Hypericum foliosum
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Elang kelabu Elang kelabu Status konservasi Risiko Rendah (IUCN 3.1)[1] Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Aves Ordo: Accipitriformes Famili: Accipiter Genus: Butastur Spesies: B. indicus Nama binomial Butastur indicus(Gmelin, 1788) Elang kelabu (Butastur indicus) adalah burung pemangsa dari famili Accipitridae yang menghuni wilayah Asia, mulai dari Korea, Jepang hingga Asia Tenggara. Burung ini adalah satwa liar dilindungi di Indonesia.[2]...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Hans Smidth; difoto oleh N.E. Sinding (1864) Hans Ludvig Smidth (2 Oktober 1839 – 5 Mei 1917) adalah seorang pelukis asal Denmark. Ia dikenal karena membuat lukisan-lukisan Jutland dan para penduduk lokalnya.[1] Referensi ^ Han...

Dewi Umaya RachmanDewi Umaya RachmanLahir18 Oktober 1970 (umur 53)IndonesiaKebangsaanIndonesiaPekerjaanProduser Dewi Umaya Rachman (lahir 18 Oktober 1970) adalah seorang produser film yang telah memberikan kontribusi berarti dalam industri perfilman Indonesia. Kontribusi di dunia perfilman Indonesia Karir Dewi Umaya Rachman dimulai ketika ia bersama Noe Letto mendirikan Pic[k]lock Films pada tahun 2008, menciptakan fondasi bagi perjalanan panjangnya dalam dunia perfilman. Pada tahun yan...
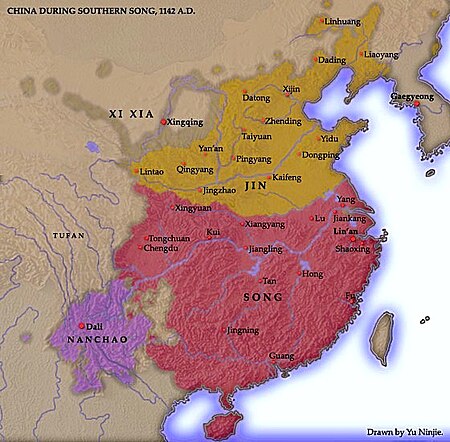
Penaklukan Dinasti Song oleh MongolBagian dari Invasi Mongol terhadap Tiongkok dan Kampanye militer Kublai KhanSong Selatan sebelum penaklukan Dunia MongolTanggal1227/35-1279LokasiTiongkok SelatanHasil Kemenangan MongolPerubahanwilayah Seluruh Tiongkok dicaplok oleh Mongol di bawah Dinasti YuanPihak terlibat Kekaisaran Mongol Dinasti Yuan Tionghoa Han Utara Khitan Jurchen Alan (Asud) Turk Asia Tengah Dinasti SongTokoh dan pemimpin ÖgedeiTsagaanKhochuTöregeneGüyük KhanMöngke Khan (kemungk...

Jembatan Ratapan IbuKoordinat0°13′46″S 100°38′08″E / 0.22942°S 100.635431°E / -0.22942; 100.635431MelintasiBatang AgamLokalKota PayakumbuhKarakteristikPanjang total40 m (131 ft 3 in)SejarahMulai dibangun1818Lokasi Jembatan Ratapan Ibu adalah sebuah jembatan yang terletak di kota Payakumbuh, Sumatera Barat. Jembatan ini dibangun tahun 1840, 8 tahun setelah Belanda masuk ke Luak Limopuluah. Belanda masuk 1832. Jembatan ini memiliki panjang 40 m...

Former railway station in England Seaforth SandsGeneral informationLocationLiverpool, Liverpool, MerseysideEnglandPlatforms2 (4 between 1905-1925)Other informationStatusDisusedHistoryPost-groupingLiverpool Overhead RailwayKey dates30 April 1894Opened30 Dec 1956Closed completely Seaforth Sands was a terminus station located on the Liverpool Overhead Railway at Seaforth, west of Crosby Road South, Knowsley Road and Rimrose Road junctions. History The station opened on 30 April 1894, as a northe...

العلاقات الإيطالية السورية إيطاليا سوريا إيطاليا سوريا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الإيطالية السورية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين إيطاليا وسوريا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة إيط�...

Castle HillNew South Wales—Legislative AssemblyInteractive map of district boundaries from the 2023 state electionStateNew South WalesCreated2007MPMark HodgesPartyLiberal PartyNamesakeCastle HillElectors58,240 (2019)Area99.95 km2 (38.6 sq mi)DemographicInner metropolitan Electorates around Castle Hill: Hawkesbury Hawkesbury Hornsby Kellyville Castle Hill Hornsby Winston Hills Winston HillsEpping Epping Castle Hill is an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in ...

2014 annexation of territory For more details, see Russian occupation of Crimea. Annexation of Crimea by the Russian FederationPart of the Russo-Ukrainian WarRussian President Vladimir Putin signs the treaty of accession (annexation) with Crimean leaders in Moscow, 18 March 2014.DateAnnexation: 18 March 2014Military operation: 27 February[note 1] – 26 March 2014[10]LocationCrimeaResult Russian victoryBelligerents Russia UkraineCommanders and leaders Vladimir...

American media personality (1923–2023) For the activist group Sea Shepherd's ship, see MY Bob Barker. For the prison supply company, see Bob Barker Company. For the rugby player, see Bob Barker (rugby union). Bob BarkerBarker in 1975BornRobert William Barker(1923-12-12)December 12, 1923Darrington, Washington, U.S.DiedAugust 26, 2023(2023-08-26) (aged 99)Los Angeles, California, U.S.Resting placeForest Lawn Memorial Park, Hollywood HillsCitizenship United States Rosebud Sioux Tribe Educ...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2023. Sjamsul Badhar Informasi pribadiLahir27 Januari 1964 (umur 60)Mojokerto, Jawa TimurSuami/istriRizki Amaliani, S.K.M.AnakHaris ZulfikarHanif FarhanJasmine Sofi AmbadarAlma materSepa Polri (1988)Karier militerPihak IndonesiaDinas/cabang Kepoli...

City in Alabama, United States For other uses, see Fairfield. City in Alabama, United StatesFairfield, AlabamaCityLocation of Fairfield in Jefferson County, Alabama.Coordinates: 33°28′36″N 86°55′0″W / 33.47667°N 86.91667°W / 33.47667; -86.91667CountryUnited StatesStateAlabamaCountyJeffersonGovernment • MayorEddie Penny[1]Area[2] • Total3.46 sq mi (8.96 km2) • Land3.46 sq mi (8.96&#...

1876 U.S. racial confrontation Ellenton riot of 18761876 News Coverage of the Ellenton Riot in Aiken County, South CarolinaDateSeptember 1876 [1]LocationAiken County, South CarolinaDeaths25 to 100 African Americans, 1 white The Ellenton riot or Ellenton massacre occurred in September 1876 and took place in South Carolina in the United States. The massacre was preceded by a series of civil disturbances earlier that year following tensions between the Democratic Party and the Republican...

Okay Cupid redirects here. For the 2012 single by Kitty Pryde, see Haha, I'm Sorry. American online dating service Not to be confused with Cupid.com. OkCupidOkCupid logoType of siteOnline dating serviceOwnerMatch GroupCreated byChris CoyneSam YaganChristian RudderMax KrohnCEOAriel CharytanURLwww.okcupid.comCommercialYesRegistrationRequired for membershipLaunchedJanuary 19, 2004; 20 years ago (2004-01-19)Current statusActive OkCupid (often abbreviated as OKC,[1&...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang fonologi bahasa Arab Moderen baku. Untuk fonologi dialek daerah lain, lihat Varietas bahasa Arab. Untuk fonologi bentuk pertengahan, lihat Bahasa Arab Klasik § Fonologi. Untuk bantuan pengucapan dan bacaan transkripsi Alfabet Fonetik Internasional (IPA) bahasa Arab untuk artikel Wikipedia, lihat Bantuan:IPA untuk bahasa Arab. Artikel ini mengandung transkripsi fonetik dalam Alfabet Fonetik Internasional (IPA). Untuk bantuan dalam membaca simbol IPA...

Biografi tokoh yang masih hidup ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber sehingga isinya tidak dapat dipastikan. Bantu memperbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan sumber tepercaya. Materi kontroversial atau trivial yang sumbernya tidak memadai atau tidak bisa dipercaya harus segera dihapus.Cari sumber: Elvyn G. Masassya – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Elvyn G. Masass...

English footballer (born 2004) Sonny Perkins Perkins warming up for West Ham UnitedPersonal informationFull name Sonny Tufail Perkins[1]Date of birth (2004-02-10) 10 February 2004 (age 20)Place of birth Waltham Forest, England[2]Height 1.78 m (5 ft 10 in)Position(s) ForwardTeam informationCurrent team Leyton Orient (on loan from Leeds United)Youth career–2019 Leyton Orient2019–2021 West Ham UnitedSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2021–2022 West Ham U...

artikel ini perlu dirapikan agar memenuhi standar Wikipedia. Tidak ada alasan yang diberikan. Silakan kembangkan artikel ini semampu Anda. Merapikan artikel dapat dilakukan dengan wikifikasi atau membagi artikel ke paragraf-paragraf. Jika sudah dirapikan, silakan hapus templat ini. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Coraciiformes Periode Eosen Pertengahan hingga kini PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K Pg N Coracias garrulusTaksonomiDivisiManiraptoriformesKelasAvesSupero...

Dire quasi la stessa cosa. Esperienze di traduzioneAutoreUmberto Eco 1ª ed. originale2003 Generesaggi Lingua originaleitaliano Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Dire quasi la stessa cosa, sottotitolato Esperienze di traduzione, è una raccolta di saggi di Umberto Eco pubblicata nel 2003 presso Bompiani, su temi di teoria della traduzione, che partono dal racconto dell'esperienza personale come traduttore, redattore di traduzioni altrui o autore tradotto da altri. I racconti sono basa...

Sporting event delegationGermany at the1998 Winter OlympicsIOC codeGERNOCGerman Olympic Sports ConfederationWebsitewww.dosb.de (in German, English, and French)in NaganoCompetitors125 (78 men, 47 women) in 14 sportsFlag bearer Jochen Behle (cross-country skiing)MedalsRanked 1st Gold 12 Silver 9 Bronze 8 Total 29 Winter Olympics appearances (overview)192819321936194819521956–1988199219941998200220062010201420182022Other related appearances United Team of Germany (1956–1964)&#...