (C. familiaris);2nd row: red wolf (C. rufus),eastern wolf (C. lycaon);3rd row: coyote (C. latrans),golden jackal (C. aureus);4th row: Ethiopian wolf (C. simensis),African wolf (C. lupaster). Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Wonder Woman Earth-Two – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2012) (Learn how and when t...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Stadion Ferenc Puskás, adalah stadion di Budapest, Hungaria yang dihancurkan pada tahun 2017. Stadion Ferenc Puskás dapat merujuk ke: Arena Puskás, stadion di Budapest, Hungaria akan dibuka pada 2019 Halaman disambiguasi ini berisi daftar artikel St...

Royal dynasty in Mesopotamia First Dynasty of Ur(26th-25th century BCE)Golden helmet of Meskalamdug, possible founder of the First Dynasty of Ur, circa 2500 BCE.Urclass=notpageimage| Location of Ur, in Western Asia, modern Iraq.Show map of West and Central AsiaUrUr (Iraq)Show map of Iraq Gold objects from tomb PG 580, Royal Cemetery at Ur. The First Dynasty of Ur was a 26th-25th century BCE dynasty of rulers of the city of Ur in ancient Sumer.[1] It is part of the Early Dynastic perio...
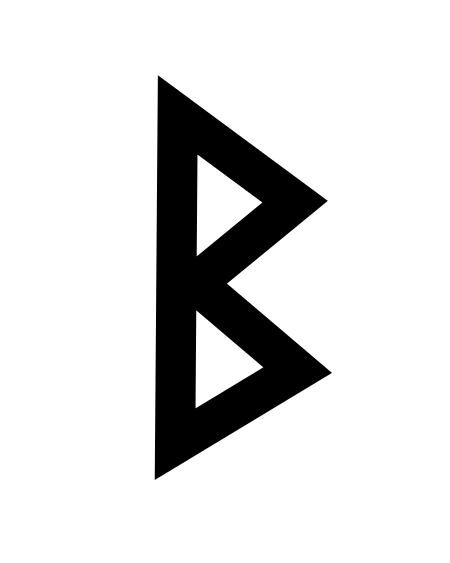
此條目介紹的是拉丁字母中的第2个字母。关于其他用法,请见「B (消歧义)」。 提示:此条目页的主题不是希腊字母Β、西里尔字母В、Б、Ъ、Ь或德语字母ẞ、ß。 BB b(见下)用法書寫系統拉丁字母英文字母ISO基本拉丁字母(英语:ISO basic Latin alphabet)类型全音素文字相关所属語言拉丁语读音方法 [b][p][ɓ](适应变体)Unicode编码U+0042, U+0062字母顺位2数值 2歷史發...

Cell type GnRH neurons, or gonadotropin-releasing hormone expressing neurons, are the cells in the brain that control the release of reproductive hormones from the pituitary. These brain cells control reproduction by secreting GnRH into the hypophyseal portal capillary bloodstream, so are sometimes referred to as “sex neurons”. This small capillary network carries GnRH to the anterior pituitary, causing release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) into the wi...

Chennai Metro Phase 1 network map The Chennai Metro is a rapid transit system serving the city of Chennai and its suburbs. Phase I of the project consisted of two corridors covering a length of 54.15 kilometres (33.65 mi).[1] The elevated section of the project began operations in June 2015, with the entire elevated stretch operational as of October 2016.[2] The entire project completed within the financial year 2019-2020. About 55% of the corridors in Phase I are underg...

Game controller for the PlayStation This article is about the original controller. For other controllers, see PlayStation § Controllers. PlayStation controllerDeveloperSony Interactive EntertainmentManufacturerSonyTypeGamepadGenerationFifthRelease date3 December 1994; 29 years ago (1994-12-03)Discontinued1997Input 10× digital buttons(, , , , Start, Select, L1, R1, L2, R2) Digital D-Pad ConnectivityPlayStation controller portSuccessorDual Analog Controller The PlayStat...

Cet article concerne un positionnement politique. Pour le groupe parlementaire français du même nom, voir Extrême gauche (groupe parlementaire). Affiche du NPA en faveur de la Révolution tunisienne, à Besançon (Doubs, France). Le terme extrême gauche est employé depuis 1920 pour désigner une partie des groupes, mouvements, organisations et partis politiques, « qui se situent à la gauche du Parti communiste et du Parti socialiste »[1], dont les principaux furent d'ob...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

Naval warfare branch of Vietnam's military This article is about the current Vietnamese navy. For the navy of South Vietnam, see Republic of Vietnam Navy. Vietnam People's NavyHải quân nhân dân Việt NamThe insignia used on the ensignFounded7 May 1955Country1955 - 1976: North Vietnam1976 - now: Socialist Republic of VietnamTypeNaval forceRoleNaval warfare and amphibious warfareSize50,000 officers and sailors109 ships (including auxiliaries)Part of People's Army of Vietna...

此條目可能包含不适用或被曲解的引用资料,部分内容的准确性无法被证實。 (2023年1月5日)请协助校核其中的错误以改善这篇条目。详情请参见条目的讨论页。 各国相关 主題列表 索引 国内生产总值 石油储量 国防预算 武装部队(军事) 官方语言 人口統計 人口密度 生育率 出生率 死亡率 自杀率 谋杀率 失业率 储蓄率 识字率 出口额 进口额 煤产量 发电量 监禁率 死刑 国债 ...

صوفيا سميث معلومات شخصية الميلاد 18 نوفمبر 1978 (العمر 45 سنة)هيوستن مركز اللعب وسط الجنسية اليونان المدرسة الأم جامعة كورنيل المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنوات فريق م. (هـ.) 2004 Houston Stars [الإنجليزية] المنتخب الوطني 2004 منتخب اليونان لكرة القدم للسيدات 31 (?) (0) المواقع مُعرِّ�...

Area in the city of Glasgow, Scotland Human settlement in ScotlandGorbalsScottish Gaelic: Gort a' bhaileGorbalsLocation within GlasgowArea0.83 km2 (0.32 sq mi) [1]Population6,030 (2015)[2]• Density7,265/km2 (18,820/sq mi)OS grid referenceNS 59100 64000Council areaGlasgow City CouncilLieutenancy areaGlasgowCountryScotlandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townGLASGOWPostcode districtG5Dialling code0141Police...


