Coat of arms of Finland
| |||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Juego de niños Programa de televisiónPresentado por Amparo Soler Leal (1988)Tina Sainz (1989)Ignacio Salas (1989-1990)Xavier Sardà (1990-1992; 2019)Protagonistas 6.ª temporada José Corbacho (2019)Juan Carlos Ortega (2019)Tema principal Pythagoras' Trousers(compuesto por Penguin Cafe Orchestra)N.º de temporadas 6 director = Miquel Obiols Prat (1.ª a 5.ª)Xavier Sardá (6.ª temporada) realización = Marcelí Gili, Amparo Solis productor = Fernando G.Tejedor (1.ª a 5.ª)N.º de episodio...

Guardia SanframondiKomuneComune di Guardia SanframondiLokasi Guardia Sanframondi di Provinsi BeneventoNegara ItaliaWilayah CampaniaProvinsiBenevento (BN)Luas[1] • Total21,1 km2 (8,1 sq mi)Ketinggian[2]428 m (1,404 ft)Populasi (2016)[3] • Total5.846 • Kepadatan280/km2 (720/sq mi)Zona waktuUTC+1 (CET) • Musim panas (DST)UTC+2 (CEST)Kode pos82034Kode area telepon0824Situs webhttp://www...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Daftar nama-nama Ketua Umum Persekutuan Gereja-Gereja di Indonesia – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Berikut adalah daftar nama-nama tokoh yang pernah menjabat sebagai Ketua Umum Persek...

Peta yang menunjukkan letak Kabugao Data sensus penduduk di Kabugao Tahun Populasi Persentase 199512.710—200013.9852.07%200714.5290.53% Kabugao adalah munisipalitas di provinsi Apayao, Filipina. Pada tahun 2000, munisipalitas ini memiliki populasi sebesar 14.529 jiwa atau 2.501 rumah tangga. Pembagian wilayah Secara politis Kabugao terbagi atas 21 barangay, yaitu: Badduat Baliwanan Bulu Dagara Dibagat Cabetayan Karagawan Kumao Laco Lenneng (Liyyeng) Lucab Luttuacan Madatag Madduang Magabta ...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (سبتمبر 2018) مسيرة الفخر العالمية، لندن 2012 نشأ مصطلح الديمقراطية على أساس نوع الجنس عن فكرة معيارية تتعلق بالعمل على تعميم مراعاة المنظور الجنساني. تهدف هذه الفكرة إلى �...

Monthly men's magazine This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: King magazine – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) KingRosa Acosta on the cover of the Winter 2010 issue of KingCategoriesAfrican-American men's magazineFr...

Upscale neighborhood in the California city This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Bankers Hill, San Diego – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2019) Quince Street pedestrian bridge in Bankers Hill neighborhood of San Diego, California. Bankers Hill (Park West) is located ...

Yakovlev Yak-130 Un Yak-130 en 2012. Constructeur Yakovlev Rôle Avion d'entraînement, de reconnaissance et d'appui-feu Statut En service Premier vol 25 avril 1996 Équipage 2 Motorisation Moteur Ivtchenko-Progress AI-222 Nombre 2 Type Turboréacteur Poussée unitaire 2 500 kgp Dimensions Envergure 10,40 m Longueur 11,49 m Hauteur 4,76 m Surface alaire 23,52 m2 Masses À vide 4 600 kg Maximale 9 000 kg Performances Vitesse maximale 1 05...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Kekerasan dalam rumah tangga di Tiongkok adalah kekerasan atau pelecehan yang melibatkan pasangan intim atau anggota keluarga terhadap satu yang lain. Kekerasan pasangan intim yang dilakukan oleh lelaki merupakan salah satu jenis kekerasan dalam rumah ...

Botanical garden in Davenport, Iowa, U.S. Vander Veer Botanical ParkThe lagoon at Vander Veer ParkTypePublic parkLocationDavenport, IowaCoordinates41°32′37.68″N 90°34′30.72″W / 41.5438000°N 90.5752000°W / 41.5438000; -90.5752000Area33-acre (0.13 km2)Created1885Operated byDavenport Parks and RecreationOpenAll yearPublic transit access Davenport CitiBus U.S. National Register of Historic PlacesDesignatedApril 9, 1985Reference no.85000784[1&...
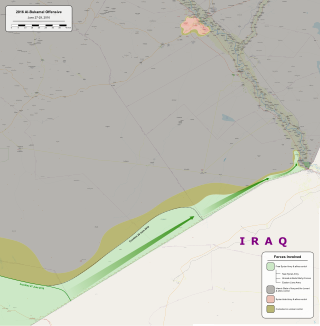
2016 military operation of the Syrian civil war Abu Kamal offensive (2016)Part of inter-rebel conflict of the Syrian civil war and the international military intervention against ISILMap of the offensiveDate28–29 June 2016(1 day)LocationAbu Kamal District, Deir-Ez-Zor Governorate, Syria34°26′47″N 40°55′16″E / 34.4463°N 40.9210°E / 34.4463; 40.9210Result ISIL victory[2][3][4][5] The FSA withdraws from all positions it h...

2019 single by Labrinth All for UsSingle by Labrinth featuring Zendayafrom the album Imagination & the Misfit Kid and Euphoria Season 1 (An HBO Original Series Soundtrack) Released30 June 2019 (2019-06-30)Genre Gospel[1] R&B electronic[2] Length3:32 (single version)3:13 (album version)[3]LabelSycoSongwriter(s)Timothy McKenzieProducer(s)LabrinthLabrinth singles chronology Mount Everest (2019) All for Us (2019) Something's Got to Give (2019) Ze...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Le ton de cet article est trop promotionnel ou publicitaire (janvier 2024). Vous êtes invité à améliorer l'article de manière à adopter un ton neutre (aide quant au style) ou discutez-en. Vous pouvez également préciser les sections non neutres en utilisant {{section promotionnelle}} et de souligner les passages problématiques avec {{passage promotionnel}}. Cyril de La PatellièreCyril de La Patellière e...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Halloween (disambiguasi). HalloweenJack-o'-lantern, labu simbol HalloweenNama lainHallowe'enAllhallowe'enMalam Para Kudus (All Hallows' Eve atau All Saints' Eve)Dirayakan olehUmat Kekristenan Barat dan banyak non-Kristen di seluruh dunia[1]MaknaHari pertama Masa Para KudusPerayaantrick or treating, pesta kostum, membuat jack-o'-lantern, api unggun dan kembang api, penenungan, mengambil apel di dalam air dengan mulut, mengunjungi atraksi berhantuKegiatanIbada...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助�...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (يناير 2022) المتغير في علم الإحصاء هو الخاصية أو السمة التي تأخذ قيما أو مستويات مختلفة من فرد إلى آخر (وتكون من قيمتين...

This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: The Association for Science Education – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The Association for Science EducationAbbreviationASEPredecessor Association of Public School Science Masters Science Masters Association Association of Women Science Te...

Species of mammal For other species called desert hare, see Desert hare (disambiguation). Desert hare Conservation status Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Lagomorpha Family: Leporidae Genus: Lepus Species: L. tibetanus Binomial name Lepus tibetanusWaterhouse, 1841 Desert hare range The desert hare (Lepus tibetanus) is a species of hare found in Central Asia, Northwest China, and...

Universitas Islam NegeriSjech M. Djamil DjambekBukittinggiUIN SMDD Gedung Rektorat UIN SMDD Bkt InformasiNama sebelumnyaSTAIN Sjech M. Djamil Djambek BukittinggiIAIN BukittinggiMotoReligius, Berbudaya, ProfesionalJenisPerguruan tinggi Islam negeri di IndonesiaDidirikan21 Maret 1997 atau 12 Zulkaidah 1417 H (Keppres RI No. 11 Tahun 1997)Lembaga indukKementerian Agama Republik IndonesiaAfiliasiIslamRektorProf. Dr. Ridha Ahida, M.Hum.Staf akademik176 orang dosen[1]Staf administras...

Everest Academy redirects here. For the Islamic K-8 school in Stafford, Texas (Greater Houston) named Everest Academy, see Islamic Education Institute of Texas. Private school in Clarkston, Michigan, United StatesEverest Collegiate High School and AcademyAddress5935 Clarkston RoadClarkston, Michigan 48348United StatesCoordinates42°45′2″N 83°23′36″W / 42.75056°N 83.39333°W / 42.75056; -83.39333InformationTypePrivateMottoSemper Altius(Always Higher)Religious ...










































