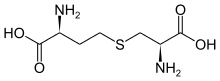
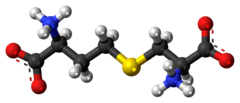
Cystathionine
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento geometria non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Questa voce sull'argomento geometria è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Sistema di riferimento cartesiano i...

2008 French filmThe BrokenTheatrical release posterDirected bySean EllisWritten bySean EllisProduced byLene BausagerStarringLena HeadeyAsier NewmanMichelle DuncanMelvil PoupaudRichard JenkinsAndrew HavillCinematographyAngus HudsonEdited byScott ThomasMusic byGuy FarleyDistributed byGaumont (France)[2]The Works (United Kingdom)[2]Release date 18 January 2008 (2008-01-18) (Sundance Film Festival) Running time88 minutesCountriesFranceUnited Kingdom[1]L...
County in Minnesota, United States County in MinnesotaWashington CountyCountyWashington County CourthouseLocation within the U.S. state of MinnesotaMinnesota's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 45°02′N 92°53′W / 45.04°N 92.89°W / 45.04; -92.89Country United StatesState MinnesotaFoundedOctober 27, 1849[1]Named forGeorge WashingtonSeatStillwaterLargest cityWoodburyArea • Total423 sq mi (1,100 km2) • Land...

PausPaulus IAwal masa kepausan29 Mei 757Akhir masa kepausan28 Juni 767PendahuluStefanus IIPenerusStefanus IIIInformasi pribadiNama lahirtidak diketahuiLahirtidak diketahuiWafat28 Juni 767RomaPaus lainnya yang bernama Paulus Paus Paulus I adalah Paus Gereja Katolik Roma sejak 29 Mei 757 hingga 28 Juni 767. Pada mulanya ia adalah seorang Diaken Gereja Katolik Roma dan sering mewakili kakaknya Paus Stefanus II dalam bernegosiasi dengan kerajaan Langobardi (Lombard). Setelah kematian Stefanus pad...

ロバート・デ・ニーロRobert De Niro 2011年のデ・ニーロ生年月日 (1943-08-17) 1943年8月17日(80歳)出生地 アメリカ合衆国・ニューヨーク州ニューヨーク市身長 177 cm職業 俳優、映画監督、映画プロデューサージャンル 映画、テレビドラマ活動期間 1963年 -配偶者 ダイアン・アボット(1976年 - 1988年)グレイス・ハイタワー(1997年 - )主な作品 『ミーン・ストリート』(1973年)...

Open-wheel formula racing car built by Dallara Dallara IR-03/04/05[1] Dallara IR-05[2]CategoryIndyCar SeriesConstructorDallaraPredecessorDallara IR-02SuccessorDallara DW12Technical specificationsChassisCarbon fiber monocoque with honeycomb structure[3]Suspension (front)double wishbones, pull rod actuated coil springs over shock absorbersSuspension (rear)double wishbones, pull rod actuated coil springs over shock absorbersLength192–196 in (4,877–4,978 mm)W...

ХристианствоБиблия Ветхий Завет Новый Завет Евангелие Десять заповедей Нагорная проповедь Апокрифы Бог, Троица Бог Отец Иисус Христос Святой Дух История христианства Апостолы Хронология христианства Раннее христианство Гностическое христианство Вселенские соборы Н...

Ai-Ai delas Alas-SibayanLahirMartina Aileen Hernandez delas Alas-Sibayan11 November 1964 (umur 59)[1]San Luis, Batangas,[2] PhilippinesTempat tinggalCalatagan, Batangas, FilipinaBauan, Batangas, FilipinaPekerjaan Aktris Pembawa acara Pelawak Artis rekaman Produser Penyanyi Manajer bakat Tahun aktif1989–sekarangAgenGMA Network (1991–2001; 2015–sekarang)ABS-CBN (1998–2014)Tinggi5 ft 6 in (168 cm)Suami/istriMiguel Vera (m. 198...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6]...

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6]...

List of events in the year 1395 ← 1394 1393 1392 1391 1390 1395 in Ireland → 1396 1397 1398 1399 1400 Centuries: 12th 13th 14th 15th 16th Decades: 1370s 1380s 1390s 1400s 1410s See also:Other events of 1395 List of years in Ireland Events from the year 1395 in Ireland. Incumbent Lord: Richard II Events Defeat of Leinster Irish under Art Mór Mac Murchadha Caomhánach, King of Leinster and submission of nearly all Irish and rebel English chiefs to King Richard II of England.[1&...

Asosiasi Sepak Bola GhanaCAFDidirikan1957Bergabung dengan FIFA1957Bergabung dengan CAF1958PresidenKwesi NyantakyiWebsitewww.ghanafa.org Asosiasi Sepak Bola Ghana (bahasa Inggris: Ghana Football Association) adalah badan pengendali sepak bola di Ghana. Kompetisi Badan ini menyelenggarakan beberapa kompetisi di Ghana, yakni: Liga Utama Ghana Liga Sepak Bola Ghana Piala Asosiasi Sepak Bola Ghana Tim nasional Badan ini juga merupakan badan pengendali dari 5 tim nasional di Ghana, yakni: Tim n...

MissundaztoodAlbum studio karya P!nkDirilis20 November 2001 (2001-11-20)Direkam2001GenrePop, R&B, Rrock, pop rockDurasi55:20LabelAristaProduserDamon Elliott, Dallas Austin, Linda Perry, Scott StorchKronologi P!nk Can't Take Me Home (2000)Can't Take Me Home2000 Missundaztood (2001) Try This (2003)Try This2003 Singel dalam album Missundaztood Get the Party StartedDirilis: 9 Oktober 2001 Don't Let Me Get MeDirilis: 19 Februari 2002 Just Like a PillDirilis: 10 Juni 2002 Family Portra...

German manufacturer of dive computers and other underwater electronics for recreational diving. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: HeinrichsWeikamp – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message)This article relies largely or entirely on a ...

Ymare La mairie. Administration Pays France Région Normandie Département Seine-Maritime Arrondissement Rouen Intercommunalité Métropole Rouen Normandie Maire Mandat Ingrid Bona 2020-2026 Code postal 76520 Code commune 76753 Démographie Gentilé Ymarois Populationmunicipale 1 212 hab. (2021 ) Densité 301 hab./km2 Géographie Coordonnées 49° 20′ 59″ nord, 1° 10′ 35″ est Altitude Min. 47 mMax. 153 m Superficie 4,03 km2...

Phrase describing excessive media coverage News media satellite up-link trucks and photojournalists gathered outside the Prudential Financial headquarters in Newark, New Jersey, in August 2004 following the announcement of evidence of a terrorist threat to it and to buildings in New York City. Media circus is a colloquial metaphor, or idiom, describing a news event for which the level of media coverage—measured by such factors as the number of reporters at the scene and the amount of materi...

Underwater diving at altitudes above 300 m SCUBA Diver in the mountain lake Lai da Marmorera 1,680 metres (5,510 ft) above sea level) Altitude diving is underwater diving using scuba or surface supplied diving equipment where the surface is 300 metres (980 ft) or more above sea level (for example, a mountain lake).[1][2] Altitude is significant in diving because it affects the decompression requirement for a dive, so that the stop depths and decompression times used ...
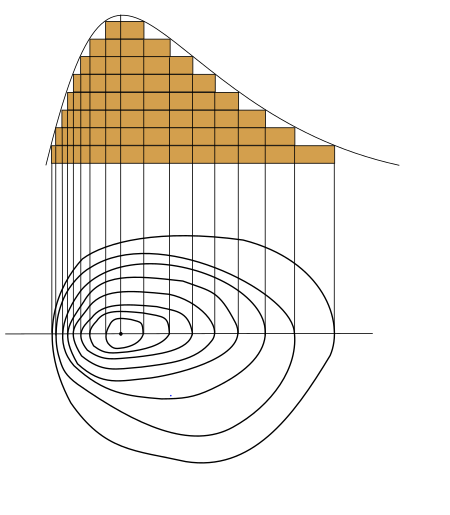
Curve along which a 3-D surface is at equal elevation This article is about lines of equal value in maps and diagrams. For more meanings of the word contour, see Contour (disambiguation). The bottom part of the diagram shows some contour lines with a straight line running through the location of the maximum value. The curve at the top represents the values along that straight line. A three-dimensional surface, whose contour graph is below. A two-dimensional contour graph of the three-dimensio...

One of the Seven Management and Planning Tools Affinity wall diagram The affinity diagram is a business tool used to organize ideas and data. It is one of the Seven Management and Planning Tools. People have been grouping data into groups based on natural relationships for thousands of years; however, the term affinity diagram was devised by Jiro Kawakita in the 1960s[1] and is sometimes referred to as the KJ Method. The tool is commonly used within project management and allows large...