Victor Lownes
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Campaign undertaken by the Spanish conquistadores Spanish conquest of El SalvadorPart of the Spanish colonization of the AmericasIndigenous ethnic groups of El Salvador, prior to Spanish conquestDate1524 – c. 1539LocationEl Salvador, Central AmericaResult Spanish victoryTerritorialchanges Incorporation of El Salvador into the Spanish EmpireBelligerents Spanish Empire, including Indian auxiliaries Indigenous peoples of El Salvador, including: Ch'orti' Maya people Lenca people Mangue people M...

Digestive organ This article is about the internal organ. For the middle part of the body, see Abdomen. For other uses, see Stomach (disambiguation). Gastric redirects here. For the sauce flavoring, see Gastrique. StomachScheme of digestive tract, with stomach in redSections of the human stomachDetailsPrecursorForegutSystemDigestive systemArteryRight gastric artery, left gastric artery, right gastro-omental artery, left gastro-omental artery, short gastric arteriesVeinRight gastric vein, left...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018)هذ قائمة بملاعب كرة القدم في ليبياهذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضا�...

GadiskuAlbum studio karya Trio LibelsDirilis1 Maret 1989Direkam1989GenrePopLabelMusica StudiosProduserSendjaya WijayaKronologi Trio Libels Gadisku (1989) Aku Suka Kamu (1990)'Aku Suka Kamu'1990 Gadisku adalah album dari grup musik trio Libels yang dirilis pada tahun 1989. Dalam album ini juga dirilis ulang hits Vina Panduwinata berjudul BIRU. Lagu yang danceable plus penampilan mereka yang fresh membuat album ini laris manis di pasaran dan menghasilkan banyak hits. Lagu ini pun pernah din...

Carl WeathersWeathers di New York Comic Con pada tahun 2017Lahir(1948-01-14)14 Januari 1948New Orleans, Louisiana, A.S.Meninggal1 Februari 2024(2024-02-01) (umur 76)Los Angeles, California, A.S.PendidikanUniversitas Negeri San Francisco (BA)Universitas Negeri San Diego (MA)PekerjaanAktorsutradaraTahun aktif1973–2024 (aktor)1970–1974 (pemain sepak bola)Suami/istriMary Ann Castle (m. 1973; c. 1983)Rhona Unsell ...

МифологияРитуально-мифологическийкомплекс Система ценностей Сакральное Миф Мономиф Теория основного мифа Ритуал Обряд Праздник Жречество Мифологическое сознание Магическое мышление Низшая мифология Модель мира Цикличность Сотворение мира Мировое яйцо Мифическое �...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Estienne. Jean Estienne Concours de l'Aéro Cyble à Mourmelon : Le colonel Estienne et le Général Herr en 1912 Surnom Le Père des chars Nom de naissance Jean Baptiste Eugène Estienne[1] Naissance 7 novembre 1860Condé-en-Barrois Décès 2 avril 1936 (à 75 ans)5e arrondissement de Paris Origine France Arme Artillerie Grade Général de division Années de service 1879 – 1922 Commandement 3e groupe d'aviation22e régiment...

Kamil Kopúnek Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Kamil KopúnekTanggal lahir 18 Mei 1984 (umur 39)Tempat lahir Trnava, CekoslowakiaTinggi 1,79 m (5 ft 10+1⁄2 in)Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini Slovan BratislavaNomor 14Karier junior Spartak TrnavaKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2002–2010 Spartak Trnava 196 (11)2010 Saturn Moscow Oblast 7 (0)2011 Bari 18 (0)2012– Slovan Bratislava 27 (0)Tim nasional‡2006– Slowakia 17 (2) * Penampilan dan go...
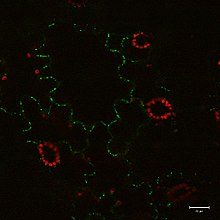
A pore connecting between adjacent plant cells The structure of a primary plasmodesma. CW=cell wall, CA=callose, PM=plasma membrane, ER=endoplasmic reticulum, DM=desmotubule, Red circles=actin, Purple circles and spokes=other unidentified proteins[1] Plasmodesmata (singular: plasmodesma) are microscopic channels which traverse the cell walls of plant cells[2] and some algal cells, enabling transport and communication between them. Plasmodesmata evolved independently in several...

Ferhat Abdi Şahin (lahir 1967), lebih dikenal dengan nom de guerre Mazloum Kobani Abdi (Kurdi : Mezlûm Ebdî – Arab : مظلوم عبدي) dan nom de guerre sebelumnya Şahin Cilo, adalah pemimpin militer Kurdi Suriah, menjabat sebagai panglima Pasukan Demokratik Suriah (SDF). Berbagai artikel berita menyebut dia dengan nama Mazlum Kobane.Mazloum AbdiMazlûm Kobanî Tahun 2019Nama asliBahasa Kurdi : Mazlûm EbdîBahasa Arab : مظلوم عبديNama lahirFerhat Abdi Sa...

1995 Rolling Stones concert film Voodoo Lounge LiveVHS videotape coverDirected byDavid MalletStarringThe Rolling StonesCinematographyToby PhillipsEdited byTim WaddellDistributed byPolyGram VideoRelease date 1995 (1995) Voodoo Lounge Live is a concert video by the rock band the Rolling Stones. It was filmed on 25 November 1994 at Joe Robbie Stadium in Miami Gardens, Florida during the Voodoo Lounge Tour. The concert was broadcast as a pay-per-view special. Voodoo Lounge Live was first rel...

History of U.S. presidents on postage stamps - George Washington -Issue of 1861Engraving modeled after the Gilbert Stuart portrait Presidents of the United States have frequently appeared on U.S. postage stamps since the mid-19th century. The United States Post Office Department released its first two postage stamps in 1847, featuring George Washington on one, and Benjamin Franklin on the other. The advent of presidents on postage stamps has been definitive to U.S. postage stamp design since ...

Contemporary hit radio station in Tacoma, Washington KBKS-FMTacoma, WashingtonBroadcast areaSeattle metropolitan areaFrequency106.1 MHz (HD Radio)BrandingHits 106.1ProgrammingFormatContemporary hit radioSubchannelsHD2: Pride RadioAffiliationsNBC News Radio (health updates only)Premiere NetworksOwnershipOwneriHeartMedia(iHM Licenses, LLC)Sister stationsKHHO, KJAQ, KJEB, KJR, KJR-FM, KPTR, KZOK-FMHistoryFirst air dateMay 1959; 65 years ago (1959-05)Former call signsKLAY-F...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Nebula. Nébula Personnage de fiction apparaissant dansAvengers, Silver Surfer. Cosplay de Nébula Alias Capitaine NébulaCommandant NébulaLady NébulaMs Peale Sexe Féminin Cheveux Chauve (Noirs à l'origine) Yeux Bleus Activité Mercenaire, Pirate Taille 1,85 m[1] Famille Gamora (sœur)Thanos (père adoptif) Affiliation Les GracesGroupes de piratesGardiens de la Galaxie Créée par Roger Stern (scénariste)John Buscema (dessinateur) Interprétée par...

Historic cemetery in Massachusetts, United States United States historic placeGriffin Street CemeteryU.S. National Register of Historic Places Show map of MassachusettsShow map of the United StatesLocationS 2nd and Griffin Sts., New Bedford, MassachusettsCoordinates41°37′42″N 70°55′22″W / 41.628323°N 70.922738°W / 41.628323; -70.922738Area1.69 acres (0.68 ha)Built1804NRHP reference No.14000062[1]Added to NRHPMarch 19, 2014 The Griffin...

Town in Java Not to be confused with the province of Banten in Java Island or the city of Batam in Riau Islands of Indonesia. 6°02′33″S 106°09′39″E / 6.0424495°S 106.1609316°E / -6.0424495; 106.1609316 Banten city from illustration c. 1724. Banten, also written as Bantam, is a port town near the western end of Java, Indonesia. It has a secure harbour at the mouth of Banten River, a navigable passage for light craft into the island's interior. The town is cl...

Contoh biak dini pada selada Dalam hortikultura, biak dini adalah produksi batang berbunga (atau batang) pada tanaman pertanian dan hortikultura sebelum panen, pada tahap ketika tanaman melakukan upaya alami untuk menghasilkan benih [1] dan berkembang biak . Batang berbunga biasanya merupakan perpanjangan kuat dari batang berdaun yang ada; untuk memproduksinya, tanaman mengalihkan sumber daya dari produksi bagian yang dapat dimakan (seperti daun atau akar), yang mengakibatkan perubah...

' تجمع بدو الرحيبة - قرية - تقسيم إداري البلد اليمن المحافظة محافظة حضرموت المديرية مديرية غيل باوزير العزلة عزلة غيل باوزير السكان التعداد السكاني 2004 السكان 57 • الذكور 30 • الإناث 27 • عدد الأسر 8 • عدد المساكن 8 معلومات أخرى التوقيت توقيت اليمن...

Process of getting coal out of the ground Coal miner redirects here. For the John J. Szaton statue, see Coal Miner (statue). A coal mine mantrip at Lackawanna Coal Mine in Scranton, Pennsylvania Coal miners exiting a winder cage at a mine near Richlands, Virginia in 1974 Surface coal mining in Wyoming, U.S. A coal mine in Frameries, Belgium Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground or from a mine. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely us...

Furniture associated with King Louis XVI of France Drop-front desk by Martin Carlin; oak veneered with tulipwood, amaranth, holly, and sycamore; six Sèvres soft-paste porcelain plaques and two painted tin plaques; gilt-bronze mounts; marble shelves; moiré silk (1776) Metropolitan Museum of Art. Louis XVI furniture is characterized by elegance and neoclassicism, a return to ancient Greek and Roman models. Much of it was designed and made for Queen Marie Antoinette for the new apartments she ...
