Gibberella zeae
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Anaita Shroff AdajaniaLahir1972/1973 (umur 51–52)[1]KebangsaanIndiaSuami/istriHomi Adajania (2002-sekarang) Anaita Shroff Adajania adalah seorang pemberi gaya mode dan perancang kostum asal India. Ia adalah Direktur Mode untuk majalah Vogue India. Filmografi Dilwale Dulhania Le Jayenge (1995) Everybody Says I'm Fine! (2001) Kal Ho Na Ho (2003) Dhoom (2004) Being Cyrus (2006) Hope and a Little Sugar (2006) Dhoom 2 (2006) Krazzy 4 (2008) Bhoothnath (2008) Love Aaj Kal (2009) Ra....

Keuskupan Agung Siena-Colle di Val d'Elsa-MontalcinoArchidioecesis Senensis-Collensis-IlcinensisKatolik Katedral SienaLokasiNegaraItaliaProvinsi gerejawiSiena-Colle di Val d'Elsa-MontalcinoStatistikLuas2.265 km2 (875 sq mi)Populasi- Total- Katolik(per 2010)185.751178,098 (95.9%)Paroki178InformasiDenominasiGereja KatolikRitusRitus RomaPendirianAbad ke-4KatedralCattedrale di S. Maria Assunta (Siena)KonkatedralConcattedrale di Ss. Marziale e Alberto (Colle di V...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

Untuk judul film fiksi ilmiah, lihat Plan 9 from Outer Space. Plan 9 from Bell LabsTampilan antarmuka sistem penjendelaan rioPerusahaan / pengembangPlan 9 Foundation, menggantikan Bell LabsDiprogram dalamDialek ANSI CStatus terkiniAktif[1][2]Model sumberSumber terbukaRilis perdana1992; 32 tahun lalu (1992) (universitas) / 1995; 29 tahun lalu (1995) (umum)Rilis finalEdisi keempat / 10 Januari 2015; 9 tahun lalu (2015-01-10)[3]Repositori9p.io/sources/...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Moria. Untuk layanan kereta api milik PT Kereta Api Indonesia, lihat kereta api Argo Muria. Gunung MuriaMoerjo, MoerijaGunung Muria, difoto pada 1999 oleh awak misi STS-93 [en]Titik tertinggiKetinggian1602 m (5253 kaki)[1][2]Masuk dalam daftarRibuKoordinatKoordinat: 6°37′00″S 110°53′00″E / 6.616667°S 110.883333°E / -6.616667; 110.883333 GeografiGunung MuriaGunung Muria (Pulau Jawa)Tampilkan peta ...

Video game series This article is about the video game series. For the first game in the series, see Metroid (video game). For the fictional species, see Metroid (fictional species). Not to be confused with Matroid or Meteoroid. Video game seriesMetroidLogo since 2017Genre(s)PlatformAction-adventureFirst-person shooterSide scrollerPinballDeveloper(s)Nintendo R&D1 (1986–2004)Intelligent Systems (1986–1994)[1]Retro Studios (2002–present)Fuse Games (2005)Nintendo Software Techn...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Papou. Danse traditionnelle. On appelle Papous les populations autochtones de la Nouvelle-Guinée, une île de l'Océanie proche et de la Mélanésie dans l'océan Pacifique, partagée entre la Nouvelle-Guinée occidentale sous souveraineté indonésienne et la Papouasie-Nouvelle-Guinée. Carte des Moluques et de la Nouvelle-Guinée, en espagnol et portugais, c. 1600. On remarquera, entre les deux, une île portant la mention Os Papos, les Papous. Carte angl...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...

The Alabama Ballet is a ballet company in Alabama, United States. The Alabama Ballet- Six Dances - Jiří Kylián History Prior to the establishment of Alabama Ballet, there were three smaller ballet companies in the state of Alabama: the Birmingham Civic Ballet, the University of Alabama at Birmingham Ballet and Ballet Alabama.[1] In 1981, dancers Sonia Arova and Thor Sutowski decided to start a bona fide ballet company in the state and created Alabama Ballet.[1] Fifteen year...

Dalam artikel ini, nama keluarganya adalah Nguyễn. Sesuai dengan kebiasaan Vietnam, tokoh ini seharusnya disebut dengan nama pemberian, Phương Khánh. Nguyễn Phương KhánhPhương Khánh di Saigon TV pada 2018.Lahir5 April 1995 (umur 29) Provinsi Bến Tre, VietnamNama lainPhoebePendidikanUniversitas CurtinTinggi172 m (564 ft 3+1⁄2 in)Gelar 2nd Runner-up Miss Sea Vietnam Global 2018 Miss Earth Vietnam 2018 Miss Earth 2018 Pemenang kontes kecantikanWarna ...
本表是動態列表,或許永遠不會完結。歡迎您參考可靠來源來查漏補缺。 潛伏於中華民國國軍中的中共間諜列表收錄根據公開資料來源,曾潛伏於中華民國國軍、被中國共產黨聲稱或承認,或者遭中華民國政府調查審判,為中華人民共和國和中國人民解放軍進行間諜行為的人物。以下列表以現今可查知時間為準,正確的間諜活動或洩漏機密時間可能早於或晚於以下所歸�...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع فيرغسون (توضيح). فيرغسون الإحداثيات 41°56′15″N 92°51′54″W / 41.9375°N 92.865°W / 41.9375; -92.865 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة مارشال خصائص جغرافية المساحة 0.6607 كيلومتر مربع0.660699 كيلومتر مربع (1 أ...

Untuk other orang dengan nama yang sama, lihat Raymond Wong (disambiguasi). Ray Wong黃台仰 Pemimpin Hong Kong IndigenousMasa jabatanJanuari 2015 – Oktober 2016 Informasi pribadiLahir15 September 1993 (umur 30)Hong Kong BritaniaPartai politikHong Kong IndigenousPendidikanSarjanaAlma materUniversitas GöttingenPekerjaanAktivis, perancang dalam ruanganDikenal karenaKerusuhan sipil Mong Kok 2016Sunting kotak info • L • B Ray Wong Hanzi tradisional: 黃台仰 Alih ...
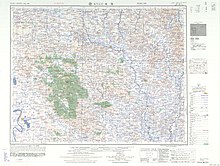
This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Guangshui – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) County-level city in Hubei, People's Republic of ChinaGuangshui 广水市KwangshuiCounty-level cityGuangshuiLocation in HubeiCoordinates: 31°37′01...

Canadian ice hockey player, coach, and executive (1943–2014) Ice hockey player Pat QuinnOC Hockey Hall of Fame, 2016 (Builder) Quinn at the 2012 NHL Winter ClassicBorn (1943-01-29)January 29, 1943Hamilton, Ontario, CanadaDied November 23, 2014(2014-11-23) (aged 71)Vancouver, British Columbia, CanadaHeight 6 ft 3 in (191 cm)Weight 215 lb (98 kg; 15 st 5 lb)Position DefenceShot LeftPlayed for Toronto Maple LeafsVancouver CanucksAtlanta FlamesCoached for...

Đường Hi Tông唐僖宗Hoàng đế Trung Hoa (chi tiết...)Hoàng đế Đại ĐườngTại vị16 tháng 8 năm 873 - 20 tháng 4 năm 888(14 năm, 248 ngày)Tiền nhiệmĐường Ý TôngKế nhiệmĐường Chiêu TôngThông tin chungSinh(862-06-08)8 tháng 6, 862[1][2]Mất20 tháng 4, 888(888-04-20) (25 tuổi)[1][2]An tángTĩnh lăng (靖陵)Hậu duệ Hậu duệ xem văn bản Tên đầy đủKị húy: Lý Huyên (李儇)B...

Candide Halaman Judul pada edisi ke-1759 yang dicetak oleh Sirène di ParisPengarangVoltaireJudul asliCandide, ou l'OptimismeIlustratorJean-Michel Moreau le JeuneNegaraPrancisBahasaPrancisGenreSatirTanggal terbitJanuari 1759Jenis mediaCetak Candide adalah sebuah novel satir yang ditulis oleh filsuf Voltaire.[1] Novel ini diterbitkan pertama kali pada 1759 di Jenewa, Swiss.[1] Namun sebelum menyerahkan naskahnya untuk dicetak di Jenewa, Voltaire telah sebelumnya ...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) فلاديمير لست معلومات شخصية الميلاد 4 يونيو 1877 [1] براغ[1] الوفاة 27 مايو 1971 (93 سنة) برنو[1] مواطنة تشيكوسلوفاكيا الحياة العملية ا�...

Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari Clergy di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pula: panduan penerjemahan arti...

Particolare del retablo di Marco Zoppo al Collegio di Spagna, Bologna. Firma di Marco Zoppo al retablo del Collegio di Spagna, Bologna. Madonna del Latte, Louvre Madonna col Bambino e santi, Staatliche Museen, Berlino Marco Ruggeri detto lo Zoppo, noto come Marco Zoppo[1] (Cento, 1433 – Venezia, 1478) è stato un pittore italiano. Indice 1 La carriera d'artista 2 Influenze artistiche 3 Opere 4 Note 5 Bibliografia 6 Altri progetti 7 Collegamenti esterni La carriera d'artista Il docum...

