John Rawlings Rees
| |||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Lingka...

Russian footballer (born 1989) Edgar Prib Prib training with Greuther Fürth in 2012Personal informationDate of birth (1989-12-15) 15 December 1989 (age 34)Place of birth Neryungri, Sakha, Soviet UnionHeight 1.81 m (5 ft 11 in)Position(s) MidfielderTeam informationCurrent team Greuther Fürth IIYouth career1996–2008 Greuther FürthSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2008–2009 Greuther Fürth II 35 (5)2009–2013 Greuther Fürth 101 (9)2013–2020 Hannover 96 128 (9)2015...

Election in Wyoming Main article: 1936 United States presidential election 1936 United States presidential election in Wyoming ← 1932 November 3, 1936 1940 → Nominee Franklin D. Roosevelt Alf Landon Party Democratic Republican Home state New York Kansas Running mate John Nance Garner Frank Knox Electoral vote 3 0 Popular vote 62,624 38,739 Percentage 60.58% 37.47% County Results Roosevelt 40-50% 50-60% 60-70%...

Patrik Ježek Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Patrik JežekTanggal lahir 28 Desember 1976 (umur 47)Tempat lahir Plzeň, CekoslovakiaTinggi 1,72 m (5 ft 7+1⁄2 in)Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini Admira WackerNomor 7Karier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1994–1998 FC Viktoria Plzeň 64 (7)1998–2000 FC Tirol Innsbruck 68 (13)2000–2001 Austria Wien 28 (2)2001–2002 FC Tirol Innsbruck 48 (7)2002–2003 Karlsruher SC 11 (0)2003–2004 Sparta Prague 11...

Public university in Chicago, Illinois Chicago State redirects here. Not to be confused with Chicago/State. Chicago State UniversityFormer nameCook County Normal School (1867–1897)Chicago Normal School (1897–1938)Chicago Teachers College (1938–1967)Chicago State College (1967–1971)TypePublic universityEstablishedSeptember 2, 1867; 156 years ago (1867-09-02)AccreditationHLCAcademic affiliationsTMCFSpace-grantEndowment$9.7 million[1]PresidentZaldwaynaka L. Scot...

Oliver Hazard Perry-class guided missile frigate (1986–2015) For other ships with the same name, see USS Samuel B. Roberts. USS Samuel B. Roberts (FFG-58), navigates in the Caribbean Sea during an exercise, 9 April 2007. History United States NameSamuel B. Roberts NamesakeCoxswain Samuel B. Roberts Awarded22 March 1982 BuilderBath Iron Works, Bath, Maine Laid down21 May 1984 Launched8 December 1984 Sponsored byMrs. Jack Yusen Commissioned12 April 1986 Decommissioned22 May 2015 HomeportMaypo...

Indian playback singer Chinmayi SripaadaChinmayi SripaadaBornChinmayi SripaadaMumbai, Maharashtra, IndiaOther namesChinmayeeIndai HazaAlma materUniversity of MadrasOccupationsSingermusicianvoice actorentrepreneurradio jockeyYears active2002–present (as singer)2005–present (as dubbing artist)Spouse Rahul Ravindran (m. 2014)Children2 (Twins)Musical careerGenres Indian classical music Playback singing Filmi Carnatic Ghazal Instrument(s)Vocals, Pi...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

† Стеллерова корова Муляж стеллеровой коровы в Лондонском музее естествознания Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:Челюстно�...
Basketball at the2020 Summer OlympicsBasketballQualificationmenwomenTournamentmenwomenRostersmenwomen3x3 basketballQualificationmenwomenTournamentmenwomenvte This article shows the rosters of all participating teams at the men's basketball tournament at the 2020 Summer Olympics in Tokyo. Group A Czech Republic The roster was announced on 8 July 2021.[1] Czech Republic men's national basketball team roster Players Coaches Pos. No. Name Age – Date of birth Height Club Ctr. PF 1 Patri...

العلاقات المغربية السعودية المغرب السعودية السفارات سفارة المغرب في السعودية السفير : مصطفى المنصوري العنوان : حي السفارات ص.ب.94392 الرياض 11693 966-11-4811858+ موقع السفارة المغربية على الويب سفارة السعودية في المغرب السفير : عبد الله ...

Lee Min-hyukLee Min-hyuk pada saat acara fansign pada November 2016Lahir29 November 1990 (umur 33)Seoul, Korea SelatanPekerjaanPenyanyi rappenyanyipenulis lagupemeranpembawa acaraKarier musikNama lainHuta[1]GenreK-popTahun aktif2012–sekarangLabelCubeArtis terkaitBtoBBtoB 4UUnited CubeSitus webbtobofficial.comNama KoreaHangul이민혁 Hanja李旼赫[2] Alih AksaraI Min-hyeokMcCune–ReischauerYi Minhyŏk Tanda tangan Lee Min-hyuk (Hangul: 이민혁; lahir 29 No...
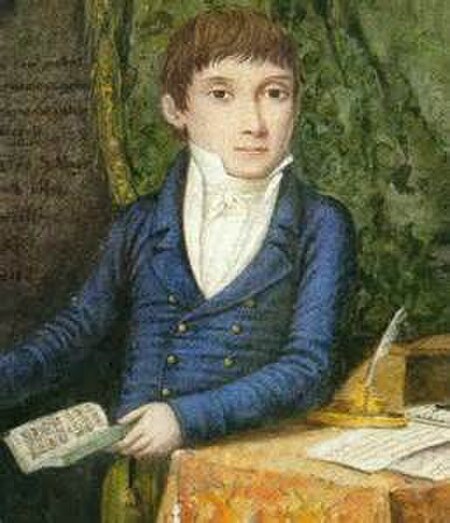

Italian opera composer (1797–1848) Donizetti redirects here. For other uses, see Donizetti (disambiguation). Portrait of Gaetano Donizetti by Francesco Coghetti, 1837 Domenico Gaetano Maria Donizetti[a] (29 November 1797 – 8 April 1848) was an Italian composer, best known for his almost 70 operas. Along with Gioachino Rossini and Vincenzo Bellini, he was a leading composer of the bel canto opera style during the first half of the nineteenth century and a probable influence on othe...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها...

Lars Tunbjörk Lars Tunbjörk på Guldbaggegalan 2013.Födelsedatum15 februari 1956FödelseplatsBoråsDödsdatum8 april 2015 (59 år)DödsplatsStockholmGenreDokumentärfotoAktiv1971–2015 Lars Erland Tunbjörk, född 15 februari 1956 i Borås, död 8 april 2015 i Stockholm,[1][2] var en svensk fotograf. Tunbjörks fotobok och utställning Landet utom sig från 1993 gjorde hans humoristiska och surrealistiska bilder av det svenska samhället kända för en bredare publik.[3] Bakgrund[4] ...

Abbazia di San Michele ArcangeloPanorama dell'abbaziaStato Italia RegioneToscana LocalitàBarberino Tavarnelle Coordinate43°34′38.28″N 11°14′51″E43°34′38.28″N, 11°14′51″E Religionecattolica di rito romano TitolareMichele Arcangelo Diocesi Fiesole Consacrazioneesistente nel IX secolo Stile architettonicoRomanico - Gotico - Rinascimentale Sito webwww.badiapassignano.com/ Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale L'abbazia di San Michele Arcangelo a Passignano è un ...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Canadian Airborne Regiment – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Canadian Airborne RegimentRégiment aéroporté canadien (French)Cap badgeActive8 April 1968 – 1 September 1995CountryC...

Questa voce sull'argomento centri abitati della provincia di Cremona è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Bordolanocomune Bordolano – VedutaLa chiesa parrocchiale LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Lombardia Provincia Cremona AmministrazioneSindacoAndrea Cigoli (lista civica) dal 9-6-2024 TerritorioCoordinate45°17′38.35″N 9°59′12.16″E45°17′38.35″N, 9°59′12.16″E (Bordolano) Altitudine64 ...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Hsiung. Xiongnu IIIe siècle av. J.-C. – Ve siècledrapeau supposé L'empire des Xiongnu vers le Ier siècle av J.C. Khanat xiongnu vers 150 av J.C.Informations générales Statut Confédération de nomades Capitale Chanyu Ting (d) Langue(s) Hunnique et mongol Religion Tengrisme et chamanisme Superficie Superficie superficie • 200 av J.C. 500 000 km² • 210 av J.C. 2 500 000 km² • 176 av J.C. 9 000 000 km² • 50 va J.C. 80...

The canal in 1865. The James River and Kanawha Canal was a partially built canal in Virginia intended to facilitate shipments of passengers and freight by water between the western counties of Virginia and the coast. Ultimately its towpath became the roadbed for a rail line following the same course. Encouraged by George Washington,[1] the canal project was begun in 1785 as the James River Company, and later restarted under the James River and Kanawha Canal Company. It was an expensi...