Child Labor Amendment
|
Read other articles:

1964 Apollo Program test flight AS-101AS-101 (SA-6)Mission typeSpacecraft aerodynamicsOperatorNASACOSPAR ID1964-025A SATCAT no.800Mission duration~5 hours, 53 minutesOrbits completed54 Spacecraft propertiesSpacecraftApollo BP-13Launch mass7,700 kilograms (17,000 lb) Start of missionLaunch dateMay 28, 1964, 17:07:00 (1964-05-28UTC17:07Z) UTCRocketSaturn I SA-6Launch siteCape Kennedy LC-37B End of missionDisposalUncontrolled reentryLast contactMay 28, 1964 (1964-05...

For the American musical review, see Star and Garter. Building in London, UKThe Royal Star and Garter HomeThe Royal Star and Garter HomeGeneral informationLocationRichmond, London, UKCoordinates51°27′01″N 0°17′51″W / 51.4502°N 0.2974°W / 51.4502; -0.2974Construction started1921Completed1924Design and constructionArchitect(s)Sir Edwin Cooper, based on a 1915 plan by Sir Giles Gilbert Scott[1] Listed Building – Grade IIOfficial nameRoyal Star and G...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir The Witness. The WitnessDéveloppeur Thekla, Inc.Éditeur Thekla, Inc.Réalisateur Jonathan Blow (conception, programmation, écriture) Ignacio Castaño, Salvador Bel Murciano, Andrew Smith (programmation) Luis Antonio, Orsolya Spanyol, Eric A. Anderson (direction artistique) Goeun Lee (écriture)Début du projet 2008Date de sortie Windows, PlayStation 426 janvier 2016 Xbox One13 septembre 2016 Nvidia Shield16 janvier 2017 Mac OS8 mars 2017 iOS21 septembre 2...

Laptop by Apple Computer PowerBook 150PowerBook 150DeveloperApple ComputerProduct familyPowerBook (100 series)TypeLaptopRelease dateJuly 18, 1994 (1994-07-18)Introductory priceUS$1,450 (equivalent to $2,981 in 2023)–US$1,600 (equivalent to $3,289 in 2023)DiscontinuedOctober 14, 1995 (1995-10-14)Operating systemSystem 7.1.1 - Mac OS 7.6.1CPUMotorola 68030 @ 33 MHzDisplay9.5 grayscale passive-matrix LCD The PowerBook 150 is a laptop personal computer...

1990 studio album by Jimmy Cauty as SpaceSpaceStudio album by Jimmy Cauty as SpaceReleased16 July 1990RecordedTrancentralGenre Ambient house space music Length38:21LabelKLF CommunicationsProducerJimmy Cauty Space is a 1990 ambient house concept album by Jimmy Cauty under the alias Space. Originally intended to be The Orb's debut album, Space was refactored for release as a solo album following Cauty's departure from that group. Space was independently released on KLF Communications, t...

Untuk makhluk hidup, lihat porifera. Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang alat kebersihan. Untuk penggunaan lain, lihat Spons (disambiguasi). Artikel ini perlu dikembangkan agar dapat memenuhi kriteria sebagai entri Wikipedia.Bantulah untuk mengembangkan artikel ini. Jika tidak dikembangkan, artikel ini akan dihapus. Spons serat alami: Spons serat kayu yang dikombinasikan dengan sabut gosok. Spons adalah alat atau alat bantu pembersih yang terbuat dari bahan yang lembut dan berpori. Biasanya di...
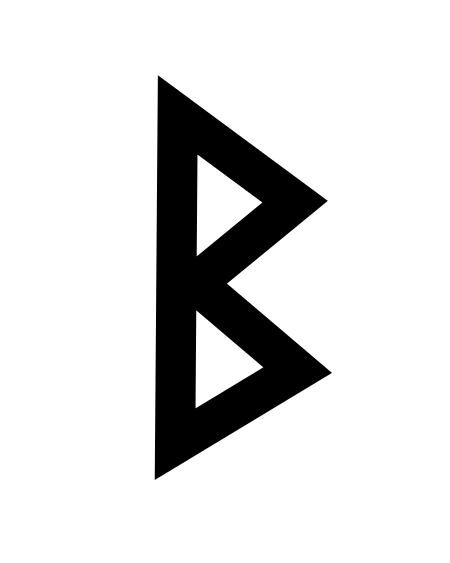
此條目介紹的是拉丁字母中的第2个字母。关于其他用法,请见「B (消歧义)」。 提示:此条目页的主题不是希腊字母Β、西里尔字母В、Б、Ъ、Ь或德语字母ẞ、ß。 BB b(见下)用法書寫系統拉丁字母英文字母ISO基本拉丁字母(英语:ISO basic Latin alphabet)类型全音素文字相关所属語言拉丁语读音方法 [b][p][ɓ](适应变体)Unicode编码U+0042, U+0062字母顺位2数值 2歷史發...

1982 French animated film Les Maîtres du tempsDirected byRené LalouxTibor Hernádi (technical director)Written byMœbiusRené LalouxJean-Patrick ManchetteStefan WulBased onL'Orphelin de Perdideby Stefan WulProduced byMiklós SalunsinskyStarringJean ValmontMichel EliasFrédéric LegrosYves-Marie MaurinMonique ThierrySady RebbotCinematographyZoltán BacsóAndrás KlauszMihály KovácsÁrpád LossonczyEdited byDominique BoischotMusic byJean-Pierre BourtayrePierre TardyChristian ZanesiProductio...

2008 Single by Cassie featuring Lil Wayne Official GirlSingle by Cassie featuring Lil WayneReleasedAugust 5, 2008 (2008-08-05)Recorded2007–08; Legacy Studios(New York City)GenreElectro-R&BLength4:17Label Bad Boy NextSelection Atlantic Songwriter(s) Balewa Muhammad Candice Nelson Ezekiel Lewis Dwayne Carter Nathaniel Hills Marcella Araica Producer(s) Danja Cassie singles chronology Addiction (2008) Official Girl (2008) Must Be Love (2009) Lil Wayne singles chronol...

馬哈茂德·艾哈迈迪-内贾德محمود احمدینژاد第6任伊朗總統任期2005年8月3日—2013年8月3日副总统帷爾維茲·達烏迪穆罕默德-禮薩·拉希米领袖阿里·哈梅內伊前任穆罕默德·哈塔米继任哈桑·魯哈尼不结盟运动秘书长任期2012年8月30日—2013年8月3日前任穆罕默德·穆尔西继任哈桑·魯哈尼德黑蘭市長任期2003年6月20日—2005年8月3日副职阿里·賽義德盧前任哈桑·馬利克邁達尼�...

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6]...

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) ...
Moosinning Lambang kebesaranLetak Moosinning di Erding NegaraJermanNegara bagianBayernWilayahOberbayernKreisErdingPemerintahan • MayorPamela Kruppa (CSU)Luas • Total39,96 km2 (1,543 sq mi)Ketinggian489 m (1,604 ft)Populasi (2013-12-31)[1] • Total5.507 • Kepadatan1,4/km2 (3,6/sq mi)Zona waktuWET/WMPET (UTC+1/+2)Kode pos85452Kode area telepon08123Pelat kendaraanEDSitus webwww.moosinning.de Moosinning adal...

1991 EP by the Cranberries UncertainEP by The CranberriesReleased28 October 1991StudioXeric Studios, Limerick, IrelandGenreIndie rockindie popalternative rockLength14:16LabelXeric Records (XER-014)ProducerPearse Gilmore[1]The Cranberries chronology Nothing Left at All(1990) Uncertain(1991) Everybody Else Is Doing It, So Why Can't We?(1993) Uncertain is the first EP by the Irish band the Cranberries.[1] The EP was released in the autumn of 1991,[1] with the band hav...

Kongres Nepal नेपाली काँग्रेसSingkatanNCPresidenSher Bahadur DeubaWakil PresidenBimalendra Nidhi Bijay Kumar Gachhadar[1]Sekretaris JenderalDr. Shashank Koirala Purna Bahadur Khadka[1]Juru BicaraBishwa Prakash Sharma[1]PendiriB. P. Koirala dan lainnyaDibentuk9 April 1950; 74 tahun lalu (1950-04-09)Digabungkan dariKongres Nasional Nepal Kongres Demokratik NepalKantor pusatB.P. Smriti Bhawan, B.P. Nagar, Lalitpur, Nepal[2]Say...

Structure constructed to convey water Not to be confused with Navigable aqueduct. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Aqueduct water supply – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The Central Arizona Project carries water from the...
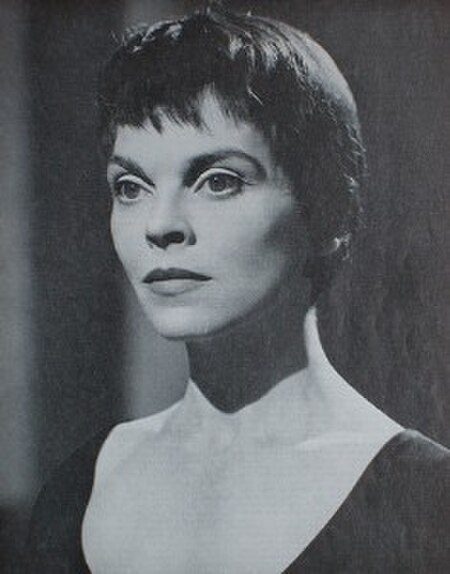

British actress (1915–1988) For other people named Mary Morris, see Mary Morris (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Mary Morris – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Mary MorrisBornMary Lilian Agnes Morris(1915-1...

هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (يونيو 2018) لقب الشرف أو لقب التشريف هو عنوان يتم منحه للأفراد أو المنظمات كجائزة تقد�...

National flag South SudanUseNational flag Proportion1:2Adopted9 July 2005; 18 years ago (2005-07-09)9 July 2011; 12 years ago (2011-07-09) (as national flag)25 August 2023; 10 months ago (2023-08-25) (colors standardized)DesignA horizontal tricolour of black, red, and green, fimbriated with white stripes; with a sky-blue equilateral triangle based on the hoist side bearing a yellow starDesigned bySamuel Ajak Use Less commonly used ver...

日本 > 兵庫県 > 神戸市 > 垂水区 > 王居殿 王居殿 大字 神戸市立東垂水小学校 王居殿王居殿の位置 北緯34度38分09秒 東経135度04分16秒 / 北緯34.63583度 東経135.07111度 / 34.63583; 135.07111国 日本都道府県 兵庫県市町村 神戸市区 垂水区地区 東垂水地区人口(2021年(令和3年)12月31日現在)[1] • 合計 1,794人等時帯 UTC+9 (日本標�...

