1965 Puget Sound earthquake
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Versi berduri dari gedik tikam petani bergagang panjang. Dari manual tempur Paulus Hector Mair Arte De Athletica Gedik tikam adalah senjata yang terdiri dari kepala pemukul yang diikatkan pada pegangan dengan tali, atau rantai yang fleksibel. Keutamaan taktis utama dari pukulan ini adalah kemampuannya untuk menyerang perisai atau tangkisan pemain bertahan. Tanggung jawab utamanya adalah kurangnya presisi dan kesulitan menggunakannya dalam pertempuran jarak dekat, atau formasi jarak dekat. Ada...
Heubach Lambang kebesaranLetak Heubach di Ostalbkreis NegaraJermanNegara bagianBaden-WürttembergWilayahStuttgartKreisOstalbkreisSubdivisions2 StadtteilePemerintahan • MayorKlaus MaierLuas • Total25,81 km2 (997 sq mi)Ketinggian466 m (1,529 ft)Populasi (2021-12-31)[1] • Total9.892 • Kepadatan3,8/km2 (9,9/sq mi)Zona waktuWET/WMPET (UTC+1/+2)Kode pos73540Kode area telepon07173Pelat kendaraanAASitus webwww....
Ettenstatt. Ettenstatt adalah kota yang terletak di distrik Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen di Bavaria, Jerman. Kota Ettenstatt memiliki luas sebesar 15.84 km² . Ettenstatt pada tahun 2006, memiliki penduduk sebanyak 861 jiwa. lbsKota dan kotamadya di Weissenburg-GunzenhausenAbsberg | Alesheim | Bergen | Burgsalach | Dittenheim | Ellingen | Ettenstatt | Gnotzheim | Gunzenhausen | Haundorf | Heidenheim | Höttingen | Langenaltheim ...
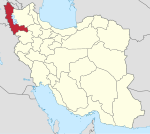
Village in West Azerbaijan province, Iran For other places with a similar name, see Haftvan. Village in West Azerbaijan, IranHaftevan Persian: هفتوانVillageSt. George Church, a 13th century Armenian churchHaftevanCoordinates: 38°10′04″N 44°45′24″E / 38.16778°N 44.75667°E / 38.16778; 44.75667[1]CountryIranProvinceWest AzerbaijanCountySalmasDistrictCentralRural DistrictZulachayPopulation (2016)[2] • Total8,203Time zoneUT...

La presse quotidienne nationale française est riche de 19 titres payants, dont 5 sont diffusés à plus de 100 000 exemplaires[1], et de 2 titres gratuits. Pour ce qui est de la diffusion, la presse gratuite a largement dépassé la presse payante. Celle-ci souffre, outre de son coût, d'un déficit de points de vente[réf. nécessaire]. Presse quotidienne nationale française payante Presse quotidienne nationale française payante nom Date de fondation Fondateur Remplace o...

Edition of USA college basketball tournament 2004 NCAA Division Imen's basketball tournamentSeason2003–04Teams65Finals siteAlamodomeSan Antonio, TexasChampionsConnecticut Huskies (2nd title, 2nd title game,2nd Final Four)Runner-upGeorgia Tech Yellow Jackets (1st title game,2nd Final Four)SemifinalistsDuke Blue Devils (14th Final Four)Oklahoma State Cowboys (6th Final Four)Winning coachJim Calhoun (2nd title)MOPEmeka Okafor (Connecticut)Attendance716,899Top scorerBen Gordon (Connecticut)...

Struktur 3D alfa-amilase. Alfa-amilase (Inggris: alpha-amylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan glucanohydrolase, pancreatic alpha-amylase, α-amilase, PA) adalah salah satu enzim yang berperan dalam proses degradasi pati, sejenis makromolekul karbohidrat.[1] Struktur molekuler dari enzim ini adalah α-1,4-glukanohidrolase.[2] Bersama dengan enzim pendegradasi pati lain, pululanase, α-amilase termasuk ke dalam golongan enzim kelas 13 glikosil hidrolase (E.C.3.2.1.1).[2][3&...

Lebanese Shia dynasty/political clan El AssaadالأسعدEmirs (Princes) of Belad Bechara and Bakaweit of South LebanonEl Assaad Headquarters 1749-1893CountryJabal Amil, LebanonPlace of originNajdFounded1706FounderAli Al-SaghirNasif al-NassarFinal rulerKamil Bey El Assaad (El-Esat)Titles Emir of Belad Bechara (Previously) Bek or Bey El-Assaad or Al As'ad (Arabic: الأسعد) is an Arab feudal political family/clan originally from Najd and a main branch of the Anizah tribe.[1] Unrel...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с именем Главк. Главк Морскойдр.-греч. Γλαῦκος Пол мужской Отец Полиб, Anthedon[d] или Посейдон Мать Евбея[d] или Алкиона Дети Деифоба[d] Медиафайлы на Викискладе Главк Морской или Главк Понтийский (др.-греч. Γλαῦκος) — в древнегр�...

Eastern Catholic ecclesiastical jurisdiction in France Ordinariate for Eastern Catholics in FranceLocationCountryFranceStatisticsPopulation- Catholics(as of 2019)25,100Parishes11InformationEstablished16 June 1954Current leadershipPopeFrancisBishopMichel AupetitBishops emeritusAndré Vingt-Trois Greek Church of Cargèse in Corsica. Melkite Church of Saint-Julien-le-Pauvre in Paris. Saint Ephrem Church in Paris, Syrian Catholic Church The Ordinariate for Eastern (Rite) Catholics in France ...

Vittorio De Sica nel film Il generale Della Rovere (1959) Vittorio De Sica, all'anagrafe Vittorio Domenico Stanislao Gaetano Sorano De Sica[1] (Sora, 7 luglio 1901 – Neuilly-sur-Seine, 13 novembre 1974), è stato un attore, regista e sceneggiatore italiano. Tra i cineasti più influenti della storia del cinema, è stato inoltre attore di teatro e documentarista. È considerato uno dei padri del neorealismo e uno dei maggiori registi e interpreti della commedia all'italiana.[2 ...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

Video game digital distribution service This article may contain an excessive amount of intricate detail that may interest only a particular audience. Please help by spinning off or relocating any relevant information, and removing excessive detail that may be against Wikipedia's inclusion policy. (July 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) SteamThe Steam client as of June 2023, showing the storeDeveloper(s)Valve CorporationInitial releaseSeptember 12, 2003; 20 years ...

Jannatul Baqi graveyard in Medina, Saudi Arabia The destruction of heritage sites associated with early Islam is an ongoing phenomenon that has occurred mainly in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia, particularly around the two holiest cities of Islam, Mecca and Medina.[1] The demolition has focused on mosques, burial sites, homes and historical locations associated with the Islamic prophet Muhammad, his companions, and many of the founding personalities of early Islamic history...
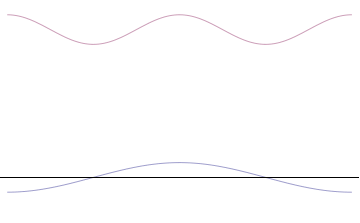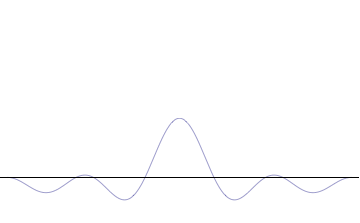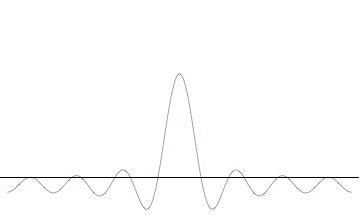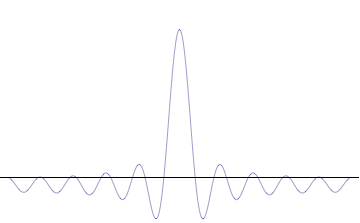
Foundational principle in quantum physics For other uses, see Uncertainty principle (disambiguation). Part of a series of articles aboutQuantum mechanics i ℏ d d t | Ψ ⟩ = H ^ | Ψ ⟩ {\displaystyle i\hbar {\frac {d}{dt}}|\Psi \rangle ={\hat {H}}|\Psi \rangle } Schrödinger equation Introduction Glossary History Background Classical mechanics Old quantum theory Bra–ket notation Hamiltonian Interference Fundamentals Complementarity Decoherence Entangle...

Ian MurdockLahir(1973-04-28)28 April 1973 Konstanz, Jerman BaratMeninggal28 Desember 2015(2015-12-28) (umur 42)AlmamaterUniversitas PurduePekerjaanIlmuwan komputer, Pengembang sumber terbuka, WirausahawanTempat kerjaDockerDikenal atasDebian GNU/Linux Ian Ashley Murdock (28 April 1973 – 28 Desember 2015[1][2]) adalah pengembang perangkat lunak, dikenal sebagai pencetus dan pembuat proyek Debian (dirintisnya sejak masih berada di bangku Universitas Purdue) ...

هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (أكتوبر 2022) مياه باطنية عميقة في منطقة الشيبة بصحراء الربع الخالي. عروق الشيبة كثبان رملي�...

South Korean girl group Le SserafimLe Sserafim in June 2022From left to right: Kazuha, Yunjin, Sakura, Chaewon, and EunchaeBackground informationOriginSeoul, South KoreaGenresK-popYears active2022–presentLabelsSourceEMI/Universal[1]Geffen[2][3]Members Sakura Chaewon Yunjin Kazuha Eunchae Past membersGaramWebsiteOfficial website Le Sserafim (/lə ˈsɛrəfɪm/ luh SERR-uh-fim;[4] Korean: 르세라핌; RR: Reuserapim; MR: Lŭs...

Junaidi Rachmat Junaidi Rachmat (lahir 8 Juli 1964) adalah seorang politikus dan birokrat Indonesia kelahiran Rengat. Ia merupakan lulusan S1 Institut Ilmu Pemerintahan Jakarta (1995) dan S2 Universitas Riau. Ia sempat diangkat menjadi Sekwilcam Tempuling di Pemkab Indragiri Hilir (1995), Camat Rengat Barat (2001), Camat Pasir Penyu (2002), Kabag Kepegawaian Pemkab Indragiri Hulu (2003), Kepala Bapemas Pemdes Pemkab Indragiri Hulu (2006), Kepala Dispenda Pemkab Indragiri Hulu (2007), Kepala B...

This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: Battle of the Bogue – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) For the 1856 battle, see Battle of the Bogue (1856). Battle of the BoguePart of the First Opium WarThe Nemesis attacking a masked battery and war junks behind Anunghoy Island on 23 Fe...

