Kunqu
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Maret 2016. Jalan Riggaشارع الرقّة Negara: Uni Emirat Arab (UEA) Panjang: 0.8 mi (1 km) Kota: Dubai Jalan Rigga (Bahasa Arab: شارع الرقّة) merupakan sebuah jalan di Deira, Dubai. Memiliki berbagai aktivitas pariwisata dan lokasi institusi ...
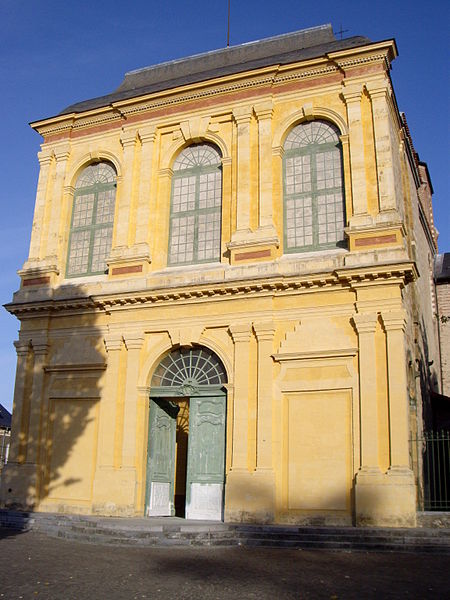

Katedral TarbesKatedral Santa MariaPrancis: Cathédrale Notre-Dame-de-la-Sède de Tarbescode: fr is deprecated Katedral TarbesLokasiTarbesNegara PrancisDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaArsitekturStatusKatedralStatus fungsionalAktifAdministrasiKeuskupanKeuskupan Tarbes et Lourdes Katedral Tarbes (Prancis: Cathédrale Notre-Dame-de-la-Sède de Tarbescode: fr is deprecated ) adalah sebuah gereja katedral Katolik yang terletak di kota dari Tarbes, Hautes-Pyrénées, Prancis. Katedral adalah monu...

Scottish footballer Stephen Pearson Pearson with Motherwell in 2015Personal informationFull name Stephen Paul Pearson[1]Date of birth (1982-10-02) 2 October 1982 (age 41)Place of birth Lanark, ScotlandHeight 1.85 m (6 ft 1 in)[2]Position(s) MidfielderSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2000–2004 Motherwell 80 (12)2004–2007 Celtic 56 (6)2007–2012 Derby County 112 (4)2008 → Stoke City (loan) 4 (0)2011–2012 → Bristol City (loan) 28 (3)2012–2014 Br...

Car of History by Carlo Franzoni, 1819, features a life size statue of Clio, the muse of history. It is the largest chariot clock ever made,[1] and is exhibited in National Statuary Hall, US Capitol. A chariot clock is a type of mantel/table figural clock in the form of a chariot whose dial is set into the wheel or elsewhere, its origins date back to the second half of the 16th century southern Germany.[2] Normally of classical mythology subject matter, it has been made in dif...

Here is a list of the administrative comarcas (administrative subdivisions) in the autonomous community of Aragon in Spain. They were officially delimited in 1999, with substantial changes over a previously proposed division. Comarcas of Aragon No. Name Capital Province 1 Jacetania Jaca Huesca, Zaragoza 2 Alto Gállego Sabiñánigo Huesca 3 Sobrarbe Boltaña Huesca 4 Ribagorza/Ribagorça Graus-Benabarre Huesca 5 Cinco Villas/Zinco Billas Ejea de los Caballeros Zaragoza 6 Hoya de Huesca/Plana ...

Kejuaraan DuniaFormula Satu FIA 1989 Juara Dunia Pembalap: Alain Prost Juara Dunia Konstruktor: McLaren-Honda Sebelum: 1988 Sesudah: 1990 Balapan menurut negaraBalapan menurut musim Alain Prost (foto tahun 2008) berhasil memenangkan gelar Kejuaraan Dunia Pembalap untuk tim McLaren-Honda dengan 76 poin. Rekan setim Prost, yaitu Ayrton Senna, menjadi runner-up, tertinggal 16 poin. Riccardo Patrese berada di urutan ketiga dengan 40 poin untuk tim Williams-Renault. Tim McLaren-Honda berhasil mem...

Jembatan Lama KediriFoto Jembatan Lama yang dipotret sebelum tahun 1922Koordinat7°48′50″S 112°0′26.65″E / 7.81389°S 112.0074028°E / -7.81389; 112.0074028Moda transportasiKendaraan R2, dan pejalan kakiMelintasiSungai BrantasLokalKota Kediri, Jawa TimurNama resmiJembatan Brug Over den Brantas te KediriKarakteristikDesainJembatan besiBahan bakuBesiPanjang total160 mLebar5.80 mTinggi7.50 mSejarahMulai dibangun1855Selesai dibangun1869Lokasi Jembatan Brug Over de...

Species of legume Acmispon brachycarpus Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Eudicots Clade: Rosids Order: Fabales Family: Fabaceae Subfamily: Faboideae Genus: Acmispon Species: A. brachycarpus Binomial name Acmispon brachycarpus(Benth.) D.D.Sokoloff Synonyms[1][2] Anisolotus brachycarpus (Benth.) Rydb. Anisolotus trispermus (Greene) Wooton & Standl. Hosackia brachycarpa Benth. Hosackia trisperma (Greene) Brand Lotu...

Public university in Vermont, U.S. Vermont state redirects here. For the U.S. state, see Vermont. Vermont State UniversityTypePublic universityEstablishedJuly 1, 2023 (2023-07-01)AccreditationNECHEPresidentDavid Bergh (interim)Students4,775LocationCastleton, Johnson, Lyndon, Randolph, and Williston, Vermont, United StatesCampusMultiple sitesColors Amaranth and cyanWebsitevermontstate.edu Vermont State University (Vermont State or VTSU) is a public university in the...

S.M. CaenCalcio Les Vikings (I vichinghi), Malherbe[1] Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali Rosso, blu Simboli Vichingo Dati societari Città Caen Nazione Francia Confederazione UEFA Federazione FFF Campionato Ligue 2 Fondazione 1913 Proprietario Oaktree Capital Management (80%) Pierre-Antoine Capton (20%) Presidente Olivier Pickeu Allenatore Nicolas Seube Stadio Stadio Michel d'Ornano(21 500 posti) Sito web www.smcaen.fr/ Palmarès Titoli nazion...
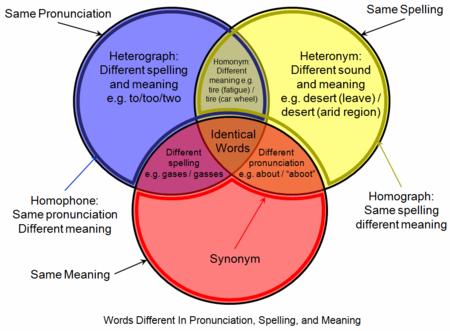
Diagram Venn ini menunjukkan perbedaan dan persamaan beberapa konsep serupa. Homofon (bahasa Yunani: ὁμός, homós, sama dan φωνή, phōnḗ, bunyi) adalah kata yang diucapkan sama dengan kata lain tetapi berbeda dari segi maksud. Homofon terdiri atas kata homo berarti sama dan foni (phone) yang berarti bunyi atau suara. homofon mempunyai pengertian sama bunyi, berbeda tulisan, dan berbeda makna.[1] Contoh homofon antara lain: buku (bahan bacaan) dan buku (bagian di antara dua ...

Wakil Kepala Staf TNI Angkatan LautLambang TNI Angkatan LautBendera pangkat laksamana madyaPetahanaLaksamana Madya TNI Erwin S. Aldedharmasejak 26 Oktober 2023Dibentuk1966Pejabat pertamaLetnan Jenderal TNI (KKO) HartonoSitus webwww.tnial.mil.id Wakil Kepala Staf TNI Angkatan Laut atau biasa disingkat dengan Wakasal adalah jabatan nomor dua tertinggi di lingkungan Tentara Nasional Indonesia Angkatan Laut (TNI AL) yang berpusat di Markas Besar TNI Angkatan Laut. Wakasal bertanggungjawab ke...

Mobil di Rusia dengan pelat nomor terpasang. Di Rusia, Pelat nomor adalah atribut yang digunakan untuk menampilkan tanda registrasi kendaraan, dan telah ada di Rusia selama beberapa dekade. Sebagian besar kendaraan bermotor yang digunakan di jalan umum diwajibkan oleh hukum untuk memasang pelat nomor. Membuat pelat nomor tidak terbaca dengan jelas seperti tertutup salju, lumpur, atau bahkan sengaja ditutupi merupakan pelanggaran hukum. Sejarah Artikel utama: Tanda Nomor Kendaraan Bermotor Uni...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

Vice Presidents of theRepublic of Costa RicaVicepresidentes de la República de Costa Rica (Spanish)Coat of arms of Costa RicaIncumbentStephan Brunner and Mary Munivesince 8 May 2022Term lengthFour years term, renewable non-consecutivelyInaugural holderAlberto Oreamuno FloresFormation7 November 1949 Politics of Costa Rica Constitution Abortion law LGBT rights Executive President (list) Rodrigo Chaves Robles Vice Presidents Stephan Brunner Mary Munive Legislature Legislative Assembly...

Alejandro VI y Jacopo Pesaro ante San Pedro, Tiziano, 1509. La escena naval del fondo, el estandarte y el yelmo ambientan bien el momento histórico. Bulas Alejandrinas es el nombre colectivo que se da al conjunto de documentos pontificios que se otorgaron a la Corona de Castilla y se le otorga el derecho a conquistar América y la obligación de evangelizarla, emitidos por la Santa Sede en 1493 a petición de los Reyes Católicos, cuya influencia ante el Papa Alejandro VI (de la valenciana ...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع مورا (توضيح). مورا (بالكتالونية: Mura)[1] - بلدية - مورا (برشلونة) مورا (برشلونة) خريطة الموقع تقسيم إداري البلد إسبانيا [2][3] المقاطعة برشلونة خصائص جغرافية إحداثيات 41°41′59″N 1°58′35″E / 41.6998219°N 1.9764684°E ...

For other uses, see Dead Man (disambiguation). The Dead ManThe Dead Man (foreground) and Yassa (drawn by John Ridgway)PublisherFleetway PublicationsPublication date28 October 1989 – 20 January 1990Genre Science fiction Title(s)2000 AD prog 650–662Creative teamWriter(s)John WagnerArtist(s)John RidgwayEditor(s)Tharg (Richard Burton)The Dead ManISBN 978-1-906735-19-7 The Dead Man was a science fiction strip in the British comic 2000 AD by writer John Wagner and artist...

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Vi burde ses noget mere – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2017) 2008 studio album by Hej MatematikVi burde ses noget mereStudio album by Hej MatematikReleased4 February 2008Recorded2007–2008GenreEuropopLabelCopenhagen Record...

Development of the table of chemical elements The American chemist Glenn T. Seaborg—after whom the element seaborgium is named—standing in front of a periodic table, May 19, 1950 Part of a series on thePeriodic table Periodic table forms 18-column 32-column Alternative and extended forms Periodic table history D. Mendeleev 1871 table 1869 predictions Discovery of elements Naming and etymology for people for places controversies (in East Asia) Systematic element names Sets o...




