Henry Drury Harness
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

André Hoekstra Informasi pribadiNama lengkap André HoekstraTanggal lahir 5 April 1962 (umur 61)Tempat lahir Baarn, BelandaPosisi bermain GelandangKarier junior De Zwervers– VV Capelle– Feyenoord RotterdamKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1981-1988 Feyenoord Rotterdam 181 (65)1988-1994 RKC Waalwijk 137 (40)Tim nasional1984 Belanda 1 (1)Kepelatihan1994-1996 RBC Roosendaal (asisten)1996-1998 ADO Den Haag (asisten)1998-1999 ADO Den Haag1999-2007 Excelsior Rotterdam (asisten) * Penam...

Prasasti Telaga Batu Prasasti Telaga Batu 1 ditemukan di sekitar kolam Telaga Biru (tidak jauh dari Sabokingking), Kel. 3 Ilir, Kec. Ilir Timur II, Kota Palembang, Sumatera Selatan, pada tahun 1935.[1] Prasasti ini sekarang disimpan di Museum Nasional dengan No. D.155. Di sekitar lokasi penemuan prasasti ini juga ditemukan prasasti Telaga Batu 2, yang berisi tentang keberadaan suatu vihara di sekitar prasasti.[2] Pada tahun-tahun sebelumnya ditemukan lebih dari 30 buah prasast...

ConservapediaBerkas:Conservapedia main Page 6 March 2013.pngScreenshot bagian depan halaman utama Conservapedia pada 6 Maret 2013URLwww.conservapedia.comTipeProyek ensiklopedia internetWikiPerdagangan ?Tidak adaRegistration (en)Opsional (diwajibkan untuk menyunting halaman)LangueInggrisLisensiBerhak cipta (pemakaian bebas)Mesin perangkat lunakMediaWiki PemilikAndrew SchlaflyPembuatPara kontributor sukarelawan[1]Service entry (en)21 November 2006; 17 tahun lalu (2006-11-21)Pe...

Oksima adalah suatu senyawa kimia yang termasuk dalam kelompok imina, dengan rumus umum R1R2C=NOH, di mana R1 adalah suatu rantai samping organik dan R2 dapat berupa hidrogen, membentuk suatu aldoksima, atau gugus organik lain, membentuk suatu ketoksima. Oksima tersubstitusi-O membentuk suatu keluarga senyawa yang terkait erat. Amidoksima adalah oksima amida dengan struktur umum RC(=NOH)(NRR'). Oksima biasanya dihasilkan oleh reaksi hidroksilamina dengan aldehida atau keton. Istilah oksima b...

Bagian dari seri tentangBuddhisme SejarahPenyebaran Sejarah Garis waktu Sidang Buddhis Jalur Sutra Benua Asia Tenggara Asia Timur Asia Tengah Timur Tengah Dunia Barat Australia Oseania Amerika Eropa Afrika Populasi signifikan Tiongkok Thailand Jepang Myanmar Sri Lanka Vietnam Kamboja Korea Taiwan India Malaysia Laos Indonesia Amerika Serikat Singapura AliranTradisi Buddhisme prasektarian Aliran Buddhis awal Mahāsāṃghika Sthaviravāda Aliran arus utama Theravāda Mahāyāna Vajrayāna Kons...

Questa voce sull'argomento canottieri francesi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. René Waleff Nazionalità Francia Canottaggio Carriera Squadre di club ?Société Nautique de la Marne Palmarès Competizione Ori Argenti Bronzi Giochi olimpici 0 1 0 Per maggiori dettagli vedi qui Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Maxime René Waleff (Ginevra, 30 novembre 1874 – Jouarre, 31 marzo 1961) è stato un canottiere francese....

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne s'appuie pas, ou pas assez, sur des sources secondaires ou tertiaires (janvier 2024). Pour améliorer la vérifiabilité de l'article ainsi que son intérêt encyclopédique, il est nécessaire, quand des sources primaires sont citées, de les associer à des analyses faites par des sources secondaires. Pour les articles homonymes, voir Laube. Lukas LaubeBiographieNaissance 22 avril 2000 (24 a...

Berkas:Wasp's Nest Radio Times Billing 1937.jpgSebuah iklan dari Radio Times edisi 13–19 Juni 1937, mengilustrasikan program-program televisi siang hari termasuk penampilan langsung Wasp's Nest Wasp's Nest adalah sebuah siaran drama televisi di BBC Television Service pada 18 Juni 1937. Ini diadaptasi dari cerpen bernama sama karya penulis kejahatan Agatha Christie yang mula-mula muncul di Daily Mail pada 20 November 1928 dan pertama kali muncul dalam bentuk buku dalam kumpulan cerpen AS Dou...
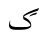
Crimean Tatar is written in both Latin and Cyrillic. Historically, the Arabic script was also used. Since 1990s when Verkhovna Rada of Crimea officially accepted the new Common Turkic-based Latin alphabet, it had been dominant mostly on the internet while the Soviet Cyrillic alphabet remained dominant in printed productions. After the 2014 Russian annexation of Crimea, the Russian government requires the use of Cyrillic script only. In 2021 the Ukrainian government started the switch of Crime...

American rock band (formed 1971) The Eagles redirects here. For other bands and other uses, see Eagles (disambiguation). EaglesThe Eagles in 2008 during their Long Road Out of Eden Tour (left to right): Glenn Frey, Don Henley, Joe Walsh, Timothy B. Schmit and (behind them) touring drummer Scott F. CragoBackground informationOriginLos Angeles, California, U.S.GenresRockcountry rocksoft rockfolk rock Country MusicDiscographyEagles discographyYears active1971–19801994–20162017–presentLabel...

此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2021年7月4日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:美国众议院 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 美國眾議院 United States House of Representatives第118届美国国会众议院徽章 众议院旗...

Pour les personnes ayant le même patronyme, voir Masson. Pierre-Maurice Masson Pierre-Maurice Masson en 1901 collection particulière Données clés Naissance 4 octobre 1879 Metz, Moselle Décès 16 avril 1916 (à 36 ans) Flirey, Meurthe-et-Moselle Nationalité Française Pays de résidence Suisse, 1904-1914 Profession Écrivain, critique. Autres activités Professeur à Fribourg Formation Normalien, agrégé, docteur (à titre posthume) Distinctions Prix d'éloquence (1906 e...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

Japanese professional wrestler Akira RaijinKawabata as Kiyoshi at an MPW event in October 2011Birth nameAkira KawabataBorn (1978-07-17) July 17, 1978 (age 45)[1]Takarazuka, Hyōgo, Japan[1]Professional wrestling careerRing name(s)Akira Raijin[2]Akira Thunder Raijin[3]Kaminari[3]Kawabata[4]Kowabata[5]Kiyoshi[2]Suicide[6]Sushi[7]Billed height6 ft 0 in (1.83 m)[1]Billed weight231 lb (...

بيامان الإحداثيات 42°13′12″N 92°49′23″W / 42.22°N 92.823055555556°W / 42.22; -92.823055555556 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة غروندي خصائص جغرافية المساحة 0.503759 كيلومتر مربع0.503761 كيلومتر مربع (1 أبريل 2010) ارتفاع 304 متر عدد �...

Legal and military structure in medieval Europe This article is about the classic, medieval, Western European form of feudalism. For feudalism in other societies, as well as that of the Europeans, see Examples of feudalism. Investiture of a knight (miniature from the statutes of the Order of the Knot, founded in 1352 by Louis I of Naples) Orava Castle in Slovakia. A medieval castle is a traditional symbol of a feudal society. Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of le...

Докладніше: Втрати силових структур внаслідок російського вторгнення в Україну У статті, наведено список втрат українських військовослужбовців у російсько-українській війні за жовтень 2023 року (включно). Втрати з українського боку публікуються в обмеженому форматі т�...

Football league seasonSingapore Premier LeagueSeason2024–25Dates11 May 2024 – 25 May 2025Matches played15Goals scored71 (4.73 per match)Top goalscorerTomoyuki Doi (8 goals)Biggest home winGeylang International 7-1 Young Lions FC (25 May 2024)Biggest away winTanjong Pagar United 0-5 Balestier Khalsa (19 May 2024)Highest scoringGeylang International 4-4 BG Tampines Rovers (17 May 2024)Geylang International 7-1 Young Lions FC (25 May 2024)Hougang United 2-6 Geylang International (14 Jun...

この記事は英語版の対応するページを翻訳することにより充実させることができます。(2021年3月)翻訳前に重要な指示を読むには右にある[表示]をクリックしてください。 英語版記事を日本語へ機械翻訳したバージョン(Google翻訳)。 万が一翻訳の手がかりとして機械翻訳を用いた場合、翻訳者は必ず翻訳元原文を参照して機械翻訳の誤りを訂正し、正確な翻訳にし�...

Prawn soupPrawn mee with whole shrimpTypeSoupServing temperatureHotMain ingredientsPrawnsVariationsChupe de camarones, kaeng som kung, Penang Prawn Mee, rækjusúpa, shrimp chowder, tom yum goong Media: Prawn soup Prawn soup, also referred to as shrimp soup, is a soup dish prepared using freshwater or saltwater prawns as a primary ingredient. Several varieties of the dish exist in various areas of the world, including Penang prawn mee in Malaysia, Peruvian chupe de camarones, Thai k...
