British Rail D0260
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Aleksander WaszkiewiczNama asliАлександр ВашкевичLahir(1901-08-24)24 Agustus 1901Białowieża, Kekaisaran RusiaMeninggal4 Mei 1945(1945-05-04) (umur 43) †Hohendubrau, Jerman Nazi †DikebumikanPemakaman Militer PowązkiWarsawa, PolandiaPengabdianUni SovietDinas/cabangTentara Merah (1919-1944)Tentara Rakyat Polandia (1944-1945)Lama dinas1919-1945Pangkat Mayor Jenderal (anumerta) Brigadir JenderalKomandanResimen Senapan ke-793PenghargaanPahlawan Uni Soviet...

Gambar tiga dimensi struktur bovine rodopsin. Ketujuh transmembran memiliki warna yang berbeda. Kromofor terlihat yang berwarna merah. Opsin adalah protein transmembran yang sensitif terhadap cahaya, yang terikat pada aldehida vitamin A. Secara umum ada dua jenis protein yang disebut opsin. Keduanya memiliki bentuk dan fungsi yang sama.[1][2] Opsin jenis pertama terdapat pada prokariota, sedangkan binatang biasanya memiliki opsin jenis kedua. Sampai sekarang belum ditemukan ad...

العلاقات الإسبانية السيراليونية إسبانيا سيراليون إسبانيا سيراليون تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الإسبانية السيراليونية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين إسبانيا وسيراليون.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدول�...
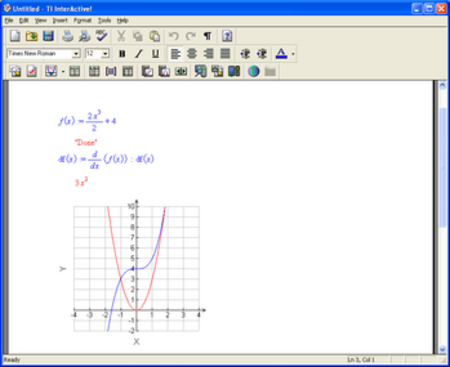
This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: TI InterActive! – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) TI InterActive!A screenshot of TI InterActive! in Windows XP.Developer(s)Texas InstrumentsStable release1.3.0.9 / July 6, 2004;...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

Australian basketball player (born 1988) Patty MillsAMMills with the Brooklyn Nets in 2022No. 88 – Miami HeatPositionPoint guardLeagueNBAPersonal informationBorn (1988-08-11) 11 August 1988 (age 35)Canberra, AustraliaListed height6 ft 2 in (1.88 m)Listed weight180 lb (82 kg)Career informationHigh school Marist College(Canberra) Lake Ginninderra(Canberra) CollegeSaint Mary's (2007–2009)NBA draft2009: 2nd round, 55th overall pickSelected by the Portland...

Extinct genus of reptiles LazarussuchusTemporal range: Late Paleocene - Early Miocene 61–20 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N (Possible Late Miocene record) Reconstruction of Lazarussuchus Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Order: †Choristodera Genus: †LazarussuchusHecht, 1992 Type species †Lazarussuchus inexpectatusHecht, 1992 Other species †L. dvoraki Evans and Klembara, 2005 Lazarussuchus (meaning Lazarus's crocodi...

Eppo Doeve, 1951 Joseph Ferdinand Doeve (2 Juli 1907 – 11 Juni 1981), lebih dikenal sebagai Eppo Doeve, adalah seorang pelukis dan kartunis terkenal berkebangsaan Belanda. Ia lahir di Bandung, Indonesia dan pindah ke Belanda pada 1927. Ia diberi gelar Ksatria dengan Order of Orange Nassau tahun 1973. Kartun-kartun karyanya banyak dipublikasikan di Elseviers Weekblad dan Elseviers Magazine. Pengawasan otoritas Umum Integrated Authority File (Jerman) ISNI 1 VIAF 1 WorldCat Perpu...

Vue aérienne de Tanjung Priok Tanjung Priok est un kecamatan (district) de la kota (municipalité) de Jakarta Nord, une des cinq qui constituent Jakarta, la capitale de l'Indonésie, où se trouve le principal port de la ville. La gare de Tanjung Priok en 1930-1940 Carte de Batavia en 1888 avec en haut à droite Tandschung Priok (Tanjung Priok) Tanjung Priok a été construit par les Hollandais à la fin du XIXe siècle. En effet, l'ancien port de Kalapa ne suffisait pour accueillir un...

ليغا باسكيت الدرجة الأولى موسم 2015–16 الدوري ليغا باسكيت الدرجة الأولى الفرق 16 عدد المباريات 240 الفترة 4 أكتوبر 2015 المنظم دوري كرة السلة الإيطالي [لغات أخرى] البلد إيطاليا البطل أولمبيا ميلانو المركز الثاني بالاكانسترو ريجيانا الجوائز أفضل لاعب بالموسم �...

1997 single by PortisheadAll MineSingle by Portisheadfrom the album Portishead B-sideCowboysReleased8 September 1997Recorded1996–1997Genre Trip hop jazz fusion Length4:00LabelGo! Discs/LondonSongwriter(s) Geoff Barrow Beth Gibbons Adrian Utley Producer(s)Portishead and Dave McDonaldPortishead singles chronology Glory Box (1995) All Mine (1997) Over (1997) All Mine is the second track and first single from English electronic music band Portishead's self-titled second album (1997). The song w...

South African paleontologist (1931–2023) Charles Kimberlin BrainBorn(1931-05-07)7 May 1931Salisbury, Southern RhodesiaDied7 June 2023(2023-06-07) (aged 92)Irene, Gauteng, South AfricaNationalitySouth AfricanOther namesC. K. BrainBob BrainEducationPretoria Boys High SchoolAlma materUniversity of the WitwatersrandChildren4Scientific careerFieldsPalaeontologyInstitutionsUniversity of the Witwatersrand Charles Kimberlin Brain (7 May 1931 – 6 June 2023), also known as C. K. Bob ...

British peer and Conservative politician His GraceThe Duke of Buccleuch and QueensberryKT GCVO TD PCBorn(1894-12-30)30 December 1894Died4 October 1973(1973-10-04) (aged 78)Spouse(s)Mary Lascelles(m. 1921)Children Elizabeth Percy, Duchess of Northumberland John Montagu Douglas Scott, 9th Duke of Buccleuch Caroline Gilmour, Baroness Gilmour of Craigmillar Parents John Montagu Douglas Scott, 7th Duke of Buccleuch Lady Margaret Bridgeman Walter John Montagu Douglas Scott, 8th Duk...

Australian rules footballer Australian rules footballer Nat Fyfe Fyfe playing for Fremantle in 2019Personal informationFull name Nathan FyfeDate of birth (1991-09-18) 18 September 1991 (age 32)Place of birth Lake Grace, Western AustraliaOriginal team(s) Claremont (WAFL)Draft No. 20, 2009 national draftDebut Round 5, 2010, Fremantle vs. Richmond, at Subiaco OvalHeight 192 cm (6 ft 4 in)Weight 96 kg (212 lb)Position(s) Midfielder / forwardClub information...

Military unit during the World Wars 9th Light Horse Regiment9th Light Horse hat badgeActive1914–19191921–1943CountryAustraliaBranchAustralian ArmyTypeMounted infantrySizeRegimentPart of3rd Light Horse BrigadeEngagementsFirst World War North African Campaign Gallipoli campaign Sinai and Palestine Campaign InsigniaUnit colour patchMilitary unit The 9th Light Horse Regiment was a mounted rifles regiment of the Australian Army during the First World War. The regiment was raised in Octobe...

صفيحة كوكوسصفيحة كوكوسالنوعصفيحة ثانويةالمساحة التقديرية2,900,000 كم2الحركة1شمال-شرقالسرعة167 ملم/عامالميزاتجزيرة كوكوس، المحيط الهادئ جزيرة كوكوس، المحيط الهادئ1بالنسبة إلى الصفيحة الإفريقية صفيحة كوكوس (بالإنجليزية: Cocos Plate)، المُسماة على جزر كوكوس في المحيط الهادئ، ه...

Republik KamerunRépublique du Cameroun (Prancis)Republic of Cameroon (Inggris) Bendera Lambang Semboyan: Paix, Travail, Patrie(Indonesia: Perdamaian, Kerja, Tanah Air)Lagu kebangsaan: Ô Cameroun, Berceau de nos Ancêtres(Indonesia: O Kamerun, Tempat Lahir Leluhur Kami) Ibu kotaYaounde3°52′N 11°31′E / 3.867°N 11.517°E / 3.867; 11.517Kota terbesarDouala4°3′N 9°42′E / 4.050°N 9.700°E / 4.050; 9.700Bahasa resmiPrancis dan...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Imam Reza Stadium – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Imam Reza Stadium[1]LocationMashhad, IranCoordinates36°19′32″N 59°34′12″E / 36.32556°N 59.57000°E&...

American music group This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: The Earls – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2019) (Learn how and ...

Pension, art galleryPension GloanecPension Gloanec in May 2016General informationTypePension, art galleryCoordinates47°51′19″N 3°44′52″W / 47.855194°N 3.747833°W / 47.855194; -3.747833Technical detailsFloor count2Known forPont-Aven SchoolWebsitewww.pensiongloanec.com The Pension Gloanec was a pension in Pont-Aven, Brittany, France, that was a base for artists of the Pont-Aven School in the last half of the 19th century. It was known for economical but excel...

