2017 Portuguese local elections
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

artikel ini perlu dirapikan agar memenuhi standar Wikipedia. Tidak ada alasan yang diberikan. Silakan kembangkan artikel ini semampu Anda. Merapikan artikel dapat dilakukan dengan wikifikasi atau membagi artikel ke paragraf-paragraf. Jika sudah dirapikan, silakan hapus templat ini. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Patung Marsupilami Marsupilami adalah karakter fiksi buku komik yang diciptakan oleh André Franquin. Karakter ini pertama kali diterbitkan pada 3...

Main article: 1808 United States presidential election 1808 United States presidential election in New York ← 1804 November 4 - December 7, 1808 1812 → Nominee James Madison George Clinton Party Democratic-Republican Democratic-Republican Home state Virginia New York Running mate George Clinton James Madison/ James Monroe Electoral vote 13 6 Percentage 68.38% 31.62% President before election Thomas Jefferson Democratic-Republican Elected President ...

Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari Vision (spirituality) di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pula: panduan pe...

German psychiatrist (1856–1926) Emil KraepelinEmil Kraepelin in his later yearsBorn(1856-02-15)15 February 1856Neustrelitz, Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, German ConfederationDied7 October 1926(1926-10-07) (aged 70)Munich, Bavaria, Weimar GermanyNationalityGermanAlma materLeipzig UniversityUniversity of Würzburg(MBBS, 1878)Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich(Dr. hab. med., 1882)Known forClassification of mental disorders, Kraepelinian dichotomySpouseIna Marie Marie ...
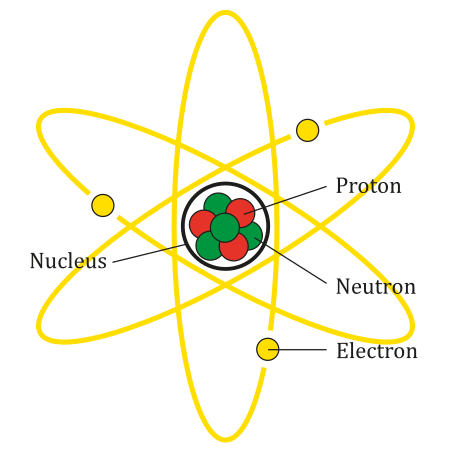
Assemblage combustible. Modèle de l'atome. Le combustible nucléaire est le produit qui, contenant des isotopes fissiles (uranium, plutonium…), fournit l'énergie dans le cœur d'un réacteur nucléaire en entretenant la réaction en chaîne de fission nucléaire. Les termes « combustible » et « combustion » sont utilisés par analogie à la chaleur dégagée par une matière en feu, mais sont inappropriés pour caractériser tant le produit que son action. En effet...

Area of the brain below the thalamus HypothalamusLocation of the human hypothalamusLocation of the hypothalamus (cyan) in relation to the pituitary and to the rest of the brainDetailsPart ofBrainIdentifiersLatinhypothalamusMeSHD007031NeuroLex IDbirnlex_734TA98A14.1.08.401 A14.1.08.901TA25714FMA62008Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy[edit on Wikidata] Not to be confused with Subthalamus. The hypothalamus (pl.: hypothalami; from Ancient Greek ὑπό (hupó) 'under', and ...

Method of bypassing authentication or encryption in a computer A backdoor is a typically covert method of bypassing normal authentication or encryption in a computer, product, embedded device (e.g. a home router), or its embodiment (e.g. part of a cryptosystem, algorithm, chipset, or even a homunculus computer—a tiny computer-within-a-computer such as that found in Intel's AMT technology).[1][2] Backdoors are most often used for securing remote access to a computer, or obtai...

Voce principale: Varese Calcio. Varese CalcioStagione 1976-1977 Sport calcio Squadra Varese Allenatore Pietro Maroso Presidente Guido Borghi Serie B8º Coppa ItaliaPrimo turno Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Mascella (38) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: De Lorentis, Ramella (7) 1975-1976 1977-1978 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti il Varese Calcio nelle competizioni ufficiali della stagione 1976-1977. Indice 1 Rosa 2 Risultati 2.1 Serie B...

Audio recordings spanning two media Double disc redirects here. For other uses, see Double disk (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Double album – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) A double album on c...
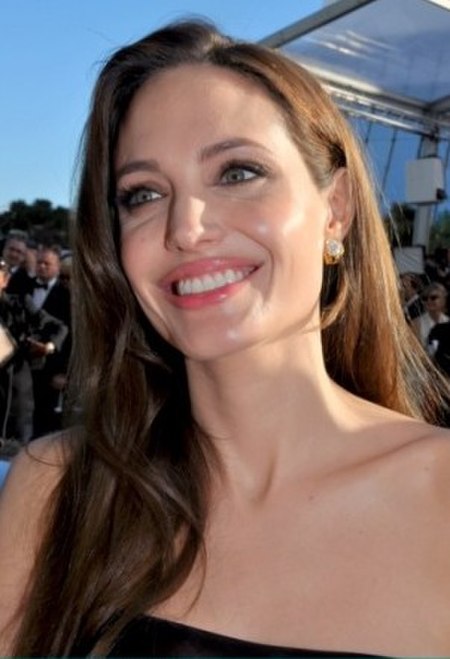

Angelina Jolie nel 2022 Oscar alla miglior attrice non protagonista 2000 Oscar Premio umanitario Jean Hersholt 2014 Angelina Jolie, nata Angelina Jolie Voight (Los Angeles, 4 giugno 1975), è un'attrice, regista, sceneggiatrice e produttrice cinematografica statunitense. Ha raggiunto notorietà internazionale interpretando l'eroina dei videogiochi Lara Croft nei film Lara Croft: Tomb Raider (2001) e Lara Croft: Tomb Raider - La culla della vita (2003). Ha vinto tre Golden Globe consecutivi: n...

A type of sealed coin holder Graded Morgan dollars within a variety of coin slabs Coin slab is a type of holder for a coin. Slabbed coins are typically from one of the coin grading companies. The practice of sending coins to third-party grading companies and then slabbing them began in 1986. When a grading company grades the coin it is sealed in a tamper proof slab with a barcode and a hologram. To prevent counterfeiting, holograms were attached to the graded coin slabs beginning in 1989. The...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Social class in France – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this messa...

Subprefecture and commune in Hauts-de-France, France For the rump state of the Roman Empire, see Kingdom of Soissons. You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in French. (December 2008) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the French article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and c...

Song by George M Cohan This article is about the song. For other uses, see Over There (disambiguation). Over There1917 sheet music cover with Nora BayesSong by Nora BayesPublished1917GenreWar-time song , March , Tin Pan AlleySongwriter(s)George M. Cohan Over There Over There sung in 1917 by Billy Murray Problems playing this file? See media help. Over There is a 1917 song written by George M. Cohan that was popular with the United States military and public during both world wars. It is a pat...

Canadian ice hockey player For the guitarist, see Alex Hutchings (guitarist). Ice hockey player Alex Hutchings Hutchings with IF Björklöven in 2015Born (1990-11-07) November 7, 1990 (age 33)Burlington, Ontario, CanadaHeight 5 ft 11 in (180 cm)Weight 179 lb (81 kg; 12 st 11 lb)Position ForwardShoots RightAllsv teamFormer teams IF BjörklövenNorfolk AdmiralsSyracuse CrunchRochester AmericansETC CrimmitschauIK OskarshamnNHL draft 93rd overall, 2009Tampa...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع نفاذية (توضيح). النفاذية البصرية القريبة من الأشعة تحت الحمراء عبر الياقوت. لاحظ أشرطة الامتصاص العريضة الخضراء والزرقاء مع شريط امتصاص ضيق عند طول موجة 684 نانومتر وهي طول موجة الليزر الياقوتي. النفاذية في علم البصريات (بالإنجليزية: transmittance) والمطيا�...

此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2023年8月1日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:2021年夏季世界大學運動會開幕式 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 2021年夏季世界大學運動會開幕式开幕典礼2023年7月28日開...

Badminton's women's singles SH6 at the 2023 European Para ChampionshipsVenueRotterdam Ahoy, Rotterdam[1]Dates15 – 20 AugustCompetitors7 from 4 nationsMedalists Oliwia Szmigiel Poland Rachel Choong Great Britain Nina Kozlova Ukraine Daria Bujnicka Poland2027 → Main article: Badminton at the 2023 European Para Championships Badminton at the2023 European Para ChampionshipsSinglesMenWome...

Pemilihan umum federal Jerman Mei 19241920192404 Mei 1924 (1924-05-04)Seluruh 472 kursi dalam Reichstag237 kursi untuk meraih status mayoritasKehadiran pemilih77.4%Kandidat Partai pertama Partai kedua Partai ketiga Ketua Otto Wels Oskar Hergt Constantin Fehrenbach Partai SPD DNVP Tengah Ketua sejak 1919 1919 1923 Pemilu sebelumnya 102 kursi 71 kursi 64 kursi Kursi yang dimenangkan 100 95 65 Perubahan kursi 2 24 1 Suara Popular 6,008,905 5,696,...

1998 single by Jewel HandsSingle by Jewelfrom the album Spirit B-side Innocence Maintained Enter from the East (acoustic) ReleasedOctober 7, 1998 (1998-10-07)StudioGroove Masters (Santa Monica, California)Length 3:54 (album version) 3:47 (radio edit) LabelAtlanticComposer(s) Jewel Kilcher Patrick Leonard Lyricist(s)Jewel KilcherProducer(s)Patrick LeonardJewel singles chronology Morning Song (1998) Hands (1998) Down So Long (1999) Music videoHands on YouTube Hands is a song by A...





