London Welsh RFC
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Powiat Wysokie Mazowieckie Lambang Powiat Włodawa Lokasi Powiat Włodawa Informasi Negara Polandia Provinsi Lublin Ibu kota Włodawa (kota) Luas 1.256,27 km² Penduduk 39 148 (30 Juni 2016) Kadar urbanisasi 34,08 % Kode internasional (+48) 82 Pelat nomor kendaraan bermotor LWL Pembagian administratif Kota 1 Kota kecamatan: - Kelurahan 7 Politik (Status: ) Bupati (Starost) Andrzej Romańczuk Alamat al. J. Piłsudskiego 24 22-200 Włodawa Situs web resmi https://powiatwlodawski.pl/ ...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (avril 2008). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? Com...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Il giardino dei ciliegi (disambigua). Il giardino dei ciliegiOpera teatrale in quattro atti AutoreAnton Čechov Titolo originaleВишнёвый сад Lingua originaleRusso Composto nel1903 Prima assoluta17 gennaio 1904Teatro d'Arte di Mosca Personaggi Ljubov' Andreevna Ranevskaja, proprietaria terriera Anja, sua figlia, 17 anni Varja, sua figlia adottiva, 24 anni Leonid Andreevič Gaiev, fratello della Ranevskaja Ermolaj Alekseev...

Greek mythology half bull and half serpent Ophiotaurus Mosaic, Yorkshire Museum, York (Eboracum)In Greek mythology, the Ophiotaurus (Ancient Greek: Ὀφιόταυρος) was a creature that was part bull and part serpent. Its only known appearance in an ancient work was in Ovid's Fasti. In this poem, it was the subject of a prophecy which warned that whoever burned the innards of the Ophiotaurus would defeat the gods. Briareus attempted to burn the Ophiotaurus but was foiled by a bird sent b...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Villard-de-Lans (race bovine), Hameaux et lieux-dits de Villard-de-Lans, Histoire de Villard-de-Lans, Personnalités liées à Villard-de-Lans et Maison du patrimoine de Villard-de-Lans. Villard-de-Lans 1. Le bourg de Villard-de-Lans depuis la colline des Bains2. L'entrée principale de l'hôtel de ville3.L'église Saint-Bonnet4. Photmontage de plusieurs lieux de la commune Blason Administration Pays France Région Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Département Isère A...

For particular legal codes of the Philippines, see Philippine legal codes. Philippine Registry of Cultural PropertyPatalaan ng mga Ari-arian Kultural ng Pilipinas (Filipino)Current logoAgency overviewFormed2009; 15 years ago (2009)Parent departmentNational Commission for Culture and the ArtsWebsitehttp://ncca.gov.ph/philippine-registry-cultural-property-precup/ The Philippine Registry of Cultural Property, abbreviated as PRECUP (Filipino: Patalaan ng mga Ari-ariang Kult...

American ice hockey player (born 1993) Ice hockey player Jonny Brodzinski Brodzinski with the Ontario Reign in 2017Born (1993-06-19) June 19, 1993 (age 30)Blaine, Minnesota, U.S.Height 6 ft 1 in (185 cm)Weight 215 lb (98 kg; 15 st 5 lb)Position ForwardShoots RightNHL teamFormer teams New York RangersLos Angeles KingsSan Jose SharksNHL draft 148th overall, 2013Los Angeles KingsPlaying career 2015–present Jonathan Brodzinski (born June 19, 1993) is ...

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) ...

Henry FurneseFonctionsMembre du 5e Parlement de Grande-Bretagne (d)5e Parlement de Grande-Bretagne (en)Membre du 11e Parlement de Grande-Bretagne (d)Membre du 9e Parlement de Grande-Bretagne (d)Membre du 8e Parlement de Grande-Bretagne (d)8e Parlement de Grande-Bretagne (d)Membre du 6e Parlement de Grande-Bretagne (d)6e Parlement de Grande-Bretagne (d)Membre du 7e Parlement de Grande-Bretagne (d)7e Parlement de Grande-Bretagne (d)Membre du 10e Parlement de Grande-Bretagne (d)BiographieDécès...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助�...

Bendera difabel Nama Bendera difabel Pemakaian Simbol komunitas difabel Perbandingan 3:5 Dipakai 2017 Rancangan Triwarna dengan tiga strip horizontal berukuran setara berwarna emas, perak, dan perunggu Perancang Eros Recio Bendera difabel atau bendera hak orang dengan kebutuhan khusus adalah sebuah bendera yang mewakili orang-orang difabel. Bendera tersebut dibuat oleh penari Valensia Eros Recio pada 2017[1][2] dan kemudian dipersembahkan kepada Perserikatan Bangsa-Bangsa. Be...

Stasiun Krueng Geukueh CM01 KA Perintis / Cut Meutia di emplasemen Stasiun Krueng GeukuehLokasiJalan Rel Kereta ApiKeude Krueng Geukueh, Dewantara, Aceh Utara, AcehIndonesiaKoordinat5°14′37.450″N 97°1′14.290″E / 5.24373611°N 97.02063611°E / 5.24373611; 97.02063611Koordinat: 5°14′37.450″N 97°1′14.290″E / 5.24373611°N 97.02063611°E / 5.24373611; 97.02063611Ketinggian+9 mOperator Sub Divisi Regional I.1 Aceh Letakkm 233+021 ...

1917 African-American protest in New York City For other uses, see Silence March. Silent ParadePart of the reaction to the East St. Louis riotsand anti-lynching movementThe 1917 Silent Parade in New YorkDateJuly 28, 1917LocationNew York City, New York, United States40°45′47″N 73°58′26″W / 40.76306°N 73.97389°W / 40.76306; -73.97389Caused byBlack people deaths during the East St. Louis riotsGoalsTo protest murders, lynchings, and other anti-black violence; t...
Запит «Військовий фільм» перенаправляє сюди; див. також інші значення. Кінематограф Загальна інформація Кіномистецтво Історія кіно Теорія кіно Кіновиробництво Сценарій Пре-продакшн Зйомки Кіновиробництво Паралельне кіновиробництво Постпродукція Монтаж Редагування ...

Country in Central Africa This article is about the country. For other uses, see Cameroon (disambiguation). Republic of CameroonRépublique du Cameroun (French) Flag Coat of arms Motto: Paix – Travail – Patrie (French)Peace – Work – FatherlandAnthem: Ô Cameroun, Berceau de nos Ancêtres (French)O Cameroon, Cradle of Our Forefathers CapitalYaoundé[1]3°52′N 11°31′E / 3.867°N 11.517°E / 3.867; 11.517Largest cityDoualaOffi...
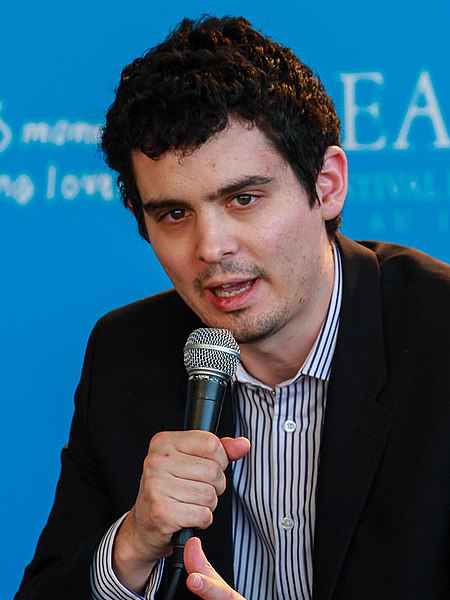

La La Land Logotipo de la película.Título La ciudad de las estrellas: La La Land(España)La La Land: Una historia de amor(México y Centroamérica)La La Land: Ciudad de sueños(Sudamérica)Ficha técnicaDirección Damien ChazelleAyudante de dirección Peter KohnDirección artística Austin GorgProducción Fred BergerGary GilbertJordan HorowitzMarc PlattDiseño de producción David WascoGuion Damien ChazelleMúsica Justin HurwitzSonido Ai-Ling LeeMildred IatrouMaquillaje Torsten WitteFotogra...

PretzelBerbagai bentuk pretzelJenisroti, pastriTempat asalEropaSunting kotak info • L • BBantuan penggunaan templat ini Buku resep: Pretzel Media: Pretzel Sebuah ilustrasi dari abad 12 Hortus deliciarum dari Alsace mungkin lukisan paling tua dari sebuah pretzel, yang terlihat pada sebuah perjamuan dengan Ratu Esther dan Raja Ahasuerus Pretzel adalah sejenis kue yang berasal dari Eropa, kemungkinan besar dari Jerman. Kue ini berupa tiga simpul atau belitan. Rasanya asin...

Отдельная Запорожская дивизияукр. Окрема Запорізька дивізія Годы существования после 29 апреля – до 16 ноября 1918 Страна Украинская Держава Подчинение Армия Украинской Державы Тип сухопутные войска Дислокация Харьковской губернии Участие в Гражданская война в России Ре...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع معدن (توضيح). مجموعة معادن. مجموعة معادن. المعدِن[1] (يسمى في بعض الدول العربية بالفلز) مركب صلب، يتكون طبيعياً من خلال عمليات جيولوجية.[2][3][4] ولا تعود الكلمة على المركب الكيميائي فقط، ولكن على البناء المعدني أيضاً. تتغاير المعادن في ا�...

French scientist (1683–1755) Thermometer of Lyon in the Science Museum in London Jean-Pierre Christin (31 May 1683 – 19 January 1755) was a French physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and musician. His proposal in 1743 to reverse the Celsius thermometer scale (from water boiling at 0 degrees and ice melting at 100 degrees, to where zero represented the freezing point of water and 100 represented the boiling point of water) was widely accepted and is still in use today.[1][2&#...
