Nectanebo I
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento Francia non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. AlsaziaCollettività territoriale a statuto specialeCollectivité européenne d'Alsace LocalizzazioneStato Francia RegioneGrande Est AmministrazioneCapoluogo Strasburgo Data di istituzione1º gennaio 2021 TerritorioCoordinatedel capoluogo48°30′N 7°30′E...

Tombe ZhaolingPrésentationType MausoléePartie de Tombes impériales des dynasties Ming et QingSurface 478 900 m2 ou 3 187 400 m2Patrimonialité Partie d'un site du patrimoine mondial UNESCO (d) (2004)Site national majeur (1982) Patrimoine mondialIdentifiant 1004-014LocalisationLocalisation Shenyang, Liaoning ChineCoordonnées 41° 51′ 08″ N, 123° 25′ 38″ E Géolocalisation sur la carte : Liaoning Géolocalisation sur...

Mark Looms Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Mark LoomsTanggal lahir 24 Maret 1981 (umur 43)Tempat lahir Almelo, BelandaTinggi 1,92 m (6 ft 3+1⁄2 in)Posisi bermain BekInformasi klubKlub saat ini NAC BredaNomor 4Karier junior Luctor et Emergo FC TwenteKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2000–2012 Heracles Almelo 321 (9)2012– NAC Breda * Penampilan dan gol di klub senior hanya dihitung dari liga domestik dan akurat per Mei 2012 Mark Looms (pelafalan dalam bahasa ...

Joaquim Gomes, AlagoasMunisipalitasNegara BrasilNegara bagianAlagoasLuas • Total298,291 km2 (115,171 sq mi)Populasi (2010) • Total22.575 • Kepadatan0,076/km2 (0,20/sq mi) Joaquim Gomes merupakan sebuah munisipalitas yang terletak di negara bagian Brasil di Alagoas. lbs Munisipalitas di AlagoasIbu kota: MaceióArapiraca Arapiraca Campo Grande Coité do Nóia Craíbas Feira Grande Girau do Ponciano Lagoa da Canoa Limoeiro de Anadia S�...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع إمبراطور (توضيح). إمبراطورفرع من عاهل النوع لقب نبيلمنصب تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات ألقاب النبلاء إمبراطور ملك أرشيدوق ولي عهد دوق أكبر أمير / إنفانتي دوق فورست [الإنجليزية] مركيزمرغريف / لاندغراف كونت / إيرل فيكونت / نائب المركيز ...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) كريثيديا دو دوفين 2010 طواف العالم للدراجات 2010 السباق 15 من 26 السلسلة طواف العالم للدراجات 2010 رقم السباق 15 س�...

British energy supply company Co-operative Energy LimitedCompany typePrivate subsidiary company of an Industrial and Provident SocietyIndustryPublic utilityFounded2010ProductsGas and electricity supplyParentThe Midcounties Co-operativeWebsiteenergy.yourcoop.coop Co-op Energy is a membership-owned British energy supply company based in Warwick that began trading in 2010. It sells renewable electricity (some from community-owned sources) and gas to its ethically concerned member owner/customers...

Public university in Portales, New Mexico, U.S. Eastern New Mexico UniversityFormer nameEastern New Mexico Junior College (1927–1940)Eastern New Mexico College (1940–1949)MottoExplore. Experience. Excel.[1]TypePublic universityEstablished1927; 97 years ago (1927)Academic affiliationsCONAHECChancellorJames N JohnstonAcademic staff156 full-time and 83 part-time (Fall 2023)[2]Students5,106 (3,833 undergraduate) (Fall 2023)[3]LocationPortales, New Me...

Russian cellist and academic (1948–2014) Alexander IvashkinАлександр Васильевич ИвашкинAlexander Ivashkin, 1990, Moscow. Photo by D. SmirnovBorn(1948-08-17)17 August 1948Blagoveshchensk, Soviet UnionDied31 January 2014(2014-01-31) (aged 65)London, United KingdomOccupation(s)Cellist, academic, writerKnown forBiographer of Alfred SchnittkeSpouseNatalia PavlutskayaAcademic backgroundEducationRussian Music Academy (M.Mus., D.M.A.)Alma materRussian State Insti...

كاتدرائية سترينغنس كاتدرائية سترينغنسكاتدرائية سترينغنس احداثيات 59°22′32.16″N 17°02′04.56″E / 59.3756000°N 17.0346000°E / 59.3756000; 17.0346000 المكان سترينغنس الطائفة كنيسة السويد الطائفة السابقة الكنيسة الرومانية الكاثوليكية الإدارة أبرشية أبرشية سترينغنس رجال الدين الأساقفة يو...

English actor Bernard ArchardBernard Archard in 1962Born(1916-08-20)20 August 1916Fulham, London, EnglandDied1 May 2008(2008-05-01) (aged 91)Witham Friary, Somerset, EnglandOccupationActorYears active1948–1994PartnerJames Belchamber Bernard Joseph Archard (20 August 1916 – 1 May 2008) was an English actor who made many film and television appearances. He was also a pupil at the Chelsea secondary school Sloane Grammar. Early life and career Archard was born in Fulham, London, whe...

The Soul HerderIklan surat kabarSutradaraJohn FordDitulis olehGeorge HivelyPemeranHarry CareySinematograferBen F. ReynoldsPerusahaanproduksiNew York Motion Picture CompanyDistributorUniversal Film Manufacturing Co.Tanggal rilis 03 Agustus 1917 (1917-08-03) Durasi30 menitNegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaAntarjudul Inggris The Soul Herder adalah sebuah film koboi bisu Amerika Serikat tahun 1917 garapan John Ford, dan menampilkan Harry Carey. Film tersebut dianggap menjadi film hilang.[1]...
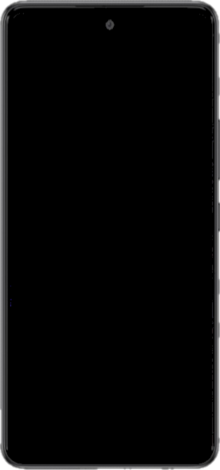
Android smartphone by Samsung Samsung Galaxy A53 5GFront of the Samsung Galaxy A53 5GCodenameGalaxy ABrandSamsung GalaxyManufacturerSamsung ElectronicsColorsAwesome Black, Awesome White, Awesome Blue, Awesome PeachSeriesGalaxy A seriesModelInternational models:SM-A536SM-A536E Indian modelSM-A536UJapanese models:SCG15 (au)SC-53C (NTT Docomo)Compatible networksGSM / HSPA / LTE / 5G NRFirst releasedMarch 17, 2022; 2 years ago (2022-03-17)PredecessorSamsung Galaxy A52SuccessorSa...

Sign language used in the United Kingdom British Sign Language (BSL)Breetish Sign Leid (Scots)Iaith Arwyddion Prydain (Welsh)Cànan Soidhnidh Bhreatainn (Scottish Gaelic)Teanga Chomharthaíochta na Breataine (Irish)Native toUnited KingdomNative speakers77,000 (2014)[1]250,000 L2 speakers (2013)Language familyBANZSL British Sign Language (BSL)Writing systemnone widely accepted SignWriting[2]Official statusOfficial language inScotland[3]...

State park in Virginia, USA Sailor's Creek Battlefield Historical State Park (Prince Edward County, Virginia), Rice, Virginia, U.S.A.Entry sign, with the Overton-Hillsman House in the backgroundLocation of Sailor's Creek Battlefield Historical State Park (Battle of Sayler's Creek - April 6th, 1865)Show map of VirginiaSailor's Creek Battlefield Historical State Park (the United States)Show map of the United StatesLocation6541 Saylers Creek Road, (Prince Edward County), Rice, Virginia 23966Coor...

Discurso presidencial a la Asamblea Federal de 2023 Vladímir Putin pronunciando el discurso en el Gostiny Dvor de Moscú.LocalizaciónPaís RusiaLugar Gostiny DvorCoordenadas 55°45′14″N 37°37′32″E / 55.754, 37.6255Datos generalesTipo Presidential Address to the Federal Assembly of Russia, acontecimiento y discursoParticipantes Vladímir PutinHistóricoFecha 21 de febrero de 2023Hora 12:05 MSK (09:05 UTC)Duración 105 minutos[1][2][editar datos en ...

غروفير الإحداثيات 36°15′46″N 101°24′18″W / 36.2628°N 101.405°W / 36.2628; -101.405 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2][3] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة هانزفورد خصائص جغرافية المساحة 2.854073 كيلومتر مربع (1 أبريل 2010) ارتفاع 968 متر عدد السكان عدد ا�...

جامعة فريدرش فيلهيلم في برلين معلومات المؤسس فريدرش فيلهلم الثالث ملك بروسيا التأسيس 1828 الموقع الجغرافي إحداثيات 52°31′05″N 13°23′36″E / 52.518056°N 13.393333°E / 52.518056; 13.393333 المكان برلين البلد بروسيا الرايخ الألماني سميت باسم فريدرش فيلهلم الثالث ملك ...

American movie studio Artisan Entertainment, Inc.FormerlyU.S.A. Home Video (1983–1987)International Video Entertainment, Inc. (1984–1990)LIVE Entertainment (1988–1998)Company typeSubsidiaryIndustryHome videoMotion picturesPredecessorVestron PicturesVestron VideoFounded1983; 41 years ago (1983) (as U.S.A. Home Video)Defunct2004; 20 years ago (2004)FateAcquired and folded into Lions Gate Entertainment, Inc.SuccessorLionsgate Home EntertainmentLionsgate ...

86-й гвардейский истребительный авиационный Борисовский Краснознамённый ордена Суворова полк Вооружённые силы ВС СССР Вид вооружённых сил ВВС Род войск (сил) истребительная авиация Почётные наименования «Борисовский» Формирование 01.05.1943 г. Расформирование (преобразов�...





