LINPACK benchmarks
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Iwana adalah nama Jepang. Tokoh-tokoh dengan nama Jepang ini antara lain: Pemain sepak bola Jepang Iwana Kobayashi Takuya Iwanami Halaman-halaman lainnya Semua halaman dengan Iwana Semua halaman dengan judul yang mengandung Iwana Halaman disambig...

D'Academy AsiaMusim 1Penayangan16 November 2015 – 29 Desember 2015Juri Hetty Koes Endang Hendro Saky DJ Daffy Hans Anuar Zul 2BY Pak Ngah Mayuni OmarPembawa acaraRamzi Rina Nose Irfan Hakim Andhika PratamaSaluranIndosiarLokasi finalStudio 5 IndosiarPemenangDanang PradanaAsalIndonesiaLagu kemenanganBidadari JiwaGenreDangdutJuara dua Lesti Kejora (1st Runner-Up) Shiha Zikir (2nd Runner-Up)Kronologi 2015 ► D'Academy Asia (Musim 1) adalah sebuah ajang kompetisi menyanyi dangdut musim pe...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: List of Miss World runners-up and finalists – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) For the Miss World titleholders, see List of Miss World titleholders.This article provides the names ...

Kolonisasi dan imperialisme pada akhir Perang Dunia II (1945) Koloni atau tanah jajahan adalah tempat yang dikuasai oleh negara lain. Negara metropolitan adalah negara yang memiliki koloni. Negara yang memiliki banyak koloni sering disebut sebagai Kerajaan. Penjajah adalah orang yang datang ke daerah asing untuk membuat koloni di sana dan kemudian mengontrol daerah itu. Kolonis adalah orang yang tinggal di koloni. Sekarang tidak lagi ada banyak negara yang de jure bersifat kolonial karena ber...

Hormone-producing glands of a body Endocrine systemMain glands of the human endocrine systemDetailsIdentifiersLatinsystema endocrinumMeSHD004703FMA9668Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] The endocrine system[1] is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endoc...

Below a weight considered healthy For the financial securities rating, see Underweight (stock market). Medical conditionUnderweightThe underweight range according to the body mass index (BMI) is the white area on the chart.SpecialtyEndocrinology Part of a series onHuman body weight General concepts Obesity (Epidemiology) Overweight Underweight Body shape Weight gain Weight loss Gestational weight gain Diet (nutrition) Weight management Overnutrition Childhood obesity (Epidemiology) Medical co...

Indian state government owned dairy cooperative society This article is about the cooperative. For other uses, see Amul (disambiguation). Anand Milk Union LimitedTrade nameAmul CoopCompany typeCooperativeIndustryDairyFounded14 December 1946; 77 years ago (1946-12-14)FounderTribhuvandas PatelHeadquartersAnand, Gujarat, IndiaArea servedWorldwideKey peopleJayen Mehta (managing director)ProductsMilk productsRevenue ₹52,000 crore (US$6.5 billion)[1] (2022)Owne...

1942 French comic book by Horst Rosenthal Mickey au Camp de Gurs(Mickey Mouse in the Gurs Internment Camp)Cover of Mickey au Camp de GursCreatorHorst RosenthalDate1942Main charactersMickey MousePage count15 pagesOriginal publicationPublished inMickey à Gurs: Les Carnets de dessin de Horst Rosenthal(Mickey in Gurs: The comic books of Horst Rosenthal)Date of publication2014LanguageFrenchISBN978-27021-438-5-8 Mickey au Camp de Gurs (Mickey Mouse in the Gurs Internment Camp)[1]...
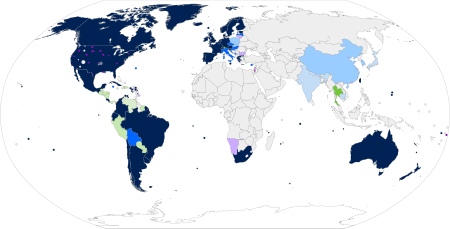
اتحاد مدني الاتحاد المدني (ويُعرف أيضًا بالشراكة المدنية) هو ترتيب معترف به قانونيًا مشابه للزواج، أُنشئ في المقام الأول وسيلةً لمنح الاعتراف القانوني للأزواج من نفس الجنس. يمنح الاتحاد المدني بعض حقوق الزواج أو كلها ما عدا التسمية ذاتها. أنشئت الاتحادات المدنية تح�...

Este artigo ou se(c)ção trata de um evento desportivo recente ou em curso. A informação apresentada pode mudar com frequência. Não adicione especulações, nem texto sem referência a fontes confiáveis.Editado pela última vez em 27 de maio de 2024. Brasileirão Série B 2024 – Betnacional Brasileirão 2024 - Série B Dados Participantes 20 Organização CBF Período 19 de abril – 26 de novembro Gol(o)s 145 Partidas 62 Média 2,34 gol(o)s por partida Melhor marcador 4 gols: Gustavo...

County in Ireland County in Leinster, IrelandCounty Wicklow Contae Chill MhantáinCounty Coat of armsNickname: The Garden of IrelandMotto(s): Meanma Saor (Irish)Free SpiritsCountryIrelandProvinceLeinsterRegionEastern and MidlandEstablished1606[1]County townWicklowLargest settlementBrayGovernment • Local authorityWicklow County Council • Dáil constituencyWicklow • EP constituencySouthArea[2] • Total2,027 km2 (...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Landström. Cet article est une ébauche concernant un athlète finlandais. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Eeles Landström Eeles Landström en 1958. Informations Disciplines Saut à la perche Nationalité Finlandais Naissance 3 janvier 1932 Viiala Décès 29 juin 2022 (à 90 ans) Helsinki Taille 1,85 m Masse 81 kg Club RU-38 Michigan Wolverines Palmarès M...

Village in Wisconsin, United StatesStoddard, WisconsinVillageLocation of Stoddard in Vernon County, Wisconsin.Coordinates: 43°39′46″N 91°13′11″W / 43.66278°N 91.21972°W / 43.66278; -91.21972Country United StatesState WisconsinCountyVernonArea[1] • Total0.71 sq mi (1.84 km2) • Land0.64 sq mi (1.65 km2) • Water0.07 sq mi (0.19 km2)Elevation[2]659 f...

Hanušovce nad Topľoucittà Hanušovce nad Topľou – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Slovacchia Regione Prešov DistrettoVranov nad Topľou TerritorioCoordinate49°01′39″N 21°30′13″E49°01′39″N, 21°30′13″E (Hanušovce nad Topľou) Altitudine197[1] m s.l.m. Superficie14,37 km² Abitanti3 792[2] (31-12-2009) Densità263,88 ab./km² Altre informazioniCod. postale094 31 Prefisso057 Fuso orarioUTC+1 TargaVT CartografiaHanušovce n...

Fell in the Lake District, Cumbria, England Grey KnottsGrey Knotts seen from above the Stonethwaite valleyHighest pointElevation697 m (2,287 ft)Prominencec. 15 mParent peakBrandrethListingWainwright, NuttallCoordinates54°30′11″N 3°12′29″W / 54.503°N 3.208°W / 54.503; -3.208GeographyGrey KnottsLocation in the Lake District National ParkShow map of the Lake DistrictGrey KnottsLocation in Allerdale, CumbriaShow map of the former Allerdale Borou...

Den här artikeln behöver källhänvisningar för att kunna verifieras. (2015-01) Åtgärda genom att lägga till pålitliga källor (gärna som fotnoter). Uppgifter utan källhänvisning kan ifrågasättas och tas bort utan att det behöver diskuteras på diskussionssidan. KékesKékes är Ungerns högsta berg och ligger i kedjan Mátra. Toppen ligger 1 014 meter över havet. Namnet Kékes kommer från bergets blåaktiga färg. På ungerska betyder kék blå medan kékes betyder blåa...

This article is about the US area. For the German area, see Steigerwald Nature Park. Steigerwald Lake National Wildlife RefugeIUCN category IV (habitat/species management area)LocationClark County, Washington, United StatesNearest cityWashougal, WashingtonCoordinates45°34′02″N 122°18′14″W / 45.5673413°N 122.3039798°W / 45.5673413; -122.3039798[1]Area1,049 acres (4.25 km2; 425 ha)Established1987Governing bodyU.S. Fish and Wildlife...

Azerbaijani politician and diplomat Hasan HasanovHəsən HəsənovHasanov in 2010Minister of Foreign AffairsIn office2 September 1993 – 16 February 1998PresidentHeydar AliyevPreceded byTofig GasimovSucceeded byTofig ZulfugarovPrime Minister of AzerbaijanIn office5 February 1991 – 4 April 1992PresidentAyaz MutallibovYagub Mammadov (acting)Preceded byPosition established(Himself as Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Azerbaijan SSR)Succeeded byFiruz Mustafayev (act...

Railway station in New Zealand PahiatuaNew Zealand Government Railways (NZGR)Regional railGeneral informationLocationPahiatua – Mangahao RoadTararuaNew ZealandCoordinates40°26′42.12″S 175°48′54.42″E / 40.4450333°S 175.8151167°E / -40.4450333; 175.8151167Elevation116 metres (381 ft)Owned byKiwiRailOperated byPahiatua Railcar Society (lessee)[1]Line(s)Wairarapa LineDistance154.62 kilometres (96.08 mi) from WellingtonPlatformsSingle sideTra...

Cette liste est une ébauche concernant l’histoire, le catholicisme et le Trentin-Haut-Adige. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Blason de l'archidiocèse de Trente. Ceci est une liste des évêques et archevêques de l'archidiocèse de Trente. En 1027, l'empereur confie le comté de Trente, ainsi que les comtés de Botzen et de Vintschgau, à l'évêque de Trente et érige la principauté ainsi f...



