Auberge Ravoux
|
Read other articles:

Regno d'Ungheria (dettagli) (dettagli) Motto: Regnum Mariae Patrona Hungariae(Regno di Maria, Patrona d'Ungheria) Regno d'Ungheria - LocalizzazioneIl regno d'Ungheria nel 1942 Dati amministrativiNome completoRegno d'Ungheria Nome ufficialeMagyar Királyság Lingue ufficialiUngherese Lingue parlateUngherese, russino InnoHimnusz Capitale Budapest (957.800 ab. / 1925) PoliticaForma di StatoMonarchia Forma di governoMonarchia costituzionale autoritaria (1920-1944)Dittatura to...

Ne doit pas être confondu avec Bora-Bora. Cet article est une ébauche concernant l’Afghanistan. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Consultez la liste des tâches à accomplir en page de discussion. Tora Bora (2006). Tora Bora (pachto : توره بوره ; « poussière noire ») est une colline fortifiée située dans les montagnes de Safed Koh dans l'Est de l'Afghanistan. Sa...

Part of a series onBritish law Acts of Parliament of the United Kingdom Year 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 1808 1809 1810 1811 1812 1813 1814 1815 1816 1817 1818 1819 1820 1821 1822 1823 1824 1825 1826 1827 1828 1829 1830 1831 1832 1833 1834 1835 1836 1837 1838 1839 1840 1841 1842 1843 1844 1845 1846 1847 1848 1849 1850 1851 1852 1853 1854 1855 1856 1857 1858 1859 1860 1861 1862 1863 1864 1865 1866 1867 1868 1869 1870 1871 1872 1873 1874 1875 1876 1877 1878 ...
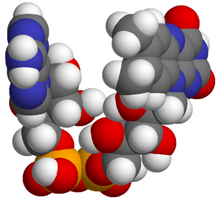
Flavin adenina dinukleotida Penanda Nomor CAS 146-14-5 N Model 3D (JSmol) Gambar interaktif 3DMet {{{3DMet}}} ChemSpider 559059 Nomor EC MeSH Flavin-Adenine+Dinucleotide PubChem CID 643975 Nomor RTECS {{{value}}} UNII ZC44YTI8KK N CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID4048307 InChI InChI=1/C27H33N9O15P2/c1-10-3-12-13(4-11(10)2)35(24-18(32-12)25(42)34-27(43)33-24)5-14(37)19(39)15(38)6-48-52(44,45)51-53(46,47)49-7-16-20(40)21(41)26(50-16)36-9-31-17-22(28)29-8-30-23(17)36/h3-4,8-9,14-16,19-21...

2022 song by Albina & Familja Kelmendi DujeSingle by Albina & Familja KelmendiLanguageAlbanianEnglish titleLove itReleased10 March 2023 (2023-03-10)GenrePopLength3:07LabelFoleComposer(s)Enis MullajLyricist(s)Eriona RushitiAlbina Kelmendi singles chronology Emri Im (2023) Duje (2023) Inat (2023) Alternative coverCover of the song's original version Music videoDuje on YouTubeEurovision Song Contest 2023 entryCountryAlbaniaArtist(s)Albina & Familja KelmendiLanguage...

Meresankh IIRatu MesirSarkofagus Meresankh IIPemakamanmastaba G 7410-7420, GizaAyahFiraun KhufuIbuRatu Meritites ISpouse(s)Pangeran HorbaefFiraun Djedefre atau KhafraAnakPutri Nefertkau IIIPutri Nebty-tepitesPangeran DjatyAgamaAgama Mesir Kuno Meresankh II (Dia Mencintai Kehidupan) adalah seorang Ratu Mesir yang hidup pada zaman Dinasti ke-IV. Keluarga Orang tua Meresankh II diduga adalah Raja Khufu dan Ratu Meritites I karena mereka disebutkan dalam mastaba Meresankh tetapi dia tidak pernah ...
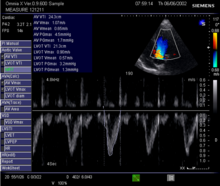
Measurement of blood pumped by the heart Major factors influencing cardiac output – heart rate and stroke volume, both of which are variable.[1] In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q {\displaystyle Q} , Q ˙ {\displaystyle {\dot {Q}}} , or Q ˙ c {\displaystyle {\dot {Q}}_{c}} ,[2] is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: that is, the volume of blood being pumped by a single ven...

Kraków-Kolna Canoe Slalom CourseTor kajakarstwa górskiego w KrakowieAboutLocaleKolna, Kraków, PolandManaging agentKrakowski Klub KajakowyMain shapeLinearAdjustableyesWater sourceVistula RiverPumpedNoFlow diversionYesPractice poolYesGrandstandsTwo sets of bleachersCanoe liftNoFacilitiesYesConstruction2003, 2013StatsLengthTotal: 320 metres (1,050 ft) Competition: 250 metres (820 ft)Width12 metres (39 ft)Drop5 metres (16 ft)Slope2.0% (105 ft/mi)Flowrate15 m3/s (530&#...

坐标:43°11′38″N 71°34′21″W / 43.1938516°N 71.5723953°W / 43.1938516; -71.5723953 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2017年5月21日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:新罕布什尔州 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源...

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі ор...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会马来西亚代表團马来西亚国旗IOC編碼MASNOC马来西亚奥林匹克理事会網站olympic.org.my(英文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員30參賽項目10个大项旗手开幕式:李梓嘉和吳柳螢(羽毛球)[1][2]閉幕式:潘德莉拉(跳水)[3]獎牌榜排名第74 金牌 銀牌 銅�...

List of events ← 1999 1998 1997 2000 in Turkey → 2001 2002 2003 Centuries: 20th 21st Decades: 1980s 1990s 2000s 2010s 2020s See also:List of years in Turkey Events in the year 2000 in Turkey. Incumbents President: Süleyman Demirel (until 16 May), Ahmet Necdet Sezer (starting 16 May) Prime Minister: Bülent Ecevit Establishments 1 February - The Abdi İpekçi Peace Monument is inaugurated. Deaths 15 April – Hayati Hamzaoğlu 25 October – Nejat Saydam References vte Years in Tu...

Cybersecurity website owned by Chronicle This article may rely excessively on sources too closely associated with the subject, potentially preventing the article from being verifiable and neutral. Please help improve it by replacing them with more appropriate citations to reliable, independent, third-party sources. (April 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) VirusTotalType of siteInternet security, file and URL analyzerAvailable inArabic, Bulgarian, Chinese, Chinese (Hong Ko...

Lighthouse in New South Wales, Australia LighthousePoint Stephens Light LocationPoint Stephens, New South Wales, Australia Coordinates32°44′49″S 152°12′04″E / 32.746931°S 152.201156°E / -32.746931; 152.201156TowerConstructed1862 Constructionsandstone (tower) Automated1973 Height21 m (69 ft) ShapeCylindrical tower with balcony and lanternMarkingswhite (tower), white (lantern) Power sourcesolar power OperatorAustral...

Eden Golan Eden Golan (lahir 5 Oktober 2003) adalah seorang penyanyi Rusia-Israel. Ia memulai karirnya pada usia sembilan tahun, mendapatkan pengakuan melalui partisipasi dalam kompetisi dan memenangkan berbagai penghargaan. Ia menjadi penyanyi utama dari grup vokal perempuan bernama Cosmos Girls, dan memiliki sederet lagu hits – termasuk Dopamine, Ghost Town, dan Let Me Blow Ya Mind – setelah bergabung dengan label rekaman Israel Session 42 pada usia 18 tahun. Pada awal 2024, ia memenang...

1812 act passed by the 12th United States Congress U.S. Declaration of War An Act Declaring War between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and the Dependencies Thereof and the United States of America and Their Territories was passed by the 12th United States Congress on June 18, 1812, thereby beginning the War of 1812. It was signed by James Madison, the 4th President of the United States. Historical background Foreign tensions The United States (US) and Great Britain have a his...

五虎將之決裂The Tigers基本资料导演曾志伟监制张国忠制片廖鳳平、葉劍峰動作指導董瑋、梁小熊、元德、咖喱编剧南燕阮世生主演劉德華梁朝伟黄日华苗侨伟汤镇业配乐劉以達、雷有暉主題曲〈與孤獨在奔往〉/劉德華摄影马楚成剪辑金馬制片商艺能影业有限公司片长110 分鐘产地 香港语言粵語上映及发行上映日期 英屬香港: 1991年7月3日 (1991-07-03) 臺灣:1991年7月25�...

British literary magazine and publisher For other uses, see Granta (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Granta – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) GrantaGranta 142EditorThomas MeaneyCategoriesLiterary magazineFrequ...

Queen consort of Poland (1588–1631) Not to be confused with Constance of Babenberg. Constance of AustriaPortrait c. 1603 by Frans Pourbus the YoungerQueen consort of PolandGrand Duchess consort of LithuaniaTenure1605–1631Coronation11 December 1605Born24 December 1588Graz, Duchy of Styria, Holy Roman EmpireDied10 July 1631(1631-07-10) (aged 42)Warsaw, Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Polish-Lithuanian CommonwealthBurialWawel Castle, Kraków, PolandSpouseSigismund III VasaIssueamong oth...

2002 single by Anastacia Why'd You Lie to MeSingle by Anastaciafrom the album Freak of Nature ReleasedSeptember 9, 2002 (2002-09-09)Studio The Dream Factory (New York City) Cove City Sound (Glen Cove, New York) Encore (Burbank, California) Genre Dance-pop R&B Length3:43Label Epic Daylight Songwriter(s) Anastacia Damon Sharpe Greg Lawson Trey Parker Damon Butler Canela Cox Producer(s)Ric WakeAnastacia singles chronology Boom (2002) Why'd You Lie to Me (2002) You'll Never Be ...





