Weißig–Böhla railway
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Bahasa liturgis atau bahasa suci/sakral (dalam konteks agama; bahasa kudus) adalah suatu bahasa yang dibudidayakan dan digunakan terutama untuk ibadah keagamaan atau alasan keagamaan lainnya oleh orang-orang yang menggunakan bahasa utama lain dalam kehidupan mereka sehari-hari. Konsep Bahasa liturgis sering kali merupakan bahasa yang diucapkan dan ditulis dalam masyarakat di mana teks-teks suci agama pertama kali ditetapkan. Namun, teks-teks ini kemudian menjadi tetap dan suci, tetap beku dan...

Radio station in Decatur, TexasKRNBDecatur, TexasBroadcast areaDallas-Fort Worth Metroplex/Decatur/Bowie/ Gainesville/Jacksboro/WeatherfordFrequency105.7 MHzBrandingSmooth R&B 105.7ProgrammingLanguage(s)EnglishFormatUrban adult contemporaryAffiliationsPremiere NetworksOwnershipOwnerService Broadcasting CorporationSister stationsKKDA-FMHistoryFirst air date1996 (28 years ago) (1996)Call sign meaningK Rhythm aNd BluesTechnical informationFacility ID9747ClassCERP93,000 wattsHAA...

American comic book company MillarworldParent companyNetflixStatusActiveFounded2003; 21 years ago (2003)[1][2]FounderMark MillarCountry of originUnited StatesHeadquarters locationWest Hollywood, CaliforniaKey peopleMark Millar(President, CCO)[3][4]Fiction genresSuperhero fictionOfficial websitehttps://www.mrmarkmillar.com Millarworld Limited is an imprint of comic books published by Scottish comic book writer Mark Millar as a creator-owned lin...

Koordinat: 7°20′00″S 112°41′58″E / 7.333372°S 112.699424°E / -7.333372; 112.699424 Karangpilang ꦏꦫꦁꦥꦶꦭꦁ KecamatanPeta lokasi Kecamatan KarangpilangNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TimurKotaSurabayaPemerintahan • CamatEko Budi Susilo, S.H.Kode pos60222Kode Kemendagri35.78.01 Kode BPS3578010 Desa/kelurahan4 Karangpilang (Jawa: ꦏꦫꦁꦥꦶꦭꦁ, translit. Karang Pilang, [karaŋ pilaŋ]) adalah sebuah kecamatan di Kota S...

L'assemblea dei monaci descritta nel Sutra del Loto con la partecipazione dei bodhisattva e dei membri dell'aṣṭasenā in un dipinto giapponese del XIII secolo conservato al Metropolitan Museum of Art di New York. La simbologia del fiore di Loto è duplice. Da un lato rappresenta la vita che pur avendo le radici nel fango della mondanità aspira come il fiore verso l'alto, verso la buddhità. Dall'altro, come suggerito dal monaco cinese Huìsī (慧思, 515-577), il Loto non ha fiore che n...

Questa voce sull'argomento Stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: Unione Sportiva Ragusa. Unione Sportiva RagusaStagione 1978-1979Sport calcio Squadra Ragusa Allenatore Evaristo Malavasi poi Carlo Cesarato poi Roberto Salafia Presidente Carmelo Vitale Serie C216º nel girone D Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Mazza (34) Miglior mar...

County in Texas, United States County in TexasClay CountyCountyClay County Courthouse in HenriettaLocation within the U.S. state of TexasTexas's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 33°47′N 98°13′W / 33.79°N 98.21°W / 33.79; -98.21Country United StatesState TexasFounded1860Named forHenry ClaySeatHenriettaLargest cityHenriettaArea • Total1,117 sq mi (2,890 km2) • Land1,089 sq mi (2,820 km2) •...

Welsh photojournalist Philip Jones GriffithsBorn(1936-02-18)18 February 1936Rhuddlan, Denbighshire, WalesDied19 March 2008(2008-03-19) (aged 72)London, EnglandNationalityWelshOccupationPhotojournalismWebsitewww.philipjonesgriffiths.org Philip Jones Griffiths (18 February 1936 – 19 March 2008) was a Welsh photojournalist known for his coverage of the Vietnam War. Biography Jones Griffiths was born in Rhuddlan in Denbighshire, North Wales, to Joseph Griffiths, who supervised the local tr...

1989 studio album by D'erlangerLa Vie En RoseOriginal first press coverStudio album by D'erlangerReleasedFebruary 10, 1989RecordedOctober 1988StudioStar ShipGenrePunk rockgothic rockalternative rockpost-punkLabelDanger CrueProducerMasahiro OishiD'erlanger chronology La Vie En Rose(1989) Basilisk(1990) La Vie En Rose is the debut album by Japanese rock band D'erlanger, released on February 10, 1989.[1] It was instantly successful, having to be reissued three times that year alo...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada April 2017. Bruno Cabrerizo Informasi pribadiTanggal lahir 19 Juli 1979 (umur 44)Tempat lahir BrasilPosisi bermain BekKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2003 Sagan Tosu * Penampilan dan gol di klub senior hanya dihitung dari liga domestik Bruno Cabrerizo (lahi...

Goddess of truth in Roman mythology For other uses, see Veritas (disambiguation). VeritasGoddess of truthVeritas depicted on the tomb of Pope Alexander VIISymbolsnudityGenderfemaleOffspringVirtusEquivalentsGreek equivalentAletheia (debated) Statue of Veritas outside the Supreme Court of Canada Veritas is the name given to the Roman virtue of truthfulness, which was considered one of the main virtues any good Roman should possess. The Greek goddess of truth is Aletheia (Ancient Greek: Ἀλή�...

Japanese media franchise For the 2008 film, see Speed Racer (film). For other uses, see Speed Racer (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Speed Race. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Speed Racer – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this m...

Railway station in North Korea Nisŏ니서Korean nameHangul니서역Hanja尼西驛Revised RomanizationNiseo-yeokMcCune–ReischauerNisŏ-yŏk General informationLocationMundŏk County,South P'yŏngan ProvinceNorth KoreaOwned byKorean State RailwayHistoryElectrifiedyesServices Preceding station Korean State Railway Following station Mundŏktowards Dandong (China) P'yŏngŭi Line Sukch'ŏntowards P'yŏngyang Nisŏ station is a railway station in Mundŏk County, South P'yŏngan Province, North K...

Multi-purpose indoor arena in Piraeus, Greece Peace and Friendship StadiumSEFLocationNeo Faliro, Piraeus, GreeceCoordinates37°56′32.91″N 23°40′02.27″E / 37.9424750°N 23.6672972°E / 37.9424750; 23.6672972Public transit OwnerGreek StateOperatorOlympiacosCapacityBasketball: 11,640[2](permanent seating)12,300[3][4][5] (including court-side seats - current for Olympiacos games)14,776 (all collapsible bleachers in use)14,940 (all c...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Le Brigand bien-aimé. Le Brigand bien-aimé Affiche du film Données clés Titre original Jesse James Réalisation Henry King et Irving Cummings Scénario Nunnally Johnson Acteurs principaux Tyrone Power, Henry Fonda, Nancy Kelly, Randolph Scott Sociétés de production Twentieth Century Fox Pays de production États-Unis Genre Western Durée 101 minutes Sortie 1939 Pour plus de détails, voir Fiche technique et Distribution. modifier Le Brigand bien-aimé ...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento storia di famiglia non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Ramirez di MontalvoD'azzurro, alla sbarra diminuita di rosso, accompagnata nel capo da un leone d'oro, rivolto e passante sulla stessa, e in punta dal castello d'argento, aperto e torricellato di tre pe...

Roman God Not to be confused with Libre. For other uses, see Liber (disambiguation). LiberGod of wine-making, wine, male fertility, freedom. Member of the Aventine TriadFestivalsLiberaliaEquivalentsGreek equivalentDionysusEtruscan equivalentFufluns Religion inancient RomeMarcus Aurelius (head covered)sacrificing at the Temple of Jupiter Practices and beliefs libation votum temples festivals ludi funerary practices imperial cult mystery religions Priesthoods Pontifices Augures Vestales Flamine...

El transmisor Rigi es un transmisor de Swisscom en el Rigi, una montaña de 1798 metros de altura en Suiza central. Una torre de hormigón armado independiente de 96 metros de altura, que se construyó entre 1995 y 1997 y tiene una plataforma para visitantes de acceso público a una altura de 6 metros, sirve como soporte de la antena. Esta torre de transmisión reemplazó una torre de transmisión más antigua de 50 metros de altura con una antena de ranura tubular (llamada Rigi-Nadel) de 19...
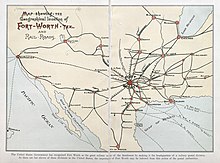
Cet article est une ébauche concernant la politique. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Map – showing – the Geographical location of Fort-Worth, Tex., and Rail-Roads, 1888. Le boosterism est un terme anglais désignant la promotion d’une ville ou d’une organisation en vue d’améliorer la perception publique de celle-ci. Il a été parfois associé aux petites villes américaines. Le boost...

Giacomo BerettaNazionalità Italia Altezza185 cm Peso80 kg Calcio RuoloAttaccante CarrieraGiovanili ????-2008 Varese2008-2009 AlbinoLeffe2009-2011 Milan Squadre di club1 2010-2011 Milan1 (0)2011-2012→ Ascoli14 (1)2012→ Juve Stabia8 (0)2012-2013→ Pavia29 (10)2013 Milan0 (0)2013-2014→ Lecce25 (4)[1]2014-2016→ Pro Vercelli59 (8)2016-2017→ Virtus Entella8 (0)2017→ Carpi14 (1)[2]2017-2018 Fog...



