Joseph E. Kuhn
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

İstanbul BaşakşehirNama lengkapİstanbul Başakşehir Futbol KulübüBerdiri1990 (34 tahun lalu) sebagai İstanbul Büyükşehir Belediyespor5 Juni 2014; 9 tahun lalu (2014-06-05) sebagai İstanbul Başakşehir Futbol KulübüStadionStadion Fatih Terim(Kapasitas: 17.300[1][2])KetuaGöksel GümüşdağManajerAbdullah AvcıLigaLiga Super Turki2022–23Liga Super Turki, ke-5Situs webSitus web resmi klub Kostum kandang Kostum tandang Kostum ketiga İstanbul Başakşeh...

70th Anti-Aircraft Artillery DivisionActiveOctober 1943–c. 1950sCountrySoviet UnionBranchRed Army (later Soviet Army)TypeAnti-Aircraft ArtilleryMilitary unit The 70th Anti-Aircraft Artillery Division (Russian: 70-я зенитная артиллерийская дивизия) was an anti-aircraft artillery division of the Soviet Union's Red Army (later the Soviet Army) during World War II and the early postwar period. Formed in the Volga Military District in late 1943, the division was mov...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Stasiun Banyuwangi. Stasiun Banyuwangi Kota PW PB TA Tampak depan Stasiun Banyuwangi Kota, 2022LokasiJalan Stasiun KarangasemBakungan, Glagah, Banyuwangi, Jawa Timur 68431IndonesiaKoordinat8°13′22″S 114°20′27″E / 8.2229077°S 114.34079°E / -8.2229077; 114.34079Koordinat: 8°13′22″S 114°20′27″E / 8.2229077°S 114.34079°E / -8.2229077; 114.34079Ketinggian+82 mOperator Kereta Api IndonesiaDaerah Opera...

Bukaan 8Poster filmSutradaraAngga Dwimas SasongkoProduser Chicco Jerikho Anggia Kharisma Ditulis olehSalman AristoPemeran Chicco Jerikho Lala Karmela Tio Pakusadewo Sarah Sechan Dwi Sasono Dayu Wijanto Penata musikMcAndersonSinematograferRobie TaswinPenyunting Ahsan Andrian Teguh Raharjo Perusahaanproduksi Visinema Pictures Chanex Ridhall Pictures Kaninga Pictures Distributor Visinema Pictures Netflix Tanggal rilis23 Februari 2017Durasi104 menitNegara IndonesiaBahasaIndonesia Bukaa...

Lambang Slowakia Lambang Slowakia terdiri dari perisai merah, dengan salib ganda putih berdiri di atas salah satu puncak tiga pegunungan dengan warna biru gelap. Salib ganda adalah simbol iman Kristen dan tiga gunung melambangkan tiga pegunungan: Tatra, Fatra, dan Matra (terletak di Hungaria utara).[1] Lambang ini diadopsi pada 1 Maret 1990. Salah satu interpretasi modern dari salib ganda adalah simbol Slowakia sebagai pewaris dan pelindung tradisi Kristen, salib ini dibawa ke wilayah...

العلاقات اليمنية البيلاروسية اليمن روسيا البيضاء اليمن روسيا البيضاء تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات اليمنية البيلاروسية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين اليمن وروسيا البيضاء.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدو...

Ini adalah nama Batak Toba, marganya adalah Manurung. Manimbul Manurung Komandan Korps Pasukan Khas ke-25Masa jabatan2014–2015 PendahuluM. Harpin OndehPenggantiAdrian Wattimena Informasi pribadiLahir(1957-11-13)13 November 1957 Porsea, Toba Samosir, Sumatera UtaraMeninggal10 Agustus 2015(2015-08-10) (umur 57) Bandung, Jawa BaratAlma materAkademi Angkatan Udara (1981)PekerjaanTentaraKarier militerPihak IndonesiaDinas/cabang TNI Angkatan UdaraMasa dinas1981—2015Pangkat Ma...

Voce principale: Eccellenza 1995-1996. Eccellenza Lombardia 1995-1996 Competizione Eccellenza Lombardia Sport Calcio Edizione 5ª Organizzatore FIGC - LNDComitato Regionale Lombardia Luogo Lombardia Partecipanti 48 Formula 3 gironi all'italiana Risultati Promozioni OggionoClusoneTecnolenoTrevigliese Retrocessioni CistellumCastaneseFulgorcardanoVirtus PetosinoVerdelloBrembilleseCernuscoCesano BosconeCastellana Cronologia della competizione 1994-1995 1996-1997 Manuale Il campionato itali...

G.I. Joe - La nascita dei CobraI G.I. Joe in una scena del trailerTitolo originaleG.I. Joe: The Rise of Cobra Paese di produzioneStati Uniti d'America Anno2009 Durata118 min Rapporto2,35:1 Genereavventura, azione, fantascienza, guerra RegiaStephen Sommers Soggettogiocattoli creati da Hasbrostoria di Michael B. Gordon, Stuart Beattie e Stephen Sommers SceneggiaturaStuart Beattie, David Elliot, Paul Lovett ProduttoreLorenzo di Bonaventura, Brian Goldner, Bob Ducsay Produttore esecut...

Korogaru Iwa, Kimi ni Asa ga FuruSingel oleh Asian Kung-Fu Generationdari album World World WorldDirilis6 Februari 2008FormatSingel CDGenreIndie rockDurasi4:38LabelKi/oon RecordsKSCL-1207PenciptaMasafumi GotohProduserAsian Kung-Fu GenerationKronologi singel After Dark (2007) Korogaru Iwa, Kimi ni Asa ga Furu (2008) Fujisawa Loser (2008) Video musikKorogaru Iwa, Kimi ni Asa ga Furu di YouTube Korogaru Iwa, Kimi ni Asa ga Furu (転がる岩、君に朝が降るcode: ja is deprecated , Batu Berg...

Approach to controlled thermonuclear fusion using magnetic fields A typical plasma in the MAST spherical tokamak machine at the Culham Centre for Fusion Energy in the UK. Magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) is an approach to generate thermonuclear fusion power that uses magnetic fields to confine fusion fuel in the form of a plasma. Magnetic confinement is one of two major branches of controlled fusion research, along with inertial confinement fusion. Fusion reactions for reactors usually combi...

Академічна конференція з реформи білоруського правопису та абетки (біл. Акадэмічная канфэрэнцыя па рэформе беларускага правапісу й азбукі; Akademičnaja kanferencyja pa reformie biełaruskaha pravapisu j azbuki) — це конференція, організована Інститутом білоруської культури, яка відбулася в Мінськ...

أوروم (باليونانيّة: Ουρούμ؛ بالتركيّة: Urúm؛ بالتتاريّة القرميّة: Urum) هو مصطلح تاريخي واسع النطاق الذي تم استخدامه من قبل بعض الشعوب الناطقة بالتركية (الأتراك وتتار القرم) لوصف اليونانيين الذين يعيشون في الدول المسلمة، وخاصًة في الدولة العثمانية وشبه جزيرة القرم. في الاثنو�...

Effect of drug opposite to expectation A paradoxical reaction (or paradoxical effect) is an effect of a chemical substance, such as a medical drug, that is opposite to what would usually be expected. An example of a paradoxical reaction is pain caused by a pain relief medication. Substances Amphetamines Amphetamines are a class of psychoactive drugs that are stimulants. Paradoxical drowsiness can sometimes occur in adults.[1] Research from the 1980s popularized the belief that ADHD st...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando l'omonima chiesa di Mosca, vedi Chiesa di San Luigi dei Francesi (Mosca). Chiesa di San Luigi dei FrancesiFacciataStato Italia RegioneLazio LocalitàRoma Indirizzopiazza San Luigi de' Francesi Coordinate41°53′58″N 12°28′29″E41°53′58″N, 12°28′29″E Religionecattolica di rito romano TitolareLuigi IX di Francia Diocesi Roma Consacrazione8 ottobre 1589 ArchitettoDomenico Fontana e Plautilla Bricci Stile architettonicoArchitettura rinas...

Romagnol Rumagnòl Pengucapan[rumɐˈɲoːl]/[rumɐˈɲoə̯l]Dituturkan diItalia, San MarinoWilayahUtamanya Emilia-Romagna, San Marino, MarcheEtnis1,1 juta (2008)[1]PenuturTidak diketahui, ca 430.000, diasumsikan Romagnol dan Emilia memiliki jumlah yang sama (2006)[2] Perincian data penutur Jumlah penutur beserta (jika ada) metode pengambilan, jenis, tanggal, dan tempat. 1.100.000 (2008) Rumpun bahasaIndo-Eropa ItalikLatino-FaliskiRomanItalo-BaratRoman Barat...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir EAN. École nationale supérieure d'architecture de Nancy Bâtiment de l'ENSarchitecture réalisé par Livio Vacchini. Histoire et statut Nom original École nationale supérieure d'architecture de Nancy Fondation 1969 Type École publique Particularités membre associé de l'INPL, de l'université de Lorraine ainsi que de la CGE Administration Directrice Gaëlle Perraudin Études Niveaux délivrés bac+3 à bac+8 Localisation Ville Nancy Pays France Site we...
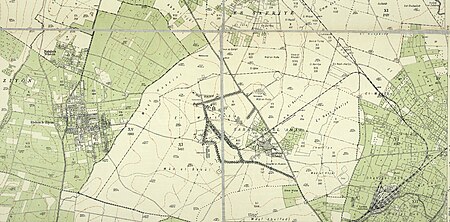
1918 massacre in Palestine by Allied troops Surafend massacrePart of the Sinai and Palestine campaignA map of Sarafand al-AmarLocationSarafand al-Amar (modern-day Tzrifin, Israel)Coordinates31°57′31″N 34°50′20″E / 31.95861°N 34.83889°E / 31.95861; 34.83889Date10 December 1918TargetMale Palestinian villagersAttack typeMassacreDeaths40-137PerpetratorsANZAC Mounted Division Scottish soldiers[citation needed]MotiveReprisal for thefts and a soldier's mur...

Defunct English merchant bank Barings BankIndustryBankingFounded1762FounderSir Francis Baring, BtDefunct26 February 1995FateCollapsed(Purchased for £1 by ING).Successor ING Group Baring Asset Management HeadquartersLondon, England Barings Bank was a British merchant bank based in London, and one of England's oldest merchant banks after Berenberg Bank, Barings' close collaborator and German representative. It was founded in 1762 by Francis Baring, a British-born member of the German–British...

Polish artist Stanisław Ignacy WitkiewiczStanisław Ignacy Witkiewicz, ca 1912Born(1885-02-24)24 February 1885Warsaw, Congress Poland, Russian EmpireDied18 September 1939(1939-09-18) (aged 54)Jeziory, PolandPen nameWitkacyOccupationWriter, painter, dramatist, philosopher, photographerAlma materKraków Academy of Fine ArtsNotable works Tumor Mózgowicz Shoemakers The Madman and the Nun Farewell to Autumn Insatiability SpouseJadwiga Unrug, m.1923PartnerJadwiga Janczewska [pl...

