IGFBP4
|
Read other articles:

American politician For other people named Joseph Dixon, see Joseph Dixon (disambiguation). Joseph Andrew DixonLeaving White House, March 7, 1938.Member of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Ohio's 1st districtIn officeJanuary 3, 1937 – January 3, 1939Preceded byJohn B. HollisterSucceeded byCharles H. Elston Personal detailsBorn(1879-06-03)June 3, 1879Cincinnati, OhioDiedJuly 4, 1942(1942-07-04) (aged 63)Cincinnati, OhioResting placeSt. Joseph's Cemetery, Cincin...

Indian author, journalist, and model (born 1974) Shweta Bachchan NandaBachchan Nanda in 2018BornShweta Bachchan (1974-03-17) 17 March 1974 (age 50)Bombay, Maharashtra, IndiaNationalityIndianAlma materBoston UniversityOccupation(s)Journalist, host, modelYears active2006–presentSpouse Nikhil Nanda (m. 1997)Children2ParentsAmitabh Bachchan (father)Jaya Bachchan (mother)RelativesAbhishek Bachchan (brother) Aishwarya Rai Bachchan (sister-in-law)Famil...
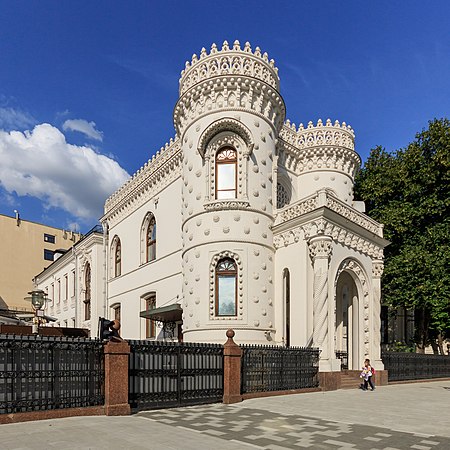

Федеральное агентство по делам Содружества Независимых Государств, соотечественников, проживающих за рубежом, и по международному гуманитарному сотрудничествусокращённо: Россотрудничество Общая информация Страна Россия Юрисдикция Россия Дата создания 6 сентября...

Ligue 1 2022-2023Ligue 1 Uber Eats 2022-2023 Competizione Ligue 1 Sport Calcio Edizione 85ª (21ª di Ligue 1) Organizzatore LFP Date dal 5 agosto 2022al 3 giugno 2023 Luogo Francia Partecipanti 20 Formula Girone all'italiana A/R Risultati Vincitore Paris Saint-Germain(11º titolo) Secondo Lens Retrocessioni Auxerre Ajaccio TroyesAngers Statistiche Miglior giocatore Kylian Mbappé Miglior marcatore Kylian Mbappé (29) Miglior portiere Brice Samba Incontri disputat...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

David Edgar David Edgar con il Newcastle nel 2008 Nazionalità Canada Altezza 188 cm Peso 78 kg Calcio Ruolo Difensore Termine carriera 1º gennaio 2021 - giocatore CarrieraSquadre di club1 2005-2009 Newcastle Utd19 (2)2009-2010 Burnley4 (0)2010→ Swansea City5 (1)2010-2014 Burnley95 (4)2014-2015 Birmingham City16 (1)2015→ Huddersfield Town12 (0)2015-2016→ Sheffield Utd36 (2)2016 Vancouver Whitecaps8 (0)2016-2017→ Vancouver Whitec...

Peta menunjukan lokasi Barili Barili adalah munisipalitas yang terletak di provinsi Cebu, Filipina. Pada tahun 2007, munisipalitas ini memiliki populasi sebesar 60.430 jiwa. Pembagian wilayah Secara politis Barili terbagi menjadi 42 barangay, yaitu: Azucena Bagakay Balao Bolocboloc Budbud Bugtong Kawayan Cabcaban Campangga Dakit Giloctog Guibuangan Giwanon Gunting Hilasgasan Japitan Cagay Kalubihan Kangdampas Candugay Luhod Lupo Luyo Maghanoy Maigang Malolos Mantalongon Mantayupan Mayana Mino...

Windows Server 2003PembangunMicrosoftKeluarga OSMicrosoft WindowsModel sumberSumber tertutup / Sumber berbagiDirilis kemanufaktur24 April 2003; 21 tahun lalu (2003-April-24)Rilis terbaru5.2 (Build 3790: Service Pack 2) / 13 Maret 2007; 17 tahun lalu (2007-03-13)[1]PlatformIA-32, x64, ItaniumTipe KernelHibridaLisensiMS-EULADidahului olehWindows 2000 ServerDigantikan olehWindows Server 2008Status dukunganDukungan tambahan hingga 14 Juli 2015.[2]Pemutakhiran keamanan ak...
Unwavering attachment to a set of irreducible beliefs For other uses, see Fundamentalism (disambiguation). Part of a series on thePhilosophy of religion Religious concepts Afterlife Apophatism Cataphatism Eschatology Enlightenment Intelligent design Liberation Miracle Mysticism Religious belief Reincarnation Religious faith Scripture (religious text) Soul Spirit Theological veto Challenges Ethical egoism Euthyphro dilemma Logical positivism Religious language Verificationism eschatological Pr...

American artistic gymnast This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Raj Bhavsar – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Raj ...

Irma GramaticaLahirMaria Francesca Gramatica(1870-11-25)25 November 1870Fiume, Kekaisaran Austria-HungariaMeninggal24 Oktober 1962(1962-10-24) (umur 91)Tavarnuzze, ItaliaPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1934-1951 (film) Irma Gramatica (25 November 1870 – 24 Oktober 1962) adalah seorang pemeran panggung dan film asal Italia. Gramatica tampil dalam sepuluh film pada masa karirnya yang meliputi The Materassi Sisters (1944).[1] Saudari-saudarinya Anna Capodaglio dan E...

STS-41-D STS-41-Dصورة STS-41-Dشعار المشغل ناسا الأعضاء هنري هارتسفيلد، ومايكل كوتس، ومايك مولان، وستيفن هولي، وجوديث ريسنيك، وتشارلز دي ووكر تاريخ الإطلاق 30 أغسطس 1984[1] موقع الإطلاق منصة إطلاق 39a [لغات أخرى][1] تاريخ الهبوط 5 سبتمبر 1984...

Disambiguazione – A&M rimanda qui. Se stai cercando l'omonima università texana, vedi Texas A&M University. Questa voce sull'argomento etichette discografiche statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. A&M Records Stato Stati Uniti Fondazione1962 Fondata daHerb AlpertJerry Moss Chiusura1999 Sede principaleSanta Monica GruppoInterscope-Geffen-A&M SettoreMusicale Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale...

Parc national de la Fosse aux LionsGéographiePays TogoRégion Région des SavanesCoordonnées 10° 45′ 09″ N, 0° 09′ 33″ ESuperficie 16,5 km2AdministrationType Parc nationalCatégorie UICN II (parc national)WDPA 2342Création 1954modifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Le parc national de la Fosse aux Lions est un parc national situé dans la région des Savanes du Togo, d'une superficie de 16,4 km2[1] (ce qui en fait le plus petit de...

تفتقر سيرة هذه الشخصية الحيّة إلى الاستشهاد بمصدر موثوق به يمكن التحقق منه. فضلاً، ساهم في تطويرها من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. في سير الأحياء، يُزال المحتوى فوراً إذا كان من غير مصدر يدعمه أو إذا كان المصدر المُستشهد به مشكوكاً بأمره. (يناير 2016) آرون ديسميوك معلومات ش�...

His EminenceLuigi DadaglioArchpriest of the Basilica di Santa Maria MaggioreDadaglio in 1988.ChurchRoman Catholic ChurchAppointed15 December 1986Term ended22 August 1990PredecessorCarlo ConfalonieriSuccessorUgo PolettiOther post(s)Cardinal-Deacon of San Pio V a Villa Carpegna (1985–90)OrdersOrdination22 May 1937Consecration8 December 1961by Amleto Giovanni CicognaniCreated cardinal25 May 1985by Pope John Paul IIRankCardinal-DeaconPersonal detailsBornLuigi Dadaglio28 September 1914Sezz...

„Europäisches Parlament“ in den 24 Amtssprachen der Europäischen Union (am Parlamentsgebäude in Brüssel) In der Europäischen Union werden aktuell 24 Sprachen als Amts- und Arbeitssprachen anerkannt. Die Sprachenfrage wurde durch die erste Verordnung festgelegt, die überhaupt von der EWG erlassen wurde (Text der VO 1/1958 siehe unten). Rechtsgrundlage für die Verordnung ist aktuell Art. 342 Vertrag über die Arbeitsweise der Europäischen Union (AEUV): „Die Regelung...

Baldersheimcomune Baldersheim – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Francia RegioneGrand Est Dipartimento Alto Reno ArrondissementMulhouse CantoneRixheim AmministrazioneSindacoPierre Logel TerritorioCoordinate47°48′N 7°22′E47°48′N, 7°22′E (Baldersheim) Altitudine225 e 233 m s.l.m. Superficie12,79 km² Abitanti2 636[1] (2020) Densità206,1 ab./km² Comuni confinantiRuelisheim; Wittenheim, Battenheim, Ottmarsheim, Sausheim Altre informazioniCod. posta...

Roberto Rosetti Datos personalesNacimiento Turín18 de septiembre de 1967 (57 años)País ItaliaNacionalidad(es) ItalianaItaliaCarreraDeporte FútbolFunción Asesor arbitralFecha debut 1997Año de retiro 2010Otra ocupación exÁrbitro de fútbol[editar datos en Wikidata] Roberto Rosetti (18 de septiembre de 1967 en Turín, Italia) es un exárbitro de fútbol italiano. Internacional desde 2003, siendo uno de los árbitros en las Copas Mundiales en Alemania 2006 y Sudáfrica 2010...

Ermanno Frattini GobbiNazionalità Italia Calcio RuoloAla CarrieraGiovanili Mantova Squadre di club1 1932-1937 Mantova59 (10)1937-1938 Cosenza? (?)1938-1949 Mantova201 (61) Carriera da allenatore 1953-1954 Mantova 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il simbolo → indica un trasferimento in prestito. Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Ermanno Frattini Gobbi (Belforte, 4 marzo 1916 – Scardovari, 3 set...