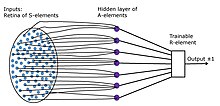
Frank Rosenblatt
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Patung Ino dan Melikertes di Taman Versailles. Dalam mitologi Yunani, Melikertes (bahasa Yunani: Μελικέρτης) adalah anak dari Athamas dari Boiotia dan Ino, putri Kadmos. Melikertes disebut juga sebagai Palaimon (bahasa Yunani: Παλαίμων). Dalam Mitologi Ino membesarkan bayi Dionisos sehingga membuat Hera marah. Hera kemudian membuat suami Ino menjadi gila dan mengejar-ngejar Ino. Ino yang dikejar-kejar oleh suaminya kemudian menjatuhkan dirinya dan Melikertes ke laut....

I testi dei sarcofagi sono formule funerarie, riportanti rituali magico-religiosi, scritte principalmente su sarcofagi prodotti tra il Primo periodo intermedio (2180 - 2055 a.C.[1]) e la fine del Medio Regno (2055 - 1650 a.C.[2]). Indice 1 Storia e caratteristiche 2 Esempi 3 Note 4 Bibliografia 5 Collegamenti esterni Storia e caratteristiche Derivati dai più arcaici Testi delle piramidi, i quali venivano scolpiti sulle pareti delle sepolture dei faraoni e dei loro famigliari,...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Homo erectus – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Homo erectusRentang fosil: 1,9–0,5 PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ Pleistosen awal – Pleistosen akhir[1] Klasifikasi ilm...

Salah satu Raja Aksum (Najasyi) yang tertera dalam lukisan enam raja c. 710–750 M. Raja-raja Aksum memerintah negara perdagangan penting di daerah yang sekarang Eritrea dan Ethiopia utara, dari sekitar 100-940 Masehi.[1] Masa awal Kerajaan Aksum Tanggal Kepemilikan Nama Catatan c. 100 Za Haqala (mungkin Nza ya Nkla atau Zoskales ) c. 200 GDRT (disuarakan oleh sejarawan sebagai Gadarat) prasasti menyebutkan putranya BYGT (disuarakan sebagai Beyga atau Ba yaga) c. 230 - c.240 `DBH (di...

Kastil DevínDevínsky hrad Bratislava DevínSlowakia Reruntuhan Kastil Devín Jenis Castle Dibangun 864 – abad ke-15Perbentengan terakhir dibangun pada abad ke-17 Kondisisaat ini Reruntuhan (direkonstruksi sebagian) Pengawas Moravia Raya, Kerajaan Hungaria, Cekoslowakia, Slowakia Kastil Devín (bahasa Slowakia: hrad Devín [ˈɦrad ˈɟɛʋiːn] atau Devínsky hrad [ˈɟɛʋiːnski ˈɦrat], Hongaria: Dévényi várcode: hu is deprecated , Jerman: Burg Thebencode: de is deprecate...

Geographic and cultural region in Florida. For the metropolitan area made up by the population centers of Miami-Dade, Broward, and Palm Beach Counties, see Miami metropolitan area. Place in Florida, United StatesSouth Florida Clockwise from top: Downtown Miami seen from Biscayne Bay, South Beach in Miami Beach, Downtown Fort Lauderdale, Mallory Square in Key West, Freedom Tower in Miami, and Anhinga Trail in Everglades National ParkCountry United StatesState FloridaLargest city Miam...

Jepang Artikel ini adalah bagian dari seri Politik dan KetatanegaraanJepang Konstitusi Konstitusi Jepang Sejarah Hukum Monarki Kaisar (daftar) Akihito Putra Mahkota Naruhito Istana Kaisar Badan Rumah Tangga Kekaisaran Badan legislatif Parlemen Jepang Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Ketua Tadamori Ōshima Wakil Ketua Hirotaka Akamatsu Majelis Tinggi Presiden Chuichi Date Wakil Presiden Akira Gunji Pemimpin Oposisi Yukio Edano Eksekutif Perdana Menteri (daftar) Shinzō Abe Wakil Perdana Menteri Tarō A...

Unincorporated community in Tennessee, United StatesSanta Fe, TennesseeUnincorporated communitySanta Fe, TennesseeShow map of TennesseeSanta Fe, TennesseeShow map of the United StatesCoordinates: 35°44′06″N 87°07′41″W / 35.73500°N 87.12806°W / 35.73500; -87.12806CountryUnited StatesStateTennesseeCountyMauryElevation673 ft (205 m)Time zoneUTC-6 (Central (CST)) • Summer (DST)UTC-5 (CDT)ZIP code38482Area code931GNIS feature ID1307028[...

Godefroy Redon de BellevilleFonctionsMaître des requêtes5 juillet 1814 - 24 mars 1815Intendantà partir de 1806Préfet de la Loire-Atlantique1804-1806PrésidentSociété académique de Nantes et de Loire-Atlantique1804-1805Député au Corps législatif25 décembre 1799 - 23 novembre 1800Titre de noblesseBaronBiographieNaissance 2 janvier 1748ThouarsDécès 10 août 1820 (à 72 ans)Château de Bailly (d)Sépulture Cimetière du Père-Lachaise, Grave of Redon (d)Nationalité françaiseFo...

Voce principale: Juventus Football Club. Juventus FCStagione 1989-1990La rosa artefice del double di coppa Sport calcio Squadra Juventus Allenatore Dino Zoff Presidente Giampiero Boniperti, poi Vittorio Caissotti di Chiusano Serie A4º Coppa ItaliaVincitore (in Coppa delle Coppe) Coppa UEFAVincitore Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Tacconi, De Agostini (33) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Schillaci (15) StadioComunale Vittorio Pozzo Abbonati12 780[1] Media spettatori29 627 ...

Details of ongoing viral pandemic in the Tibet Autonomous Region This article needs to be updated. The reason given is: Missing 2022 content. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (August 2022) COVID-19 pandemic in TibetYellow: District with one or more casesDiseaseCOVID-19Virus strainSARS-CoV-2LocationTibetArrival date30 January 2020 This article documents the situation of the COVID-19 pandemic in the Tibet Autonomous Region. Background On 1...

Questa voce sull'argomento stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: Società Sportiva Maceratese. Associazione Calcio MacerataStagione 1941-1942Sport calcio Squadra Macerata Allenatore Giuseppe Rossetti Presidente Duilio Palombi Serie C9º posto nel girone eliminatorio F 1940-1941 1942-1943 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce ...
Census Town in West Bengal, IndiaPalladahaCensus TownPalladahaLocation in West Bengal, IndiaShow map of West BengalPalladahaPalladaha (India)Show map of IndiaCoordinates: 22°56′19″N 88°27′59″E / 22.9387°N 88.4665°E / 22.9387; 88.4665Country IndiaStateWest BengalDistrictNorth 24 ParganasArea • Total1.77 km2 (0.68 sq mi)Population (2011) • Total5,994 • Density3,400/km2 (8,800/sq mi)Languages&#...

تحتاج هذه المقالة كاملةً أو أجزاءً منها لإعادة الكتابة حسبَ أسلوب ويكيبيديا. فضلًا، ساهم بإعادة كتابتها لتتوافق معه. (أغسطس 2020) خانات زونغارمعلومات عامةالبداية 1635 الاسم الأصل Зүн Һарин хана улс (بالxal) Зүүнгарын хаант улс (بالمنغولية) الدِّين البوذية اللغة الرسمية لغة الأو...

此條目需要擴充。 (2009年5月13日)请協助改善这篇條目,更進一步的信息可能會在討論頁或扩充请求中找到。请在擴充條目後將此模板移除。 此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2009年5月13日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而被移除。 南羅德西亞殖民地Colony of Southern Rhodesia1923年-1953年1953年-1965...

A stone carving at Banteay Srei of goddessTilottama, an Angkorian temple consecrated in 967 CE. Part of a series on theCulture of Cambodia Society Khmers Ethnic groups Folklore History Languages Holidays Religion Script Women Youth Topics Art Architecture Ceramics Cinema Clothing Cuisine (Royal cuisine) Dance Literature Media Newspapers Radio Television Music Sculpture Sports Theatre Symbols Flag Coat of arms Anthem World Heritage Sites Cambodia portalvte The history of art (Khmer: ស�...

Northwest district of ancient Thessaly For the region of ancient Euboea, see Histiaeotis (Euboea). Histiaeotis in NW Thessaly Histiaeotis (Ancient Greek: Ἱστιαιῶτις, romanized: Histiaiotis) or Hestiaeotis (Ἑστιαιῶτις - Hestiaiotis) was a northwest district of ancient Thessaly, part of the Thessalian tetrarchy, roughly corresponding to the modern Trikala regional unit. Anciently, it was inhabited by the Hestiaeotae (Ἑστιαιῶται), and the Peneius may be d...

1947年の日本 2千年紀 19世紀 - 20世紀 - 21世紀 1930年代 - 1940年代 - 1950年代 1942年 1943年 1944年 1945年 1946年1947年1948年 1949年 1950年 1951年 1952年 日本の国旗 (1870年-1999年) 1947年の海外領土 北マリアナ諸島 | パラオ | マーシャル諸島 | ミクロネシア 1947年の日本の話題 歴史&#...

Anti-surface ship torpedo Bliss–Leavitt Mark 8 torpedo Bliss–Leavitt Mark 8 torpedo sitting on the deck of PT 21TypeAnti-surface ship torpedo[1]Place of originUnited StatesService historyIn service1911–1945[1]Used byUnited States NavyRoyal NavyWarsWorld War IWorld War IIProduction historyDesignerFrank McDowell LeavittDesigned1911[1]ManufacturerNaval Torpedo Station[1]Naval Gun FactoryVariantsMod 1[2]Mod 2Mod 2AMod 2BMod 3[3...

British particle physicist For the climate scientist, see Peter Kalmus (climate scientist). For the Slovak artist, see Peter Kalmus (artist). Peter I. P. KalmusOBE HonFInstPBorn (1933-01-25) 25 January 1933 (age 91)Prague, CzechoslovakiaNationalityBritishAwardsRutherford Medal and Prize (1988), Kelvin Prize (2002)Scientific careerFieldsPhysics/Particle Physics Peter Ignaz Paul Kalmus OBE HonFInstP (born 25 January 1933), is a British particle physicist, and emeritus professor of ...