Adrian helmet
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Belgia padaOlimpiadeKode IOCBELKONKomite Olimpiade dan Interfederal BelgiaSitus webwww.olympic.be (dalam bahasa Belanda)Medali 42 55 59 Total 156 Penampilan Musim Panas1900190419081912192019241928193219361948195219561960196419681972197619801984198819921996200020042008201220162020Penampilan Musim Dingin192419281932193619481952195619601964196819721976198019841988199219941998200220062010201420182022Penampilan terkait lainnyaPermainan Interkala 1906 Belgia berkompetisi dalam sebagi...

Beware of BlondieIklan surat kabarSutradaraEdward BerndsProduserMilton FeldmanSkenarioJack HenleyCeritaJack HenleyBerdasarkanBeware of Blondie karya Chic YoungPemeranPenny SingletonArthur LakeLarry SimmsMarjorie Ann MutchiePenata musikMischa BakaleinikoffJohn LeipoldSinematograferVincent J. FarrarHenry FreulichPenyuntingRichard FantlPerusahaanproduksiKing Features SyndicateDistributorColumbia PicturesTanggal rilis13 April 1950Durasi64 menitNegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaInggris Beware of Bl...

Pour la commune, voir Suze-la-Rousse. Cet article est une ébauche concernant la vigne et le vin. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Suze-la-rousse cave coopérative de Suze la Rousse Désignation(s) Suze-la-rousse Appellation(s) principale(s) côtes-du-rhône villages Type d'appellation(s) AOC Reconnue depuis 2017 Pays France Région parente vignoble de la vallée du Rhône Sous-région(s) vallée ...
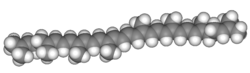
Likopen Nama Nama IUPAC (6E,8E,10E,12E,14E,16E,18E,20E,22E,24E,26E)- 2,6,10,14,19,23,27,31-Octamethyldotriaconta-2,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24,26,30-tridecaene Nama lain ψ,ψ-Carotene Penanda Nomor CAS 502-65-8 Y Model 3D (JSmol) Gambar interaktif 3DMet {{{3DMet}}} ChEBI CHEBI:15948 Y ChEMBL ChEMBL501174 Y ChemSpider 394156 Y Nomor EC PubChem CID 446925 Nomor RTECS {{{value}}} UNII SB0N2N0WV6 Y CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID2046593 InChI InChI=1S/C40H56/c1-33(2)19-1...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Tutankhamun – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTORArtikel atau bagian artikel ini diterjemahkan secara buruk. Kualitas terjemahannya masih kurang bagus. Bagian-bagian yang mungkin diterjemah...

For other places with the same name, see Dąb. Village in Lubusz Voivodeship, PolandDąbVillageDąbCoordinates: 51°54′13″N 16°0′52″E / 51.90361°N 16.01444°E / 51.90361; 16.01444Country PolandVoivodeshipLubuszCountyWschowaGminaSława Dąb [dɔmp] is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Sława, within Wschowa County, Lubusz Voivodeship, in western Poland.[1] It lies approximately 6 kilometres (4 mi) north-west of Sława, 23 ...

Savoyard nobleman and antipope (1383–1451) Antipope Felix VPortrait of antipope Felix V in the Nuremberg Chronicle (1493)Count of SavoyReign1391–1416PredecessorAmadeus VIIRegentBonne of Bourbon (1391–1397)Duke of SavoyReign1416–1440SuccessorLouis IRegentLouis I (c. 1434 – 5 February 1440)Spouse Mary of Burgundy (m. 1386–1428)Issue(among others) Marie Louis I Margaret HouseSavoyFatherAmadeus VII, Count of SavoyMother...
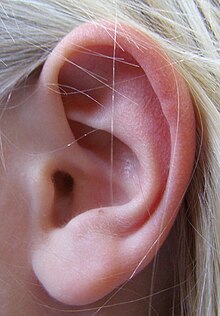
У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Ухо (значения). Анатомия уха. Наружное ухо: 1 — височная кость 2 — слуховой канал 3 — ушная раковина среднее ухо: 4 — барабанная перепонка 6 — молоточек 7 — наковальня 8 — стремечко внутре...

Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens MCOLN3IdentifiersAliasesMCOLN3, TRP-ML3, TRPML3, mucolipin 3, mucolipin TRP cation channel 3External IDsOMIM: 607400 MGI: 1890500 HomoloGene: 10118 GeneCards: MCOLN3 Gene location (Human)Chr.Chromosome 1 (human)[1]Band1p22.3Start85,018,082 bp[1]End85,048,500 bp[1]Gene location (Mouse)Chr.Chromosome 3 (mouse)[2]Band3 H2|3 71.03 cMStart145,823,205 bp[2]End145,847,561 bp[2]RNA expression patternB...

Эту страницу предлагается объединить со страницей Верхний, нижний, свитч (БДСМ).Пояснение причин и обсуждение — на странице Википедия:К объединению/28 апреля 2023.Обсуждение длится не менее недели (подробнее). Не удаляйте шаблон до подведения итога обсуждения. Эта статья ...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Тур. Запрос «Bos taurus primigenius» перенаправляется сюда; см. также другие значения. † Тур Скелет тура Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:В...

Type of area in the nervous system This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Neuropil – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) NeuropilDetailsSystemNervous systemIdentifiersLatinneuropilusMeSHD019581THH2.00.06.2.02005 Anatomical terms of mic...
本表是動態列表,或許永遠不會完結。歡迎您參考可靠來源來查漏補缺。 潛伏於中華民國國軍中的中共間諜列表收錄根據公開資料來源,曾潛伏於中華民國國軍、被中國共產黨聲稱或承認,或者遭中華民國政府調查審判,為中華人民共和國和中國人民解放軍進行間諜行為的人物。以下列表以現今可查知時間為準,正確的間諜活動或洩漏機密時間可能早於或晚於以下所歸�...

Electronic dance music compilation album Fuck Me I'm Famous is a series of electronic dance music compilation albums by the French DJ David Guetta.[1] His now ex-wife Cathy Guetta collaborated in the production. The first album in the series was released in 2003. The albums have traditionally been released during the summer months of their respective years. Fuck Me I'm Famous (2003) Fuck Me I'm FamousCompilation album by David GuettaReleasedJuly 1, 2003Recorded2001–2003GenreHous...

Non-printing character used in computerized typesetting Not to be confused with Zero-width non-joiner or Word joiner. This article contains Indic text. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks or boxes, misplaced vowels or missing conjuncts instead of Indic text. ISO keyboard symbol for ZWJ The zero-width joiner (ZWJ, /ˈzwɪdʒ/)[1] (‍) is a non-printing character used in the computerized typesetting of writing systems in which the shape or positioni...

MarkiplierMarkiplier di acara PAX West 2018Informasi pribadiLahirMark Edward Fischbach28 Juni 1989 (umur 34)Honolulu, Hawaii, Amerika SerikatNegaraAmerika SerikatSitus webmarkiplier.comInformasi YouTubeKanal Markiplier PembuatMark Edward FischbachTahun aktif2012–sekarangGenreLet's Play • Komedi • Horror • VlogPelanggan34.6 juta[1]Total tayang19.7 miliar[1]Artis terkaitPewDiePieJacksepticeyePokimaneJack Douglass Penghargaan Kreator 100.000 pelanggan 2013 ...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Church of Saint Jerome the Royal – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) San Jerónimo el RealView from the north angleReligionAffiliationRoman CatholicDistrictRetiroRegionCommunity of MadridEcclesi...

MakatiKota terurbanisasi tinggiLungsod ng Makati Dari atas searah jarum jam: Panorama Makati dari atas, Legazpi Village, Segitiga Ayala, Makati saat malam hari, Gereja Don Bosco Makati, Makati Avenue Lambang resmi MakatiLambangJulukan: Ibu Kota Finansial FilipinaWall Street dari FilipinaMotto: Makati, Mahalín Natin, Atin Itó.(Makati, biarkan kami mencintainya, itu milik mami.)Lokasi di Metro ManilaMakatiLokasi di FilipinaKoordinat: 14°33′24″N 121°01′17″E / ...

此條目或其章節极大或完全地依赖于某个单一的来源。 (2019年5月12日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:搜索引擎 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引) 本條目屬於網路搜索引擎系列 網路搜索引擎 元搜索引擎 國際性搜索引擎(多语言) Google Yahoo! Search Bi...

この記事には参考文献や外部リンクの一覧が含まれていますが、脚注による参照が不十分であるため、情報源が依然不明確です。 適切な位置に脚注を追加して、記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(2020年10月) 三浦 逸平 生年月日 (1870-02-18) 1870年2月18日出生地 愛知県碧海郡刈谷町大字熊字元屋敷(現在の刈谷市)没年月日 (1936-11-12) 1936年11月12日(66歳没) 衆議院議�...












