Welsh Government roads review
|
Read other articles:

Terasering di Indonesia Diagram yang menampilkan teknik terasering suku Inca dalam pertanian Terasering atau sengkedan merupakan metode konservasi dengan membuat teras-teras yang dilakukan untuk mengurangi panjang lereng, menahan air sehingga mengurangi kecepatan dan jumlah aliran permukaan, serta memperbesar peluang penyerapan air oleh tanah.[1] Jenis terasering antara lain teras datar (level terrace), teras kredit (ridge terrace), Teras guludan (contour terrace), dan teras bangku/ta...

Daniel Ek Daniel Ek dikenal sebagai co-founder dan CEO dari layanan streaming musik Spotify. Daniel Ek lahir pada 21 Februari 1983 di Stockholm, Swedia. Ia merupakan lulusan dari Royal institusi teknologi di Sundbyberg pada tahun 2002. Pada saat remaja, Daniel menciptakan website untuk bisnis dan menjalankannya pelayanan web-hosting nya dari luar ruangan. Ia keluar dari pendidikannya dan berkerja di perusahaan web-based untuk sementara waktu sebelum membangun Advertigo, yaitu sebuah perusahaa...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Logo IDTUG. Indonesia Telecommunication User Group (IDTUG) adalah sebuah organisasi yang bertujuan memperjuangkan hak pengguna jasa dan sarana telekomunikasi di Indonesia.[1] IDTUG merupakan salah satu anggota dari organisasi induk berskala in...

HistadrutNama lengkapFederasi Umum Pekerja di IsraelNama asliההסתדרות הכללית של העובדים בארץ ישראלHaHistadrut HaKlalit shel HaOvdim B'Eretz YisraelBerdiri1920; 104 tahun lalu (1920)Anggota800.000AfiliasiITUCSitus webwww.histadrut.org.il Histadrut atau Organisasi Pekerja Umum di Israel (Ibrani: ההסתדרות הכללית של העובדים בארץ ישראל, HaHistadrut HaKlalit shel HaOvdim B'Eretz Yisrael) adalah organisasi buruh nasional Israel...

Location of Rockland County in New York Map all coordinates using OpenStreetMap Download coordinates as: KML GPX (all coordinates) GPX (primary coordinates) GPX (secondary coordinates) List of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Rockland County, New York This is intended to be a complete list of properties and districts listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Rockland County, New York. The locations of National Register properties and districts (at least for al...

3rdBerkas:Club velez sarsfield crest.pngNama lengkapClub Atlético Vélez SársfieldJulukanEl FortínBerdiri1 Januari, 1910StadionStadion José Amalfitani,Liniers, Buenos Aires, Argentina(Kapasitas: 49,540)KetuaMiguel Ángel Russo[1]ManajerRicardo Antonio LaVolpeLigaLiga Utama ArgentinaClausura 20079 klasemen Kostum kandang Kostum tandang Tim Velez Sarsfield 1942 yang bermain di Divisi II. Penjaga gawangnya adalah Miguel Rugilo Singa Wembley. José M. Noguera juga bermain di tim ini. ...

Art movement This article is about the art movement. For other uses, see Pop art (disambiguation). Eduardo Paolozzi, I was a Rich Man's Plaything (1947). Part of his Bunk! series, this is considered the initial bearer of pop art and the first to display the word pop. Andy Warhol, Campbell's Tomato Juice Box, 1964. Synthetic polymer paint and silkscreen ink on wood, 10 inches × 19 inches × 9½ inches (25.4 × 48.3 × 24.1 cm), Museum of Modern Art, New York City Pop art is an art movement th...

Main airport serving Rio de Janeiro, Brazil For the military use of this facility, see Galeão Air Force Base. Rio de Janeiro Airport redirects here. For the second commercial airport serving the city, see Santos Dumont Airport. Rio de Janeiro/Galeão–Antonio Carlos Jobim International AirportAeroporto Internacional do Rio de Janeiro/Galeão–Antonio Carlos JobimIATA: GIGICAO: SBGLLID: RJ0001SummaryAirport typePublic / MilitaryOperator ARSA (1973–1986) Infraero (1986–2013) RIOgaleão (...
City in North Dakota, United StatesFlasher, North DakotaCityPost office in Flasher, North DakotaNickname: Little Town on the Black Hills TrailMotto: The past is appreciated but we must move forward[citation needed]Location of Flasher, North DakotaCoordinates: 46°27′08″N 101°13′57″W / 46.45222°N 101.23250°W / 46.45222; -101.23250CountryUnited StatesStateNorth DakotaCountyMortonFounded1902Area[1] • Total0.65 sq ...

Protected area in central Alberta, Canada This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's notability guideline for geographic features. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notab...

German orthodox Lutheran theologian This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (May 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Valentin Ernst Löscher Valentin Ernst Löscher (born at Sondershausen 29 December 1673; died at Dresden 12 December 1749) was a German orthodox Lutheran theologian. At the University of W...

American baseball player (born 1950) Baseball player Lloyd AllenPitcherBorn: (1950-05-08) May 8, 1950 (age 74)Merced, California, U.S.Batted: RightThrew: RightMLB debutSeptember 1, 1969, for the California AngelsLast MLB appearanceJuly 27, 1975, for the Chicago White SoxMLB statisticsWin–loss record8–25Earned run average4.69Strikeouts194 Teams California Angels (1969–1973) Texas Rangers (1973–1974) Chicago White Sox (1974–1975) Lloyd Cecil Allen (b...

This article is written like a personal reflection, personal essay, or argumentative essay that states a Wikipedia editor's personal feelings or presents an original argument about a topic. Please help improve it by rewriting it in an encyclopedic style. (April 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The 29th Provisional Ranger Battalion was a United States Army unit in World War II. Formed in December 1942 in England as a detachment of volunteers from the 29th Infantry Division, t...

Railway station in Bihar, India Anugraha Narayan Road Indian Railways stationAnugraha Narayan Road railway stationGeneral informationLocationAnugraha Narayan Road, Aurangabad, BiharIndiaCoordinates24°51′21″N 84°19′47″E / 24.8558°N 84.3297°E / 24.8558; 84.3297Elevation104 metres (341 ft)Owned byIndian RailwaysLine(s)Gaya–Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Junction sectionPlatforms4Tracks6ConnectionsAuto and bus stand, food stall, drinking waterConstructionSt...

Keresahan makanan di Indonesia 2005 adalah keresahan makanan yang terjadi pada tahun 2005 di Jakarta, Indonesia, ketika pemerintah menemukan bahwa 60% dari toko mie di ibu kota telah menjual mie yang dicampur dengan formaldehida, suatu karsinogen yang cukup dikenal. Mie pada keresahan makanan di Vietnam pada tahun 2007 juga memiliki kontaminan yang sama, dan pengawet kimia yang juga jelas ditemukan pada tahu, mie, dan ikan asin. Thailand[1] memiliki masalah formaldehida yang serupa. R...

Public radio station in Hesse, Germany You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (August 2023) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia. Consider addin...

الإقليم الكشفي اليوروآسيوي الإقليم الكشفي اليوروآسيوي المالك المنظمة العالمية للحركة الكشفية المقر كييف الموقع الإلكتروني https://www.scout.org/eurasia تعديل مصدري - تعديل الإقليم الكشفي اليوروآسيوي (بالروسية: Региональное Бюро Евразия) هو المكتب الشعبي للمكتب الكشفي العالمي ل�...
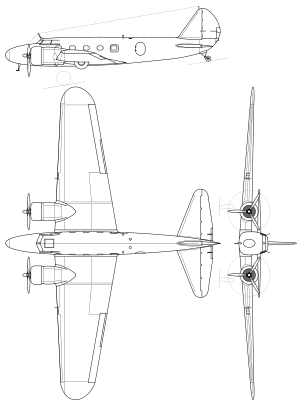
Boeing Model 247 adalah pesawat awal sayap rendah (low wing) Amerika Serikat, dianggap sebagai pesawat yang pertama untuk sepenuhnya menggabungkan[1][2] kemajuan seperti semua logam (aluminium anodized) konstruksi semi-monocoque, sayap kantilever dan landing gear tarik. Fitur canggih lainnya termasuk kontrol permukaan memangkas tab, autopilot dan deicing sepatu untuk sayap dan tailplane.[3] Referensi ^ Model 247 Commercial Transport. boeing.com, 2009. Retrieved: June ...

Bagian dari seriKonservatisme Varian Budaya Fiskal Hijau Liberal Libertarian Nasional Neo- Kanan Baru Satu bangsa Paleo- Agama Sosial Tradisionalis Konsep Konformitas Tradisi Norma sosial Familisme Tatanan sosial Patriotisme Hierarki sosial Hukum statuta Properti pribadi Proteksionisme Tokoh Edmund Burke Joseph de Maistre Louis de Bonald Adam Müller Pope Pius X Lucas Alamán François de Chateaubriand Antoine de Rivarol Klemens von Metternich Leopold von Ranke Nikolay Karamzin John A. Macdon...

Type of punch found in boxing This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Cross boxing – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2010) Cross (Straight punch)Cross for the stop in Burmese boxingAlso known as France: Direct (bras arrière) Albania:Direkt Serbia: Задњи дире...


