Halle aux blés (Paris)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Not to be confused with the Supercars Challenge, a former support event to the Australian Grand Prix. For other uses, see Supercar Challenge (disambiguation). V8 Supercar Challenge Race Information Venue Surfers Paradise Street Circuit Number of times held 15 First held 1994 Last held 2009 Race Format Race 1 Laps 34 Distance 150 km Race 2 Laps 34 Distance 150 km Race 3 Laps 34 Distance 150 km Race 4 Laps 34 Distance 150 km Last Event (2009) Overall Winner Mark Winterbottom Ford Performance Ra...

Raja Christian IX dari DenmarkRaja DenmarkBerkuasa15 November 1863 – 29 Januari 1906PendahuluFrederik VIIPenerusFrederik VIIIPerdana MenteriLihat daftarInformasi pribadiKelahiran(1818-04-08)8 April 1818Kastil Gottorf, Schleswig, Kadipaten SchleswigKematian29 Januari 1906(1906-01-29) (umur 87)Istana Amalienborg, Kopenhagen, DenmarkPemakaman15 Februari 1906Katedral RoskildeWangsaGlücksburgAyahFriedrich Wilhelm, Adipati Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-GlücksburgIbuPutri Louise Caroline ...

Peta Mesir menunjukkan lokasi Minufiyah Kegubernuran Minufiyah (Arab: محافظة المنوفيةcode: ar is deprecated al-Menofeyya / al-Monofeyya IPA: [elmenoˈfejjæ, -monoˈ-]) adalah satu dari dua puluh enam kegubernuran di Mesir. Ibu kotanya Syibin Al Kaum. Terletak di utara Mesir, di delta sungai Nil, wilayahnya berbatasan dengan Kegubernuran Gharbiyah di selatan dan Kegubernuran Kairo di utara. Pranala luar (Arab) Situs Resmi Artikel bertopik geografi atau tempat Me...

TNA Knockouts World Championship Données générales Autres noms TNA Women's World Championship (2007–2008) TNA Women's Knockout Championship (2008–2010) TNA Knockouts Championship (2010–2017) Impact Wrestling Knockouts Championship (2017) Unified GFW Knockouts Championship (2017) GFW Knockouts Championship (2017) Impact Knockouts Championship (2017-2021) Impact Knockouts World Championship (2021-2024) TNA Knockouts World Championship (2024-...) Création 14 octobre 2007 Fédération ...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі ор...

1998 single by Hole Celebrity SkinSingle by Holefrom the album Celebrity Skin B-side Best Sunday Dress Dying (demo) ReleasedAugust 31, 1998 (1998-08-31)Recorded1997StudioConway Recording, Record Plant West (Los Angeles)Genre Alternative rock[1] power pop[1] Length2:42LabelGeffenSongwriter(s) Courtney Love Billy Corgan Eric Erlandson Producer(s)Michael BeinhornHole singles chronology Gold Dust Woman (1996) Celebrity Skin (1998) Malibu (1998) Music videoCelebrity ...

Government ministry in Mongolia Ministry of Justice and Home Affairs of MongoliaМонгол Улсын Хууль зүй, дотоод хэргийн яамAgency overviewFormed29 December 1911JurisdictionGovernment of MongoliaHeadquartersKhudaldaany St 6/1, Government Building V, Ulaanbaatar, MongoliaEmployees108Annual budgetMNT 11.8 billion (about US$4.1 million) (2020) [1]Minister responsibleKhishgeegiin NyambaatarChild agenciesNational Police AgencyGeneral Authority for Border Pr...

Facial muscles Facial toning, or facial exercise, is a type of cosmetic procedure or physical therapy tool which alters facial contours by means of increasing muscle tone and facial volume by promoting muscular hypertrophy, and preventing muscle loss due to aging or facial paralysis. Facial toning and exercise is therefore in part a technique to achieve facial rejuvenation by reducing wrinkles, sagging, and expression marks on the face and skin.[1] As a physical therapy, facial tonin...

Politics of Bahrain Member State of the Arab League Constitution Human rights Monarchy King Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa Cabinet Prime Minister Salman bin Hamad Al Khalifa Minister of Foreign Affairs Minister of Interior Minister of Justice Minister of Finance Minister of Housing National Assembly Consultative Council Chairman Council of Representatives Speaker Judiciary Elections Recent elections General: 2010201420182022 Referendums: 2001 (National Action Charter) Political parties Politicians...

L'istruzione in Lombardia è coordinata dal relativo ufficio scolastico regionale, il quale fa capo al ministero dell'istruzione della Repubblica Italiana, nonché dal ministero dell'università e della ricerca per quanto concerne gli istituti universitari e di ricerca. Sul territorio regionale sono presenti un totale di 8.038 scuole, tra pubbliche e private/paritarie, che offrono accesso all'istruzione e alla formazione a più di 1,4 milioni di studenti, secondo i dati di settembre 2016 forn...

This article is about the city in Ontario, Canada. For other uses, see Sarnia (disambiguation). City in Ontario, CanadaSarniaCity (lower-tier)City of Sarnia FlagNickname: The Imperial CityMotto(s): Sarnia Semper (Latin for Sarnia Always)SarniaShow map of CanadaSarniaShow map of Southern OntarioSarniaShow map of Lambton CountyCoordinates: 42°58′53″N 82°19′04″W / 42.98139°N 82.31778°W / 42.98139; -82.31778[1]CountryCanadaProvinceOntarioCount...
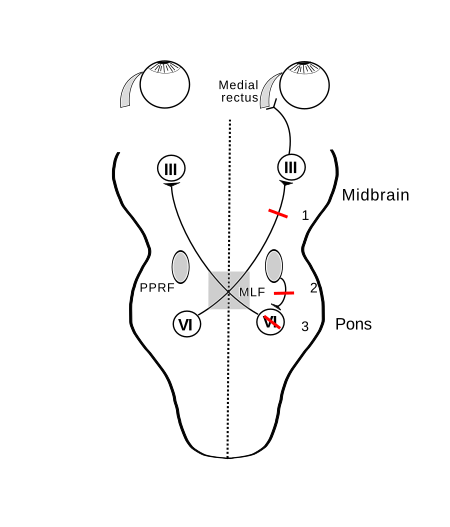
Medical conditionOne and a half syndromeOther namesOn-and-a-half syndromeDiagram of normal eye movement compared to left one-and-a-half syndrome (i.e. left lateral gaze palsy, with left Internuclear ophthalmoplegia (inability to adduct))Causes Demyelinating disease, e.g. Multiple sclerosis Infarction Infections, e.g. Brainstem encephalitis and Neurocysticercosis Tumours Arteriovenous malformation Pontine haemorrhage Basilar artery aneurysms Trauma Differential diagnosis Neuromyelitis optica s...

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Sauwerd railway station – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2016) SauwerdGeneral informationLocationNetherlandsCoordinates53°17′29″N 6°32′24″E / 53.29139°N 6.54000°E / 53.29139; 6.54000Line(s)Gronin...

Côte de Beaune Une bouteille de Côte de Beaune. Désignation(s) Côte de Beaune Appellation(s) principale(s) côte-de-beaune Type d'appellation(s) AOC Reconnue depuis 1937[1] Pays France Région parente vignoble de Bourgogne Sous-région(s) vignoble de la côte de Beaune Localisation Côte-d'Or Climat tempéré océanique à tendance continentale Sol argilo-calcaire Superficie plantée 34,53 hectares en 2008[2] Cépages dominants pinot noir (pour les rouges) et chardonnay (pour les blancs)...

Part of a series onJainism Jains History Timeline Index Philosophy Anekantavada Cosmology Ahimsa Karma Dharma Mokṣa Kevala Jnana Dravya Tattva Brahmacarya Aparigraha Gunasthana Saṃsāra EthicsEthics of Jainism Mahavratas (major vows) Ahiṃsā (non-violence) Satya (truth) Asteya (non-stealing) Brahmacarya (chastity) Aparigraha (non-possession) Anuvratas (further vows) Sāmāyika Sallekhana Jain prayers Bhaktamara Stotra Micchami Dukkadam Ṇamōkāra mantra Jai Jinendra Major figures The...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Bennett. Alex Bennett Biographie Nom Alexander Bennett Nationalité Britannique Nat. sportive Écossais Naissance 20 octobre 1881 Glasgow (Écosse) Décès 9 janvier 1940 (à 58 ans) Écosse Poste Milieu gauche Parcours professionnel1 AnnéesClub 0M.0(B.) 1900-1903 Rutherglen Glencairn F.C. (en) 00? 0(?) 1903-1908 Celtic 124 (47) 1908-1918 Rangers 188 (51) 1918-1920 Dumbarton 00? 0(?) 1920-1921 Albion Rovers 00? 0(?) Sélections en équipe national...

New Zealand born British historian and classicist (1903–1989) This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Ronald Syme – news · newspapers · books · scholar · ...

Battle in the War of the Spanish Succession Battle of AlmansaPart of the War of the Spanish SuccessionThe Battle of Almansa by Ricardo BalacaDate25 April 1707LocationAlmansa, Albacete, SpainResult Franco-Spanish victoryBelligerents Kingdom of Spain Kingdom of France Kingdom of England Kingdom of Portugal Dutch Republic Holy Roman EmpireCommanders and leaders Duke of Berwick Earl of Galway Marquess of Minas Jacques-Louis Comte de Noyelles[1]Strength 25,500 25,000[...

Questa voce sull'argomento attori statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Florence Barker (1908) Florence Barker (Los Angeles, 22 novembre 1891 – Los Angeles, 15 febbraio 1913) è stata un'attrice statunitense teatrale e cinematografica che lavorò alla Biograph, in prevalenza sotto la direzione di David W. Griffith. Morì di polmonite, il 15 febbraio 1913, a soli ventun anni. In...







