Negro National League (1920–1931)
|
Read other articles:

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento tecnologia audiovideo non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Un 7″ dell'etichetta M-G-M Il 45 giri o 7″ è una tipologia di disco in vinile per la memorizzazione e la riproduzione analogica di segnali sonori che viene registrato e riprodotto ad una velocità di rotazione di 45 giri al minuto.[1]&#...

Beltway around central Moscow, Russia This article is about the Third Ring Road in Moscow. For similarly named roads in other cities, see Third Ring Road (disambiguation). Third Ring RoadТре́тье Tра́нспортное Kольцо́The Third Ring Road (in green) in Moscow[1]Route informationMaintained by the city of MoscowLength35 km (22 mi)HistoryConstruction started in 1960 and finished on December 5, 2003.Major junctionsOrbital around central Moscow, Russia ...

Ираклеониты — ученики гностика Ираклеона (II век). Упоминаются как особая секта Епифанием и Августином; при крещении и миропомазании они соблюдали обряд помазания елеем и при этом произносили воззвания на арамейском языке, которые должны были освободить душу от власт�...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

Marshal of the People's Republic of China (1896–1969) In this Chinese name, the family name is He. YuanshuaiHe Long贺龙Marshal He Long in 1955Member of Central Committee of the Chinese Communist PartyIn officeOctober 1954 – 9 June 1969ChairmanMao ZedongVice Premier of the People's Republic of ChinaIn officeOctober 1954 – 9 June 1969PremierZhou Enlai Personal detailsBorn賀龍(1896-03-22)22 March 1896Sangzhi, Hunan, Qing EmpireDied9 June 1969(1969-06-09) (aged 73...

ألكسندر ليابونوف (بالروسية: Александр Михайлович Ляпунов) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 6 يونيو 1857 [1][2][3] ياروسلافل[4] الوفاة 3 نوفمبر 1918 (61 سنة) [5][1][2] أوديسا[4] سبب الوفاة إصابة بعيار ناري مواطنة الإمبراطورية الروسية عضو ...

Sebuah kerah emas sungguhan. Pekerja Kerah Emas istilah ini diciptakan oleh Profesor Robert E Kelley dari Carnegie Mellon University.[1] Robert Earl Kelley menggunakan istilah ini untuk pertama kalinya 1985 untuk menggambarkan pekerja muda dengan gaji rendah namun senang memberi barang mewah. Namun, istilah ini juga bisa berarti orang yang sangat terampil dan pandai seperti pengacara, periset dan dokter.[2] Dia juga menggunakan istilah manajer kerah emas bagi mereka yang menga...

Extinct subfamily of dinosaurs It has been suggested that this article be merged into Ankylosauridae. (Discuss) Proposed since April 2024. AnkylosaurinesTemporal range: Cretaceous, 105–66 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Skeleton of Scolosaurus thronus, once referred to Euoplocephalus. Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Clade: Dinosauria Clade: †Ornithischia Clade: †Thyreophora Clade: †Ankylosauri...

Aliansi Kebebasan Rakyat Sri Lanka ශ්රී ලංකා නිදහස් පොදුජන සන්ධානයஶ்ரீ லங்கா பொதுஜன சுதந்திர கூட்டமைப்புNama dalam bahasa InggrisSri Lanka People's Freedom AllianceSingkatanSLPFAKetua umumMahinda Rajapaksa[1]Ketua umumMaithripala Sirisena[1]Sekretaris UmumBasil Rajapaksa[1]Dibentuk31 Oktober 2019; 4 tahun lalu (2019-10-31)Dibubarkan5 April 2...

Political party in Hong Kong Kowloon West New Dynamic 西九新動力ChairpersonPriscilla LeungFounded16 March 2008 (2008-03-16)HeadquartersCapital CommercialBuilding, 448Shanghai Street,Mongkok, KowloonIdeologyConservatism (HK)Economic LiberalismPolitical positionCentre-rightRegional affiliationPro-Beijing campColorsGreenLegislative Council1 / 90District Councils0 / 470Websitewww.kowloonwest.hkPolitics of Hong KongPolitical partiesElections Kowloon West New DynamicTra...

The Last OutlawIklan surat kabar kontemporerSutradaraJohn FordDitulis olehEvelyn CampbellJohn FordH. Tipton SteckPemeranEdgar JonesDistributorUniversal Film Manufacturing CompanyTanggal rilis 15 Juni 1919 (1919-06-15) NegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaBisuIntertitel Inggris The Last Outlaw adalah sebuah film koboi pendek Amerika Serikat tahun 1919 yang disutradarai oleh John Ford. Sebagian film tersebut disimpan di arsip film British Film Institute dan arsip film Museum of Modern Art.[1]...

Utility company based in Edmonton, Alberta EPCOR Utilities Inc.FormerlyEdmonton Power CorporationCompany typeMunicipally owned corporationIndustryPublic utilityFounded1996[1][2]HeadquartersEdmonton, Alberta, CanadaAreas servedCanadaUnited StatesKey peopleJohn Elford (President and CEO)[3]Revenue1.3 bil USDOwnerCity of EdmontonNumber of employees3600 (2020)Websiteepcor.com EPCOR Utilities Inc., formerly known as Edmonton Power Corporation, is a utility company base...

The Decline of Western CivilizationPoster film yang menampilkan penyanyi Germs Darby CrashSutradaraPenelope SpheerisProduserJeff PrettymanPenelope SpheerisDitulis olehPenelope SpheerisSinematograferSteve ConantPenyuntingCharlie MullinDistributorMedia Home EntertainmentTanggal rilis 1 Juli 1981 (1981-07-01) Durasi100 menitNegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaInggris The Decline of Western Civilization adalah sebuah film dokumenter Amerika yang difilmkan dari 1979 sampai 1980. Film tersebut berkisah...

Raiffeisen Zentralbank Österreich AG v Five Star General Trading LLCRaiffeisen Zentralbank Österreich headquartersCourtCourt of AppealFull case nameRaiffeisen Zentralbank Österreich AG v Five Star General Trading LLC Decided26 January 2001Citations[2001] QB 825[2001] 2 WLR 1344[2001] EWCA Civ 68[2001] 1 Lloyd's Rep 597[2001] 1 LLR 597[2001] Lloyd's Rep IR 460[2001] 1 All ER (Comm) 961[2001] 3 All ER 257[2001] Lloyds Rep IR 460[2001] CLC 843Case historyAppealed from[2000] 2 Ll.R. 684Court ...

怪談レストラン ジャンル 児童文学、怪談、ホラー、子供向け 小説 著者 怪談レストラン編集委員会編(松谷みよ子責任編集) イラスト たかいよしかず、かとうくみこ 出版社 童心社 刊行期間 1996年 - 巻数 50巻(2010年9月時点) アニメ 原作 松谷みよ子・「怪談レストラン」原作チーム シリーズディレクター 池田洋子 シリーズ構成 米村正二 キャラクターデザイン 高�...

Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens SOX14IdentifiersAliasesSOX14, SOX28, SRY-box 14, SRY-box transcription factor 14External IDsOMIM: 604747; MGI: 98362; HomoloGene: 31224; GeneCards: SOX14; OMA:SOX14 - orthologsGene location (Human)Chr.Chromosome 3 (human)[1]Band3q22.3Start137,764,315 bp[1]End137,766,334 bp[1]Gene location (Mouse)Chr.Chromosome 9 (mouse)[2]Band9 E3.3|9 52.11 cMStart99,756,159 bp[2]End99,758,223 bp[2]RNA express...
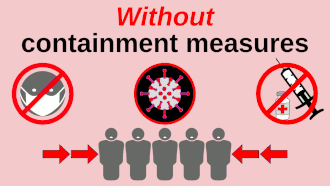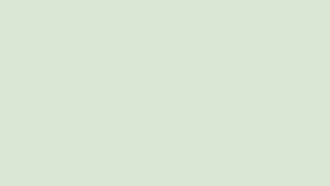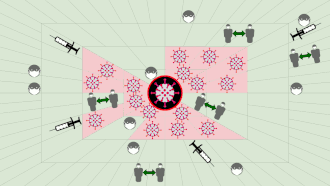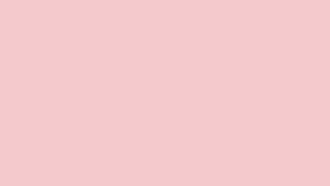
Infection control technique by keeping a distance from each other Not to be confused with social distance or social isolation. For the Lil Baby song, see My Turn (Lil Baby album). People socially distancing while queuing to enter a supermarket in London during the COVID-19 pandemic Without social distancing and other pandemic containment measures, pathogens can spread exponentially.[1] This graphic shows how early adoption of containment measures tends to protect wider swaths of the p...

Districts du canton de Saint-Gall en 2002. Cet article présente une liste des anciens districts du canton de Saint-Gall en Suisse. Ils ont été remplacés en 2003 par huit circonscriptions électorales. Histoire Découpage initial Le canton de Saint-Gall (en allemand : Kanton Sankt Gallen) a été créé par le chapitre IX de l'acte de médiation du 19 février 1803. Son article 1er le divisa en huit districts (en allemand : Berzike), subdivisés en quarante-quatre cercles (en all...

علم نيو جيرسي ألوان أصفر برتقالي [لغات أخرى] الاعتماد 11 مارس 1896 الاختصاص نيوجيرسي تعديل مصدري - تعديل علم ولاية نيوجرسي اعتمد هذا العلم رسميا في ولاية نيوجرسي الأمريكية في 11 مارس من سنة 1896 .[1] مراجع ^ معلومات عن علم نيو جيرسي على موقع britannica.com. britannica...

American actor (1833–1893) This article is about the American actor. For other people with the same name, see Edwin Booth (disambiguation). Edwin BoothPortrait of Booth, c. 1886BornNovember 13, 1833Bel Air, Maryland, U.S.DiedJune 7, 1893(1893-06-07) (aged 59)New York City, U.S.Resting placeMount Auburn CemeteryCambridge, MassachusettsOther namesThe MasterOccupationActorSpouses Mary Devlin (m. 1860; died 1863) Mary McVicker ...

