City physician
|
Read other articles:

Cekungan Nias. Cekungan Nias (juga dikenal dengan nama Cekungan Sumatera Barat atau Cekungan Sibolga) adalah cekungan busur muka yang terletak di lepas pantai barat Sumatra, Indonesia, di Samudra Hindia. Namanya berasal dari nama pulau yang berbatasan dengan sisi baratnya, pulau Nias. Cekungan Nias, pulau Nias (kompleks akresi darat), dan perairannya, kompleks akresi bawah laut, membentuk busur muka di perbatasan tubrukan/subduksi Lempeng Sunda/Lempeng Indo-Australia. Busur muka terletak di a...

Aleksandr IIOsvoboditel (sang Pembebas)Kaisar dan Autokrat seluruh RusiaBerkuasa2 Maret 1855 – 13 Maret 1881Penobatan7 September 1855PendahuluNicholas IPenerusAlexander IIIInformasi pribadiKelahiran(1818-04-29)29 April 1818Kremlin, Moskwa, Kekaisaran RusiaKematian13 Maret 1881(1881-03-13) (umur 62)Istana Musim Dingin, St. Petersburg, Kekaisaran RusiaPemakamanPeter and Paul CathedralWangsaWangsa Holstein-Gottorp-RomanovNama lengkapAleksandr Nikolaevich RomanovAyahNikolai I dari RusiaIbu...

Подгруппы китайцев (ханьцев) основаны на языках схожих с путунхуа, культуре и региональных особенностях в пределах материкового Китая. В севернокитайском языке принято обозначать как «миньси» (кит. трад. 民系, пиньинь mínxì, буквально: «этнород») или «цзуцюнь» (кит. трад. 族�...

OrpoOrdnungspolizeiBendera panjang komandan OrdnungspolizeiOrpo berada dibawah administrasi menteri dalam negeri, tapi dipimpin oleh anggota SS.Seorang polisi berseragam Berlin, Januari 1937.Informasi lembagaDibentuk26 Juni, 1936Lembaga pengganti Landespolizei (Jerman Barat) Volkspolizei (Jerman Timur)JenisPolisi negaraWilayah hukum JermanOccupied EuropeKantor pusatHauptamt Ordungspolizei, Prinz-Albrecht-Straße, BerlinPegawai401,300 (1944)[1]MenteriHeinrich Himmler 1936–1945, Kepal...

Children's animated television series This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (June 2023) Rosie's RulesGenrePreschoolEducationalChildren's animationCreated byJennifer HamburgDeveloped byKaren FowlerDirected by Heejung Yun Steve Daye Paul Riley Starring Ellora López Ana Sofia Ferrer Denise Oliver Gabby Clarke Oscar Whalen Carlos Diaz Amanda...
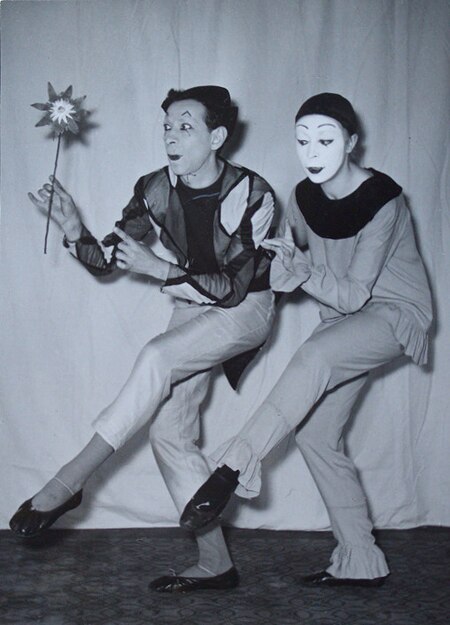

تمثيل صامت الاسم الرسمي ممثل تسمية الإناث ممثلة فرع من ممثل، ومؤدي المجال فن مهن متعلقة تمثيل تعديل مصدري - تعديل التمثيل الصامت أو التمثيلية الإيمائية[1] هو أحد أنواع التمثيل الذي يتم بدون كلام.[2][3] العرض يتم على شكل مسرحية قصيرة لا تنطق فيها كلمات، ي...

Museum in Pingxi, New Taipei, Taiwan Taiwan Coal Mine Museum台灣煤礦博物館Established2001LocationPingxi, New Taipei, TaiwanCoordinates25°03′10″N 121°46′25″E / 25.05278°N 121.77361°E / 25.05278; 121.77361TypemuseumWebsiteOfficial website (in Chinese) Taiwan Coal Mine Museum entrance The Taiwan Coal Mine Museum (traditional Chinese: 台灣煤礦博物館; simplified Chinese: 台湾煤矿博物馆; pinyin: Táiwān Méikuàng Bówùguǎn) is...

Hungarian pop-rock singer-songwriter (born 1968) The native form of this personal name is Kovács Ákos. This article uses Western name order when mentioning individuals. Ákos Kovács in 2008 Ákos Kovács (born in Budapest, 6 April 1968) is a Hungarian pop-rock singer-songwriter. He is known for his solo career writing and performing serious, poetic pop songs, as well as a member of the now defunct group Bonanza Banzai. Kovács uses his given name, Ákos, in his career. His name is writ...

American boxer This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Orlando Canizales – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Orlando...

5th Electromagnetic Warfare SquadronEmblem of the 5th Electromagnetic Warfare SquadronCountryUnited StatesBranch United States Space ForceTypeSpace Electromagnetic WarfarePart ofSpace Delta 3Garrison/HQPeterson Space Force Base, ColoradoMotto(s)We plea the fifth!Decorations AFOUACommandersCurrentcommanderLt Col Andy WangNotablecommandersJohn W. RaymondInsigniaEmblem of the 5th Space Surveillance SquadronMilitary unit The United States Space Force's 5th Electromagnetic Warfare Squad...

American football player (born 1991) American football player Cornelius LucasLucas with the Washington Football Team in 2021No. 78 – Washington CommandersPosition:Offensive tacklePersonal informationBorn: (1991-07-18) July 18, 1991 (age 32)New Orleans, Louisiana, U.S.Height:6 ft 8 in (2.03 m)Weight:327 lb (148 kg)Career informationHigh school:Edna Karr (New Orleans)College:Kansas StateUndrafted:2014Career history Detroit Lions (2014–2016) Los Angeles Rams (20...

Ernst von DobschützErnst von Dobschütz, Desember 1922LahirErnst Adolf Alfred Oskar Adalbert von Dobschütz9 Oktober 1870Halle, JermanMeninggal20 Mei 1934(1934-05-20) (umur 63)Halle, JermanPekerjaanpenulis, profesor, teolog Ernst Adolf Alfred Oskar Adalbert von Dobschütz (9 Oktober 1870 – 20 Mei 1934) adalah seorang teolog, tekstual kritikus asal Jerman penulis dari banyak buku dan profesor di Universitas Halle, Universitas Breslau, dan University of Strasbourg. Dia j...

New Zealand minister of the Crown Deputy Prime Minister of New ZealandCoat of Arms of New ZealandFlag of New ZealandIncumbentWinston Peterssince 27 November 2023Department of the Prime Minister and CabinetStyle Mr Deputy Prime Minister (informal) The Honourable (formal) His Excellency (diplomatic) Member ofCabinet of New ZealandExecutive CouncilReports toPrime Minister of New ZealandAppointerGovernor-General of New ZealandTerm lengthNo fixed termFormation13 December 1949; 74...

برودوس الاسم الرسمي (بالإنجليزية: Broadus) الإحداثيات 45°26′34″N 105°24′33″W / 45.442777777778°N 105.40916666667°W / 45.442777777778; -105.40916666667 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة بودير ريفير عاصمة لـ مقاطعة بودير ريفير خصائص جغ...
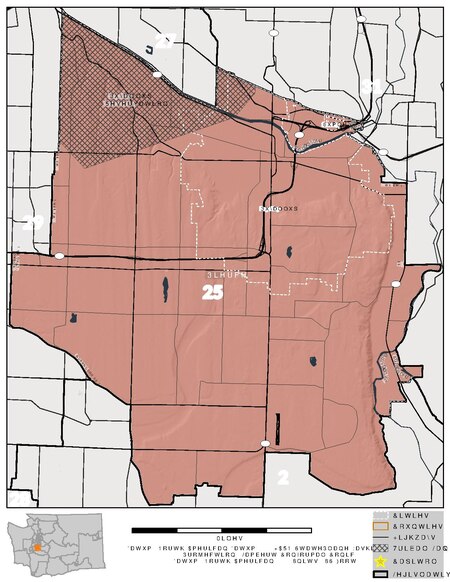
Map of Washington's 25th legislative district Washington's 25th legislative district is one of forty-nine districts in Washington state for representation in the state legislature. The district includes Puyallup and the surrounding area in Pierce County.[1] The district's legislators are state senator Chris Gildon and state representatives Kelly Chambers (position 1) and Cyndy Jacobsen (position 2), all Republicans. See also Washington Redistricting Commission Washington State Legisl...

American economist and statistician (1912–2006) Milton FriedmanFriedman in 2004Born(1912-07-31)July 31, 1912Brooklyn, New York City, U.SDiedNovember 16, 2006(2006-11-16) (aged 94)San Francisco, California, U.SEducation Rutgers University (BA) University of Chicago (MA) Columbia University (PhD) Political partyRepublican[3]Spouse Rose Friedman (m. 1936)ChildrenDavid D. FriedmanJan MartelAcademic careerInstitution National Resources Planning Board (...

ItalyA frecciarossa high-speed train next to an older E.444R at Milano CentraleOperationNational railwayFerrovie dello StatoMajor operatorsTrenitalia (national)Nuovo Trasporto Viaggiatori (national)Trenord (local)Trenitalia Tper (local) Thello (international)Mercitalia (freight)StatisticsRidership883.3 million (2019)[1]System lengthTotal16,723 km (10,391 mi)[2]Double track7,505 km (4,663 mi)[2]Track gaugeMain1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄...

Partai Unionis Demokrat Democratic Unionist Party SingkatanDUPKetua umumJeffrey DonaldsonKetua umumThe Lord MorrowPemimpin dalam Dewan BangsawanThe Lord Dodds of DuncairnWakil PemimpinGavin RobinsonPemimpin Fraksi dalam Dewan RakyatJeffrey DonaldsonSekretaris JenderalMichelle McIlveenPendiriIan PaisleyDibentuk30 September 1971; 52 tahun lalu (1971-09-30)Didahului olehPartai Unionis ProtestanKantor pusat91 Dundela Avenue BelfastBT4 3BU[1]IdeologiUnionisme di Britania Raya[...

Medlemmar i RGFD vid Harbins järnvägsstation till ära för Anastasy Vonsyatsky 26 april 1934.[1] Ryska Kvinnors Fasciströrelse eller «Российское женское фашистское движение», Rossiiskoye Zhenskoye Fashistskoye Dvizheniye (RGFD) var ett autonomt kvinnoförbund inom Ryska Fascistpartiet (VFP) i Manchukuo under 1930- och 1940-talet.[2] Det förespråkade partiets konservativa syn på kvinnor som skönhetens, hemlivets och gudstrons försvarare. Deras unif...

Questa voce sull'argomento lingua olandese è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Fiammingo orientaleOost-VlaamsParlato inBelgioPaesi Bassi LocutoriTotale1,1 milioni TassonomiaFilogenesiLingue indoeuropee Germaniche Occidentali Olandese Dialetti fiamminghi fiammingo orientale Codici di classificazioneLinguist Listvls-oos (EN) Glottologoost1241 (EN) Linguasphe...