Charles De Koninck
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
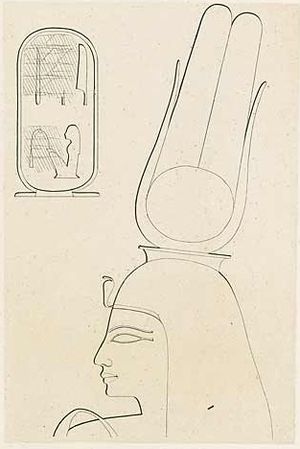
تي معلومات شخصية تاريخ الميلاد القرن 14 ق.م الوفاة القرن 14 ق.م طيبة الزوج خپر خپرو رع آي الأولاد موت نجمت عائلة الأسرة المصرية الثامنة عشر الحياة العملية المهنة سياسية تعديل مصدري - تعديل لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع تي (توضيح). تي في الهيروغليفية...

Miss Universe 1968Tanggal13 Juli 1968TempatMiami Beach Auditorium, Miami Beach, Florida, United StatesPembawa acaraBob BarkerPenyiaranCBSPeserta65Finalis/Semifinalis15DebutKongo-KinshasaMaltaYugoslaviaTidak tampilKubaPanamaParaguayTampil kembaliAustraliaCeylonEkuadorHaitiJamaikaLebanonNikaraguaThailandTunisiaPemenangMartha Vasconcellos BrazilPersahabatanYasuyo Iino JepangKostum Nasional TerbaikLuz Elena Restrepo González KolombiaFotogenikDaliborka St...

Girls' Generation 1979Poster promosiJudul asli란제리 소녀시대 GenreComing-of-ageRemajaMisteri[1]BerdasarkanLingerie Girls' Generation (란제리 소녀시대)oleh Kim Yong-heePengembangKBS Drama ProductionDitulis olehYoon Kyung-ahSutradaraHong Seok-guPemeranBonaChae Seo-jinSeo Young-jooLee Jong-hyunYeo Hoe-hyunDoheeNegara asalKorea SelatanBahasa asliKoreaJmlh. episode8ProduksiProduser eksekutifAhn Suk-joonLee Sung-jinMin Hyun-ilMoon Joon-ha[2]ProduserNoh Sang-hoon&...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (janvier 2022). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références » En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? Co...

1976 1985 Élections générales québécoises de 1981 122 sièges de l'Assemblée nationale (Majorité absolue : 62 sièges) 13 avril 1981 Type d’élection Élection législative Corps électoral et résultats Inscrits 4 409 276 Votants 3 638 575 82,52 % 2,8 Votes exprimés 3 600 097 Votes nuls 38 523 PQ – René Lévesque Voix 1 773 237 49,26 % 7,9 Sièges obtenus 80 9 PLQ ...

Indian scientist A. SeemaA. Seema receiving the Nari Shakti PuraskarBornKozhikodeNationalityIndianEducationM.Tech and PhDOccupationscientistEmployerCentre for Materials for Electronics Technology (C-MET)Known forcreating a portable device to indicate breast cancer A. Seema is an Indian scientist from Kerala who led a team that developed a bra that indicates whether the person wearing it has breast cancer. After it was sent for commercial development, she was awarded the Nari Shakti Puras...
Deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family Architeuthidae For other uses, see Giant squid (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Colossal squid. Giant squid Giant squid, Architeuthis sp., modified from an illustration by A. E. Verrill, 1880 Conservation status Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Cephalopoda Order: Oegopsida Superfamily: Architeuthoidea Family: ArchiteuthidaePfeffer, 1900 Genus: Ar...

Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Daerah Kabupaten TulungagungDewan Perwakilan RakyatKabupaten Tulungagung2019-2024JenisJenisUnikameral Jangka waktu5 tahunSejarahSesi baru dimulai24 Agustus 2019PimpinanKetuaMarsono, S.Sos. (PDI-P) sejak 1 Oktober 2019 Wakil Ketua IDrs. H. Ali Masrup (PKB) sejak 27 April 2023 Wakil Ketua IIDrs. H. Asmungi, M.Si. (Golkar) sejak 1 Oktober 2019 Wakil Ketua IIIAhmad Baharudin (Gerindra) sejak 1 Oktober 2019 KomposisiAnggota50Partai & kursi PDI...
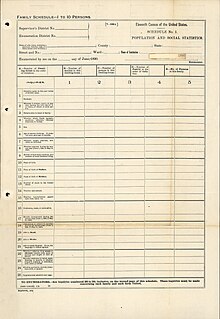
Sensus Amerika Serikat 1890Segel Biro Sensus Amerika SerikatHasil sensus tahun 1890Informasi umumNegaraAmerika SerikatTanggal diambil02 Juni 1890 (1890-06-02)Total populasi62.979.766Perubahan persen 25.5%state paling padatNew York6,003,174state paling kurang padatNevada47.335 Sensus Amerika Serikat 1890 dimulai pada 2 Juni 1890 namun kebanyakan material-material sensus tahun 1890 hancur pada 1921 saat bangunan penyimpanannya terbakar dan kemudian pembuangan catatan-catatan rusak yang mas...

François CaronPeta Jepang dalam Deskripsi sebenarnya Kerajaan Besar Jepang dan Siam François Caron. Direktur Jenderal French East India Company PertamaMasa jabatan1667–1673Gubernur Formosa ke-8Masa jabatan1644–1646PendahuluMaximiliaan le MairePenggantiPieter Anthoniszoon OvertwaterOpperhoofd di Japan ke-12Masa jabatan2 Februari 1639 – 13 Februari 1641PendahuluNicolaes CouckebackerPenggantiMaximiliaan le Maire Informasi pribadiLahir1600BrusselsMeninggal5 April 1673...

You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Portuguese. (May 2013) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the Portuguese article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wi...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant la guerre de Sécession. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. William Nelson Rector Beall William N. R. Beall Naissance 20 mars 1825Bardstown, État du Kentucky Décès 25 juillet 1883 (à 58 ans)McMinnville, État du Tennessee Allégeance États-Unis Arme Confederate States Army Grade Capitaine Brigadier général Années de service 1848-1861 (USA)18...
هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (يونيو 2016) علي بن أحمد النسوي معلومات شخصية اسم الولادة أبو الحسن علي بن أحمد النسوي ال...

Ligne deSaint-Omer-en-Chaussée à Vers Carte de la ligne La halte de Blicourt. Pays France Villes desservies Saint-Omer-en-Chaussée, Crèvecœur-le-Grand, Conty, Vers-sur-Selle Historique Mise en service 1874 – 1876 Fermeture 1939 – 1979 Concessionnaires Nord (1872 – 1937)SNCF (1938 – 1997)RFF (1997 – 2001)Ligne déclassée (à partir de 2001) Caractéristiques techniques Numéro officiel 320 000 Longueur 42,4 km Écartement ...
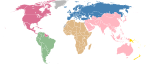
Organizer of the Island Games International Island Games AssociationFormation1985 (1985)HeadquartersDouglas, Isle of ManMembership 24 islandsWebsitehttps://www.iiga.org/ The International Island Games Association (IIGA) is the organising body for the Island Games, a friendly biennial multi-sport competition between teams from several European islands and other small territories (24 members from 8 nations). The IIGA liaises with the member island associations and with sponsors of the game...

This article is about wrestling promotion based in New Jersey, USA. For the Russian wrestling promotion, see Independent Wrestling Federation (Russia). 1998 American TV series or program Independent Wrestling FederationCreated byKevin KnightOpening themeLive To Win by Paul StanleyCountry of originUnited StatesNo. of episodes399ProductionCamera setupMulticamera setupRunning timeApproximately 2 hours per eventOriginal releaseReleaseMarch 14, 1998 (1998-03-14) –2017 (2017) The I...

この項目では、日本のお笑いトリオについて説明しています。東京23区およびその周辺の一部地域における市外局番については「日本の市外局番」をご覧ください。 東京03 2023年、芸術選奨贈呈式にて(左から、飯塚、角田、豊本)メンバー 飯塚悟志 角田晃広 豊本明長 別名 03(ぜろさん)結成年 2003年事務所 プロダクション人力舎活動時期 2003年9月30日 -出身 スクール...

Field of mathematics and science based on non-linear systems and initial conditions For other uses, see Chaos theory (disambiguation). A plot of the Lorenz attractor for values r = 28, σ = 10, b = 8/3 An animation of a double-rod pendulum at an intermediate energy showing chaotic behavior. Starting the pendulum from a slightly different initial condition would result in a vastly different trajectory. The double-rod pendulum is one of the simplest dynamical systems with chaotic ...

American filmmaker (born 1957) Chris WedgeWedge in 2014BornJohn Christian Wedge (1957-03-20) March 20, 1957 (age 67)Binghamton, New York, U.S.Alma materState University of New York at PurchaseOhio State UniversityOccupations Filmmaker animator designer voice actor cartoonist Years active1982–presentEmployers Blue Sky Studios (1987–2021) Annapurna Animation (2023–present) SpouseJeanne Markel[1]Children2AwardsAcademy Award for Best Animated Short FilmBunny (1998)Sig...
