Distin family
|
Read other articles:

Bagian dari seriIslam Rukun Iman Keesaan Allah Malaikat Kitab-kitab Allah Nabi dan Rasul Allah Hari Kiamat Qada dan Qadar Rukun Islam Syahadat Salat Zakat Puasa Haji Sumber hukum Islam al-Qur'an Sunnah (Hadis, Sirah) Tafsir Akidah Fikih Syariat Sejarah Garis waktu Muhammad Ahlulbait Sahabat Nabi Khulafaur Rasyidin Khalifah Imamah Ilmu pengetahuan Islam abad pertengahan Penyebaran Islam Penerus Muhammad Budaya dan masyarakat Akademik Akhlak Anak-anak Dakwah Demografi Ekonomi Feminisme Filsafat...

Åke FalckLahir(1925-04-03)3 April 1925Gothenburg, SwediaMeninggal12 Oktober 1974(1974-10-12) (umur 49)Danderyd, SwediaPekerjaanSutradaraTahun aktif1958-1972 Åke Falck (3 April 1925 – 12 Oktober 1974) adalah seorang sutradara asal Swedia. Ia menyutradarai 13 film antara 1958 dan 1972. Film tahun 1966 buatannya The Princess masuk dalam Festival Film Internasional Moskwa ke-5.[1] Referensi ^ 5th Moscow International Film Festival (1967). MIFF. Diarsipkan dari...

DNA reverse transcribed from RNA CDNA redirects here. For other uses, see CDNA (disambiguation). For the general property of complementarity in molecular biology, see Complementarity (molecular biology). For complementation tests used in genetics research, see Complementation (genetics). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Compleme...

Concert venue in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S. The MasqueradeThe MasqExterior of the venue at its former location, DuPre Mill (c. 2006)Address50 Lower Alabama St SW, Ste. 22Atlanta, Georgia 30303-7602LocationUnderground AtlantaCoordinates33°45′06″N 84°23′31″W / 33.751539°N 84.3920599°W / 33.751539; -84.3920599Capacity1,000 (Heaven)550 (Hell)300 (Purgatory)250 (Altar)OpenedSeptember 1989WebsiteVenue Website The Masquerade is a mid-sized concert venue located i...
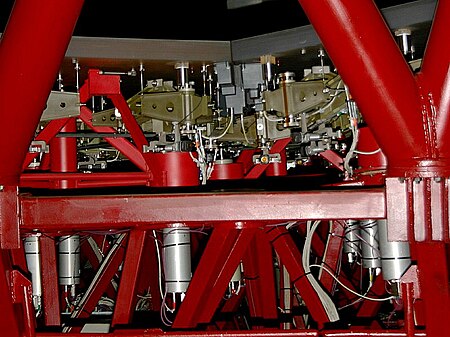
This article is about telescope mirror support cells. For the neurological colloquialism mirror cell, see Mirror neuron. Mirror of the Large Binocular Telescope In astronomy, a mirror support cell - more commonly mirror cell - is a component of a reflecting telescope that supports the mirror in place to hold optical alignment, allow collimation adjustment, and protect it from falling out. The common usage of the word denotes the cell that holds the primary mirror (M1), however technically it ...

List of events ← 1788 1787 1786 1789 in the United States → 1790 1791 1792 Decades: 1770s 1780s 1790s 1800s See also: History of the United States (1789–1849) Timeline of the American Revolution List of years in the United States 1789 in the United States1789 in U.S. states States Connecticut Delaware Georgia Maryland Massachusetts New Hampshire New Jersey New York North Carolina Pennsylvania Rhode Island South Carolina Virginia List of years in the United States by state or ter...

ImmeyaLukisan genggaman gada dengan nama Hotepibre, hadiah dari ImmeyaRaja EblaBerkuasaskt. 1750-1725 SMPenerusdiduga Hammu[rabi]Informasi pribadiPemakamanMakam Tuan Kambing, di Ebla Immeya merupakan seorang raja Ebla di Suriah modern. Ia memerintah pada sekitar tahun 1750–1725 SM.[1] Pemerintahan Immeya kemungkinan besar dimakamkan di lokasi yang disebut Makam Tuan Kambing, di Nekropolis kerajaan istana barat Ebla,[2] seperti yang dinyatakan oleh sebuah cangkir perak yang d...

Kerajaan Muna1210–1956 BenderaIbu kotaKotano WunaBahasa yang umum digunakanMunaAgama Animisme dan Dinamisme (1210 - 1527)Islam (1527 - sekarang)PemerintahanKerajaan mutlakRaja • 1210 La Eli gelar Bheteno ne Tombula• 1947-1956 La Ode Pandu Sejarah • Pengangkatan La Eli menjadi Raja 1210• Dibubarkan 1956 Didahului oleh Digantikan oleh Berkas:Bendera Kerajaan Muna.jpg krjKerajaan Muna Indonesia Sunting kotak info • Lihat • BicaraBantuan ...

坐标:43°11′38″N 71°34′21″W / 43.1938516°N 71.5723953°W / 43.1938516; -71.5723953 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2017年5月21日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:新罕布什尔州 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源...

American cycling team Team Novo NordiskTeam informationUCI codeTNNRegisteredUnited StatesFounded2008 (2008)Discipline(s)RoadStatusUCI ProTeamBicyclesArgon18ComponentsShimanoWebsiteTeam home pageKey personnelGeneral managerVassili DavidenkoTeam name history2008–201020112011–20122013–Team Type 1 (TT1)Team Type 1–Sanofi Aventis (TT1)Team Type 1–Sanofi (TT1)Team Novo Nordisk (TNN) Team Novo Nordisk jerseyJersey Current season Team Novo Nordisk (UCI team code: TNN) is an all-diabet...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. SMP Negeri 1 SronoInformasiDidirikan9 Oktober 1982Jumlah kelas9 kelas di setiap tingkatRentang kelasVII, VIII, IXKurikulumKurikulum Tingkat Satuan PendidikanStatusSekolah Standar NasionalAlamatLokasiJalan Raya Srono, Sukonatar, Srono, Jawa Timur, ...

The World Veterans FederationPredecessorFIDAC (The Interallied Federation of War Veterans Organisation)Formation1876HeadquartersRue de la Cité 1Location1204 Genève, SwitzerlandRegion served WorldwideMembership 172 veteran organizations from 121 countries representing some 60 million veterans worldwidePresidentDoctor El Mostafa El Ktiri (Marocco)Secretary GeneralDan Viggo Bergtun (Norway)Main organExecutive BoardWebsitehttp://www.theworldveterans.org/ The World Veterans Federation (WVF) is t...

一中同表,是台灣处理海峡两岸关系问题的一种主張,認為中华人民共和国與中華民國皆是“整個中國”的一部份,二者因為兩岸現狀,在各自领域有完整的管辖权,互不隶属,同时主張,二者合作便可以搁置对“整个中國”的主权的争议,共同承認雙方皆是中國的一部份,在此基礎上走向終極統一。最早是在2004年由台灣大學政治学教授張亞中所提出,希望兩岸由一中各表�...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع الحديدة (توضيح). 14°48′08″N 42°57′04″E / 14.80222°N 42.95111°E / 14.80222; 42.95111 هذه المقالة عن المدينة الساحلية في اليمن. لاستخدامات أخرى، طالع حديدة. مدينة الحُدَيْدَة عاصمة إقليم تهامة تقسيم إداري البلد اليمن[1] عاصمة لـ محافظة الحديدة �...

佩德拉-杜因达亚Pedra do Indaiá市镇佩德拉-杜因达亚在巴西的位置坐标:20°15′28″S 45°12′32″W / 20.2578°S 45.2089°W / -20.2578; -45.2089国家巴西州米纳斯吉拉斯州面积 • 总计349.092 平方公里(134.785 平方英里)人口 • 總計3,921人 • 密度11.2人/平方公里(29.1人/平方英里) 佩德拉-杜因达亚(葡萄牙语:Pedra do Indaiá)是巴西米纳斯吉�...

Ukrainian cyclist Andriy VynokurovPersonal informationFull nameAndriy Vynokurov (2016)Born (1982-08-14) August 14, 1982 (age 41)Kharkiv, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet UnionTeam informationDisciplineTrackRoleRiderRider typeSprint Medal record Representing Ukraine Men's track cycling European Championships 2016 Yvelines Keirin 2016 Yvelines Sprint 2017 Berlin Keirin World Junior Championships 2000 Fiorenzuola 1 km time trial 2000 Fiorenzuola Sprint European U23 Championships 2001 B...

Brazilian racing driver (born 1976) Ricardo ZontaZonta in 2007, as a Stock Car Brasil driverBornRicardo Luiz Zonta (1976-03-23) 23 March 1976 (age 48)Curitiba, Paraná, BrazilFormula One World Championship careerNationality BrazilianActive years1999–2001, 2004–2005TeamsBAR, Jordan, ToyotaEntries38 (36 starts)Championships0Wins0Podiums0Career points3Pole positions0Fastest laps0First entry1999 Australian Grand PrixLast entry2005 United States Grand Prix24 Hours of Le Mans careerYe...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: Juventus Football Club. FBC JuventusStagione 1903-1904Sport calcio Squadra Juventus Presidente Giacomo Parvopassu Prima Categoria2° Palla DapplesFinalist...

此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2012年7月16日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而被移除。 愛三路是台灣基隆市市中心的主要道路之一,位於仁愛區,該路不分段。仁一路至仁二路為雙向四線道,南向為一線道,北向為三線道;仁二路至仁五路為北向單行道共四線道,路寬16.3公尺。本路段為�...

Experiment to measure elementary electric charge Not to be confused with Pitch drop experiment. Millikan's setup for the oil drop experiment The oil drop experiment was performed by Robert A. Millikan and Harvey Fletcher in 1909 to measure the elementary electric charge (the charge of the electron).[1][2] The experiment took place in the Ryerson Physical Laboratory at the University of Chicago.[3][4][5] Millikan received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 19...





