396th Rifle Division
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Dua Sisi. Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Dua Sisi album RED – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Dua SisiAlbum studio karya REDDirilis1 Januari 2001GenreHip HopLabelMusica Studio'sKro...

This article contains translated text and the factual accuracy of the translation should be checked by someone fluent in Afrikaans and English. Cinema ofSouth Africa List of South African films South African Animation pre 1910 1910s 1920s 1930s 1940s 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s 2010s 2020s By language Afrikaans vte This is a list of Afrikaans-language films. For a more comprehensive list see Category:Afrikaans-language films 1898 Pres. Paul Kruger filmed in front of his house in Pret...

2003 Japanese filmBright FutureDirected byKiyoshi KurosawaWritten byKiyoshi KurosawaProduced byTakashi AsaiStarringJoe OdagiriTadanobu AsanoTatsuya FujiCinematographyTakahide ShibanushiEdited byKiyoshi KurosawaMusic byPacific 231 (Shigeomi Hasumi, Takemasa Miyake)Distributed byUplink Company (Japan)Palm Pictures (U.S.)Release dateJanuary 18, 2003 (Japan)Running time115 minutes (Original Version)92 minutes (International Version)CountryJapanLanguageJapaneseBox office$5,166 (US)[1] Brig...

Mion Mukaichi向井地 美音Informasi latar belakangLahir29 Januari 1998 (umur 26)AsalPrefektur Saitama, JepangGenreJ-popPekerjaanIdola, penyanyi, aktrisInstrumenVokalTahun aktif2002 (2002) – sekarangLabelAKSArtis terkaitAKB48 Mion Mukaichi (向井地 美音code: ja is deprecated , Mukaichi Mion, lahir 29 Januari 1998) adalah anggota dari grup vokal wanita idola Jepang AKB48. Ia adalah anggota dari Tim A di AKB48. Biografi Mukaichi bermain tenis dari kelas 1 di sekolah dasar samp...
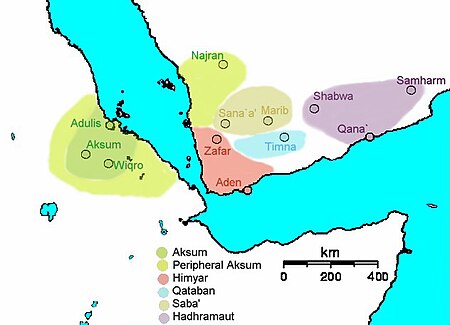
Bahasa SabaDituturkan diYaman, Oman, Arab SaudiWilayahJazirah ArabKepunahanAbad ke-6 Rumpun bahasaAfroasiatik SemitikSemitik SelatanSemitik Selatan BaratArabia Selatan KunoSaba Kode bahasaISO 639-3xsaLINGUIST ListxsaGlottologsaba1279[1]QIDQ1070391 Status konservasi Punah EXSingkatan dari Extinct (Punah)Terancam CRSingkatan dari Critically endangered (Terancam Kritis) SESingkatan dari Severely endangered (Terancam berat) DESingkatan dari Devinitely endangered (Terancam) VUSingkata...

Meriam Oerlikon 20 mm adalah serangkaian meriam otomatis, didasarkan pada desain Becker 20 mm dari Jerman yang muncul pada sangat awal dalam Perang Dunia I. Meriam ini banyak diproduksi oleh Oerlikon Contraves dan lain-lain, dengan berbagai model yang digunakan oleh Sekutu dan pasukan Axis selama Dunia perang II, dan banyak versi masih digunakan sampai sekarang. Referensi Campbell, John. Naval Weapons of World War Two. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press, 1985. Johnson, Melvin M., Jr. Rifl...

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддій�...

الشهيد ديدوش مراد معلومات شخصية الميلاد 13 يوليو 1927(1927-07-13)المرادية، الجزائر الوفاة 18 يناير 1955 (27 سنة)زيغود يوسف الجنسية جزائري والدان ديدوش سعيد الحياة العملية المهنة عسكري الحزب حزب الشعب الجزائري اللغات العربية الخدمة العسكرية الرتبة عقيد المعار�...

Branch of veterinary medicine Dog undergoing dental treatment Dog with periodontal disease A canine with gingivitis English bulldog with underbite Veterinary dentistry involves the application of dental care to animals, encompassing not only the prevention of diseases and maladies of the mouth, but also considers treatment. In the United States, veterinary dentistry is one of 20 veterinary specialties recognized by the American Veterinary Medical Association.[1] Among other servi...

American judge (born 1955) Mark RecktenwaldChief Justice of the Hawaii Supreme CourtIncumbentAssumed office September 14, 2010Nominated byLinda LinglePreceded byRonald MoonJustice of the Hawaii Supreme CourtIn officeMay 5, 2009 – September 14, 2010Nominated byLinda LinglePreceded bySteven LevinsonSucceeded bySabrina McKenna Personal detailsBorn (1955-10-08) October 8, 1955 (age 68)Detroit, Michigan, U.S.Children2EducationHarvard University (BA)University of Chicago (JD) Ma...

Pour la commune, voir Billund (commune). Cet article est une ébauche concernant une localité danoise. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. BillundNom officiel (da) BillundNom local (da) BillundGéographiePays DanemarkRégion Danemark du SudCommune BillundAltitude 58 mCoordonnées 55° 43′ 51″ N, 9° 06′ 55″ EDémographiePopulation 6 194 hab....

British leisure travel group TUI Travel plcCompany typePublicTraded asLSE: TT.IndustryTransportFounded2007Defunct2014 (Merged with TUI AG)HeadquartersCrawley, England, UKKey peopleFriedrich Joussen(Chairman)Sir Michael Hodgkinson(Deputy Chairman)Peter Long(Chief Executive)ProductsPassenger transport, travel agency, accommodationRevenue£15,051 million (2013)[1]Operating income£297 million (2013)[1]Net income£63 million (2013)[1]OwnerTUI AG (56.4%)[2]Numb...

Головне управління оперативного забезпечення — формування Збройних сили України, яке існувало до 2020 року і забезпечувало оперативне забезпечення частин і підрозділів ЗСУ. У 2020 році було перетворене на Командування Сил підтримки Збройних сил України.[1][2] Змі...

«UTE» redirige aquí. Para otras acepciones, véase UTE (desambiguación). Administración Nacional de Usinas y Trasmisiones Eléctricas del Estado La energía que nos une Palacio de la LuzAcrónimo U T ETipo PúblicaIndustria Energética, eólicaForma legal Ente AutónomoFundación 21 de octubre de 1912 (111 años)Fundador Gobierno de José Batlle y OrdóñezNombres anteriores Administración General de Usinas y Teléfonos del EstadoSede central Palacio de la LuzÁrea de operación Re...

Vocales Anterior Semiant. Central Semipost. Posterior Cerrada i • y ɨ • ʉ ɯ • u e̞ • ø̞ ɪ • ʏ ɯ̽ • ʊ e • ø ɘ • ɵ ɤ • o ɪ̈ • ʊ̈ ə ɤ̞ • o̞ ɛ • œ ɜ • ɞ ʌ • ɔ æ ɐ • ɞ̞ ɑ̝ • ɒ̝ a • ɶ ä • ɒ̈ ɑ • ɒ Casi cerr. Semicerr. Media Semiab....
Questa voce sull'argomento tuffatori statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Georgia ColemanGeorgia Coleman nel 1938Nazionalità Stati Uniti Tuffi Hall of fameInt. Swimming Hall of Fame (1966) Palmarès Competizione Ori Argenti Bronzi Olimpiadi 1 2 1 Vedi maggiori dettagli Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Georgia Coleman (St. Maries, 23 gennaio 1912 – Los Angeles, 14 settembre 1940) è stata una tuffatri...

2018年冬季奥林匹克运动会葡萄牙代表團葡萄牙国旗IOC編碼PORNOC葡萄牙奧林匹克委員會網站comiteolimpicoportugal.pt(葡萄牙文)2018年冬季奥林匹克运动会(平昌)2018年2月9日至2月25日運動員2參賽項目2个大项旗手开幕式:Kequyen Lam(越野滑雪)[1]闭幕式:Arthur Hanse(高山滑雪)[2]历届奥林匹克运动会参赛记录(总结)夏季奥林匹克运动会19121920192419281932193619481952195619601...
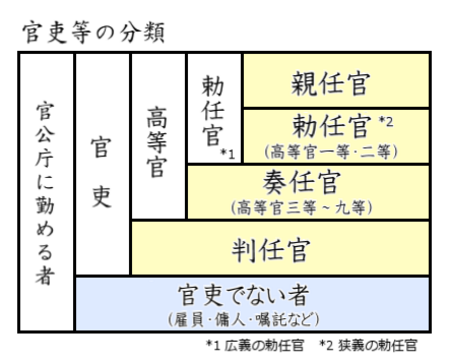
親任官の位置づけ 親任官(しんにんかん)は、1886年(明治19年)に設けられた官吏の分類の一つで[1]、1890年(明治23年)から明治憲法の下で用いられ1948年(昭和23年)に廃止した[2]。官僚制度における最高の位置付けにあり高等官の中の勅任官に含まれた。天皇の親任式を経て任命され、官記には天皇が親署する。親任官と勅任官に対しては、敬称に閣下を...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant une localité italienne et le Latium. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Greccio Sanctuaire et couvent de la crèche, à Greccio. Administration Pays Italie Région Latium Province Rieti Code postal 02040 Code ISTAT 057031 Code cadastral E160 Préfixe tel. 0746 Démographie Gentilé grecciani Population 1 549 hab. (31-08-2017[1]) Densité...

Lycoming T55 adalah mesin turboshaft dirancang dan diproduksi oleh perusahaan Lycoming Turbine Engine Division di Stratford, Connecticut, dan digunakan terutama oleh helikopter berat Boeing CH-47 Chinook dari tahun 1950-an, tetapi juga digunakan oleh beberapa pesawat yang menjadi diproduksi massal. Versi skala yang lebih kecil Lycoming T53 . Kedua mesin tersebut sekarang diproduksi oleh Honeywell Aerospace . T55 juga berfungsi sebagai inti dari Lycoming ALF 502 . Aplikasi CH-47 Chinook Bell ...