John Hugh Seiradakis
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Fixed-point theorem for set-valued functions In mathematical analysis, the Kakutani fixed-point theorem is a fixed-point theorem for set-valued functions. It provides sufficient conditions for a set-valued function defined on a convex, compact subset of a Euclidean space to have a fixed point, i.e. a point which is mapped to a set containing it. The Kakutani fixed point theorem is a generalization of the Brouwer fixed point theorem. The Brouwer fixed point theorem is a fundamental result in t...

3-Metilpentana Nama Nama IUPAC 3-Metilpentana Nama lain Dietilmetilmetana Penanda Nomor CAS 96-14-0 Y Model 3D (JSmol) Gambar interaktif 3DMet {{{3DMet}}} ChEMBL ChEMBL357767 Y ChemSpider 7010 Y Nomor EC Nomor RTECS {{{value}}} CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID8052647 InChI InChI=1S/C6H14/c1-4-6(3)5-2/h6H,4-5H2,1-3H3 YKey: PFEOZHBOMNWTJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N YInChI=1/C6H14/c1-4-6(3)5-2/h6H,4-5H2,1-3H3Key: PFEOZHBOMNWTJB-UHFFFAOYAC SMILES CC(CC)CC Sifat Rumus kimia C6H...

Əkinçi (Akinchi)Halaman muka Akinchi, 1875TipeMingguanPemilikHasan bey ZardabiPemimpin redaksiHasan bey ZardabiDidirikan22 Juli 1875; 148 tahun lalu (1875-07-22)BahasaAzerbaijaniBerhenti publikasi29 September 1877PusatBaku, AzerbaijanSirkulasi surat kabar300-400 (1875) Akinchi (bahasa Azerbaijan: Əkinçi, اکينچی), sering dialihaksarakan sebagai Ekinchi (The Cultivator, Sang Penggarap atau Sang Pembajak), adalah koran berbahasa Azerbaijani yang pertama.[1] Terbit anta...

Rugby and football stadium in Grenoble, France Stade des AlpesFull nameStade des AlpesLocationGrenoble, FranceOwnerGrenoble Alpes MetropoleCapacity20,068Field size10,000 m2SurfaceGrassConstructionOpened15 February 2008Construction cost€88 millionTenantsGrenoble Foot 38 (2008–present)FC Grenoble (2008–present) The Stade des Alpes is a rugby and football stadium in Grenoble, France. The stadium seats 20,068 and hosts the home games of Grenoble Foot 38 and the FC Grenoble rugby club. Situa...

2020 novel A Theatre for Dreamers Cover artworkAuthorPolly SamsonCountryUnited KingdomLanguageEnglishGenreLiterary fictionPublished2020 (2020)PublisherBloomsburyMedia typePrint (hardback)Pages368ISBN978-1526600554 A Theatre for Dreamers is a 2020 literary fiction novel by Polly Samson, which entered the Sunday Times Bestseller List at Number 2 upon its April 2020 release.[1] It is a fictionalized account of life on the Greek island of Hydra in the 1960s, featuring real-life ...

Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari Venezuela national football team di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pula:...

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі ор...

Paul Hunter ClassicTournament informationDates22–27 August 2017 (2017-08-22 – 2017-08-27)VenueStadthalleCityFürthCountryGermanyOrganisationWorld SnookerFormatRanking eventTotal prize fund£100,000Winner's share£20,000Highest break Mark Selby (ENG) (143)FinalChampion Michael White (WAL)Runner-up Shaun Murphy (ENG)Score4–2← 2016 2018 → Snooker tournament Fürthclass=notpageimage| Location in Germany The 2017 Paul Hunter Class...

American college basketball season 2016–17 Western Kentucky Hilltoppers basketballConferenceConference USARecord15–17 (9–9 C-USA)Head coachRick Stansbury (1st season)Assistant coaches Chris Cheeks Shammond Williams Quannas White Home arenaE. A. Diddle ArenaSeasons← 2015–162017–18 → 2016–17 Conference USA men's basketball standings vte Conf Overall Team W L PCT W L PCT Middle Tennessee † 17 – 1 .944 31 ̵...

Per HjertquistNazionalità Svezia Altezza183 cm Peso73 kg Tennis Carriera Singolare1 Vittorie/sconfitte 59-73 Titoli vinti 1 Miglior ranking 68º (22 dicembre 1980) Risultati nei tornei del Grande Slam Australian Open Roland Garros 3T (1981) Wimbledon 1T (1980, 1983) US Open 1T (1981, 1982) Doppio1 Vittorie/sconfitte 54-85 Titoli vinti 1 Miglior ranking 106º (26 agosto 1985) Risultati nei tornei del Grande Slam Australian Open Roland Garros 3T (1981) ...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento centri abitati del Veneto non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Concamarisecomune Concamarise – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Veneto Provincia Verona AmministrazioneSindacoMarco Bonadiman (Lega) dal 10-6-2024 TerritorioCoordinate45°12′26.24″N 11°08′18.6″E45°1...

Untuk lagu Green Day, lihat Nimrod (album). Take BackLagu oleh Kumi Kodadari album AffectionSisi-BYour SongDirilis6 Desember 2000 (Jepang)22 Mei 2001 (Amerika Serikat)Format712CDunduhan digitalDirekamPertengahan 2000 (Avex Studios, On Air Azabu Studios, Toyko, Jepang)GenrePop, R&BDurasi4:58LabelRhythm ZoneAvex Music Creative Inc.PenciptaKodaProduserMax Matsuura Take Back (ditulis sebagai TAKE BACK) adakah sebuah lagu yang direkam oleh penyanyi-penulis lagu Jepang Kumi Koda, yang dijadikan...

Spanish politician A picture of Cristóbal Martín de Herrera Cristóbal Martín de Herrera (29 March 1831 in Aldeadávila de la Ribera, Spain – 1878 in Madrid, Spain) was a Spanish politician who served as Ministry of Public Works in the reign of Alfonso XII.[1] References ^ Cristóbal Martín de Herrera | Real Academia de la Historia. dbe.rah.es. Retrieved 2022-09-26. Authority control databases: National Spain This article about a Castilian and Leónese politician is a stub. You ...
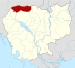
District in Oddar Meanchey, CambodiaChong Kal ចុងកាលChong KhanDistrict (srok)Chong KalLocation in CambodiaCoordinates: 14°10′N 103°35′E / 14.167°N 103.583°E / 14.167; 103.583Country CambodiaProvinceOddar MeancheyElevation32 m (105 ft)Time zone+7Geocode2203 Chong Kal District is a district in Oddar Meancheay province in northern Cambodia. According to the 1998 census of Cambodia, it had a population of 18,843.[1] Administration...

Ministerio de Desarrollo Social Ministerio de Asistencia Social Logo del ministerio Sede del Ministerio en Buenos Aires.LocalizaciónPaís ArgentinaInformación generalSigla MDSJurisdicción NacionalTipo MinisterioSede Edificio del Ministerio de Obras Públicas, Av. 9 de Julio 1925, Buenos AiresOrganizaciónDepende de Poder Ejecutivo NacionalEntidad superior Presidencia de la NaciónDependencias Ver listaCentralizados: Secretaría de Inclusión Social Secretaría de Economía ...

Railway line in Malaysia KTM West Coast LineKTM West Coast Line at Batu Gajah Railway Depot.OverviewNative name Landasan Keretapi KTM Pantai Barat (Malay) மலாயா மேற்கு கடற்கரை தொடருந்து வழித்தடம் (Tamil) 西海岸鐵路線 (Chinese) StatusOperationalOwner Keretapi Tanah MelayuLocalePeninsular MalaysiaTerminiPadang BesarWoodlands Train CheckpointContinues fromPadang Besar BranchStations121ServiceType Higher-speed rail Inte...

American politician Uri Gilbert (1809–1888) Uri Gilbert (July 10, 1809–June 17, 1888) was an American carriage maker from Troy, New York, making both passenger and freight cars.[1] He was apprenticed at the age of 14 to learn the carriage-building trade. At the end of his apprenticeship he became partner with Oramus Eaton of the Eaton & Gilbert Company. He kept pace with technological advancements and expanded the business by the time Eaton retired and Gilbert establis...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Никарагуа (значения). Озеро Никарагуаисп. Lago de Nicaragua Морфометрия Абсолютная высота32 м Площадь8157 км² Объём108 км³ Наибольшая глубинадо 70[1] м Средняя глубина13 м Бассейн Площадь бассейна23 844 км² Впа�...

Lietuvos Lyga 1943-1944 Competizione A Lyga Sport Calcio Edizione 23ª Organizzatore LFF Luogo Lituania Partecipanti 9 Formula Girone all'italiana Statistiche Incontri disputati 66 Gol segnati 300 (4,55 per incontro) Cronologia della competizione 1942-1943 1945 Manuale L'edizione 1943-1944 della Lietuvos Lyga fu la 23ª del massimo campionato di calcio lituano; il campionato non fu portato a termine. Formula Si tornò a disputare il campionato su un girone unico: le squadre partec...

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: 2000–01 Deportivo Alavés season – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2012) Deportivo Alavés 2000–01 football seasonDeportivo Alavés2000–01 seasonManagerJosé Manuel EsnalLa Liga10thCopa del ReyRound of 64UEFA CupRunners-upTop g...

