Zeppelin L 30
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Untuk organisasi nirlaba, lihat Artforum Culture Foundation. ArtforumSampul Artforum edisi Mei 2019EditorDavid VelascoMantan editorMichelle Kuo, Ingrid Sischy, Jack BankowskyKategorimajalah seniFrekuensiBulananPendiriJohn P. Irwin, Jr.Didirikan1962NegaraASBerpusat diNew York CityBahasaInggrisSitus webwww.artforum.comISSN0004-3532 Artforum adalah sebuah majalah bulanan internasional khusus seni rupa kontemporer. Kontributor terkenal Walter Darby Bannard Andrew Berardini Maurice Berger Yve-Alai...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Ab MorgenSutradaraStefan ElsenbruchRaphael WallnerSkenarioStefan ElsenbruchRaphael WallnerPemeranAnno KoehlerGordana Heyden-GueliSabina SidroAdem SmailhodzicPenata musikPhilipp F. KölmelSinematograferFabian SpangPenyuntingDaniel FalkTanggal ril...

Lange Flate Ballær IIkover DVDSutradaraHarald ZwartProduserHarald Zwart, Espen HornDitulis olehPål Sparre-EngerPemeranDon JohnsonJan Edgar FjellAnders FjellPetter JørgensenEirik Stener TobiassenKai Helge HansenHenrik Morken NielsenFrode LieLisa StokkeMarc SheltonLouise DedichenSteve BridgesPenata musikJohn GrahamSinematograferGeir Hartly AndreassenDistributorZwart ArbeidTanggal rilis17 Maret 2008Durasi90 menitNegara NorwegiaBahasaNorwegiaInggrisPrekuelLange Flate Ballær Lange Flate ...

Koordinat: 7°45′51″S 110°41′53″E / 7.764097°S 110.698194°E / -7.764097; 110.698194 CawasKecamatanPeta lokasi Kecamatan CawasNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TengahKabupatenKlatenPemerintahan • CamatDrs. Much. Nasir,MMPopulasi • Total54,756 jiwa (2.010)[1] jiwaKode pos57463Kode Kemendagri33.10.05 Kode BPS3310050 Luas34,37 km²Desa/kelurahan20 Kecamatan Cawas (Jawa: ꦕꦮꦱ꧀, translit. Cawas) adalah sebuah kecamat...

Ini adalah nama Korea; marganya adalah Park. Park Ji-yeonNama asal박지연LahirPark Ji-yeon7 Juni 1993 (umur 30)Seoul, Korea SelatanPekerjaanPenyanyiaktrisKarier musikGenreK-popInstrumenVokalTahun aktif2009 (2009)–sekarangLabelLongzhen Culture DevelopmentArtis terkaitT-araT-ara N4 Korean nameHangul박지연 Hanja朴芝妍[1] Alih AksaraBak Ji-yeonMcCune–ReischauerPak Chiyŏn Templat:Korean membutuhkan parameter |hangul=. Park Ji-yeon (lahir 7 Juni 1993), l...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's notability guideline for biographies. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be shown, the article is likely to b...

Former office in the English and British Royal Household Henry Pelham-Clinton, 2nd Duke of Newcastle served Cofferer of the Household between 1747 and 1754. The Cofferer of the Household was formerly an office in the English and British Royal Household. Next in rank to the Comptroller, the holder paid the wages of some of the servants above and below stairs, was a member of the Board of Green Cloth, and sat with the Lord Steward in the Court of the Verge.[1][2] The cofferer wa...

American girl group and dance ensemble Not to be confused with The Pussycats or Pussycat (band). The Pussycat DollsThe Pussycat Dolls in 2007 (L–R: Kimberly Wyatt, Jessica Sutta, Carmit Bachar, Nicole Scherzinger, Melody Thornton, Ashley Roberts)Background informationAlso known asPCDOriginLos Angeles, California, U.S.Genres R&B pop dance-pop Years active2003–20102019–2021Labels Interscope Access[1] Past members Carmit Bachar Nicole Scherzinger Ashley Roberts Kimberly Wyatt J...

IDELIS Logo du réseau Idelis. Véhicule du réseau Situation Pau et son agglomération Type BHNS, Autobus, Transport à la demande Entrée en service 3 juillet 2010 Lignes 23 Stations 903 arrêts Fréquentation 9.623.000 (2023) Propriétaire Syndicat mixte des transports urbains Pau-Porte des Pyrénées Exploitant Stap Site Internet idelis.fr Lignes du réseau BHNS : Temporis : Proximité : ...

Edition of USA college basketball tournament 2010 NCAA Division Imen's basketball tournamentTeams65Finals siteLucas Oil StadiumIndianapolis, IndianaChampionsDuke Blue Devils (4th title, 10th title game,15th Final Four)Runner-upButler Bulldogs (1st title game,1st Final Four)SemifinalistsWest Virginia Mountaineers (2nd Final Four)Michigan State Spartans (8th Final Four)Winning coachMike Krzyzewski (4th title)MOPKyle Singler (Duke) NCAA Division I men's tournaments «2009 2011» The 2010...

Konten dan perspektif penulisan artikel ini tidak menggambarkan wawasan global pada subjeknya. Silakan bantu mengembangkan atau bicarakan artikel ini di halaman pembicaraannya, atau buat artikel baru, bila perlu. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Inflation rate, United States and eurozone, January 2016 through November 2022 Tingkat inflasi[1] Negara/Regional 2020 2021 Aug 2022 Europe/Central Asia 1.2% 3.1% 9.1% Latin America/Caribbean 1.4% 4.3% 9.9% ...
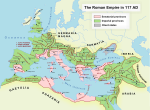
Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Makedonia. Provincia MacedoniaeΕπαρχια Μακεδονιας146 SM–Abad ke-7Provinsi Makedonia dalam Kekaisarn Romawi, sek. 117Ibu kotaThessalonika pada Antikuitas akhir: Thessalonica (Macedonia Prima) dan Stobi (Macedonia Salutaris)[1]Era SejarahAntikuitas• Didirikan setelah Perang Makedonia Keempat 146 SM• Balkan diserbu oleh bangsa Slav Abad ke-7 Kode ISO 3166MK Sunting kotak info • Lihat • BicaraBantuan penggunaan temp...

Artikel ini perlu dikembangkan dari artikel terkait di Wikipedia bahasa Inggris. (April 2024) klik [tampil] untuk melihat petunjuk sebelum menerjemahkan. Lihat versi terjemahan mesin dari artikel bahasa Inggris. Terjemahan mesin Google adalah titik awal yang berguna untuk terjemahan, tapi penerjemah harus merevisi kesalahan yang diperlukan dan meyakinkan bahwa hasil terjemahan tersebut akurat, bukan hanya salin-tempel teks hasil terjemahan mesin ke dalam Wikipedia bahasa Indonesia. Janga...

Football League Two 2012-2013Npower League Two 2012-2013 Competizione Football League Two Sport Calcio Edizione 55ª (9ª come League Two) Organizzatore Football League Date dal 18 agosto 2012al 18 maggio 2013 Luogo Inghilterra Galles Partecipanti 24 Formula girone all'italiana+play-off Risultati Vincitore Gillingham(2º titolo) Altre promozioni Rotherham United Port Vale Bradford City (dopo play off) Retrocessioni Aldershot Town Barnet Statistiche Miglior marcatore T...

Nicola Farron Nicola Farron, pseudonimo di Nicola Puddu (Oristano, 8 febbraio 1964), è un attore italiano. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Filmografia 2.1 Cinema 2.2 Televisione 3 Doppiatori italiani 4 Note 5 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Figlio di un imprenditore sardo e di un'insegnante irlandese da cui prende il cognome d'arte, cresce a Cagliari; dopo la scuola media si trasferisce a Chicago, dove consegue il diploma superiore per poi frequentare l'Actors Studio per due anni.[1][2] ...

KedunguterDesaNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TengahKabupatenBanyumasKecamatanBanyumasKode pos53192Kode Kemendagri33.02.11.2007 Luas... km²Jumlah penduduk... jiwaKepadatan... jiwa/km² Kedunguter adalah sebuah desa di kecamatan Banyumas, Banyumas, Jawa Tengah, Indonesia. Pranala luar (Indonesia) Keputusan Menteri Dalam Negeri Nomor 050-145 Tahun 2022 tentang Pemberian dan Pemutakhiran Kode, Data Wilayah Administrasi Pemerintahan, dan Pulau tahun 2021 (Indonesia) Peraturan Menteri Dalam Neg...
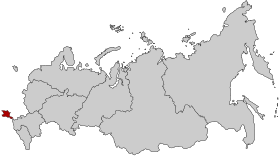
هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (مارس 2022) منطقة القرم الفيدرالية Крымский федеральный округКримський федеральний округ كيان اتحادي في روسيا موقع منطقة القرم الفيدرالية داخل روسيا الإحداثيات 44°56′53...

YouTube channel Star Wars TheoryStar Wars TheoryYouTube informationAlso known asToosChannelsStar Wars TheoryYears active2016–presentGenre(s)Entertainment/Film and TV/ AnimationSubscribers3.29 millionTotal views1.15 billion Creator Awards1,000,000 subscribers Last updated: 4 Apr 2024 Niatoos Dadbeh, better known by his YouTube channel, Star Wars Theory, is a Canadian YouTuber with 3.29 million subscribers,[1] and is a self-described Star Wars fan making content for other St...

American college basketball season 2014–15 Michigan State Spartans men's basketballNCAA tournament, Final FourConferenceBig Ten ConferenceRankingCoachesNo. 7APNo. 23Record27–12 (12–6 Big Ten)Head coachTom Izzo (20th season)Associate head coachDwayne Stephens (12th season)Assistant coaches Mike Garland (8th season) Dane Fife (4th season) Captains Branden Dawson Travis Trice Denzel Valentine Home arenaBreslin CenterSeasons← 2013–142015–16 ͛...

يوسف إدعيس مناصب وزير الأوقاف والشؤون الدينية في المنصب2 يونيو 2014 – 13 أبريل 2019 مجلس الوزراء حكومة رامي الحمد الله الثالثة محمود الهباش محمد اشتية معلومات شخصية الميلاد 19 أبريل 1964 (60 سنة) بدو (القدس) مواطنة دولة فلسطين عضو في حكومة رامي الحمد ال�...





