VA spacecraft
|
Read other articles:

Koordinat: 1°16′0″N 103°41′45″E / 1.26667°N 103.69583°E / 1.26667; 103.69583 Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Jurong. Nama Inggris: Jurong Island Tionghoa: 裕廊岛 (Pinyin: yùláng dǎo) Melayu: Pulau Jurong Tamil: - Pulau Jurong merupakan sebuah pulau buatan yang terletak di barat daya Singapura, pulau ini merupakan bagian dari Kawasan industri Jurong, salah satu kawasan industri di Singapura. Pulau ini terbentuk dari beberapa pulau kecil dari proses reklamas...

Zurich Insurance Group Ltd.JenisAktiengesellschaftKode emitenSIX: ZURNOTCQX: ZURVYIndustriJasa keuanganDidirikan1872KantorpusatZürich, SwissTokohkunciTom de Swaan (Ketua)Martin Senn (CEO)ProdukAsuransi jiwa dan non-jiwa, pensiun, investasiPendapatan AS$ 70.414.000.000 (2012)[1]Total aset AS$ 409.267.000.000 (2012)[1]Total ekuitas AS$ 34.494.000.000 (2012)[1]Karyawan60.000 (2012)[1]Situs webwww.zurich.com Zurich Insurance Group Ltd. (SIX: ZURN) a...

Содержание 1 Доисторический период 2 Ранняя история 2.1 Королевство Тондо 3 Испанский период (1521—1898) 4 Американский период (1898—1946) 5 Независимые Филиппины 6 Примечания 7 Литература 8 Ссылки Доисторический период Основная статья: Доисторические Филиппины Начиная с V века на т...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir DPJ. Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (juillet 2021). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique :...
此條目介紹的是拉丁字母中的第2个字母。关于其他用法,请见「B (消歧义)」。 提示:此条目页的主题不是希腊字母Β、西里尔字母В、Б、Ъ、Ь或德语字母ẞ、ß。 BB b(见下)用法書寫系統拉丁字母英文字母ISO基本拉丁字母(英语:ISO basic Latin alphabet)类型全音素文字相关所属語言拉丁语读音方法 [b][p][ɓ](适应变体)Unicode编码U+0042, U+0062字母顺位2数值 2歷史發...

New Zealand minister of the Crown Minister of EmploymentCoat of arms of New ZealandFlag of New ZealandIncumbentLouise Upstonsince 27 November 2023Ministry of Business, Innovation and EmploymentStyleThe HonourableMember of Cabinet of New Zealand Executive Council Reports toPrime Minister of New ZealandAppointerGovernor-General of New ZealandTerm lengthAt His Majesty's pleasureFormation22 September 1931First holderGordon CoatesSalary$288,900[1]Websitewww.beehive.govt.nz Politics of...

Bakteri lipofilik adalah sejenis bakteri yang memiliki lipofilisitas, dapat berkembang biak dalam lipid (zat lemak yang tidak larut dalam air, tetapi umumnya larut dalam alkohol dan eter). Risiko kesehatan Kebanyakan material/perlengkapan di laboratorium dan pusat kesehatan memiliki sejumlah kecil lipid pada permukaan bakteri ini dan dengan demikian dapat mendukung proliferasi bakteri lipofilik,[1] tetapi karena bakteri ini tidak patogenik,[2] hal tersebut bukan merupakan suat...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Bruno Ballarini Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Difensore Termine carriera 1972 Carriera Squadre di club1 1956-1957 Rovereto23 (11)1957-1958 Verona0 (0)1958-1970 Como350 (21)1971-1972 Chiasso4 (0) Carriera da allenatore 1971-1972 Chiasso 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le...

State legislative election 2022 Massachusetts Senate election ← 2020 November 8, 2022 2024 → All 40 seats in the Massachusetts Senate21 seats needed for a majorityRegistered4,884,076 [1] ( 1.48 pp)Turnout51.42% ( 24.58 pp) Majority party Minority party Leader Karen Spilka Bruce Tarr Party Democratic Republican Leader since February 28, 2018 January 3, 2011 Leader's seat 2nd Middlesex and Norfolk 1st Essex and Middlesex Last election 3...

Randwick Racecourse pada Derby Day 2007 Royal Randwick Racecourse adalah sebuah lintasan balap untuk balap kuda di Eastern Suburbs di Sydney, New South Wales. Randwick Racecourse dioperasikan oleh Australian Jockey Club dan digunakan banyak penyelenggara balap sebagai kantor pusat mereka. Lintasan balap ini terletak sekitar 6 km dari Sydney Central Business District di kota pinggiran Randwick. Lihat pula Daftar organisasi Australia dengan perlindungan kerajaan Pranala luar Australian Joc...
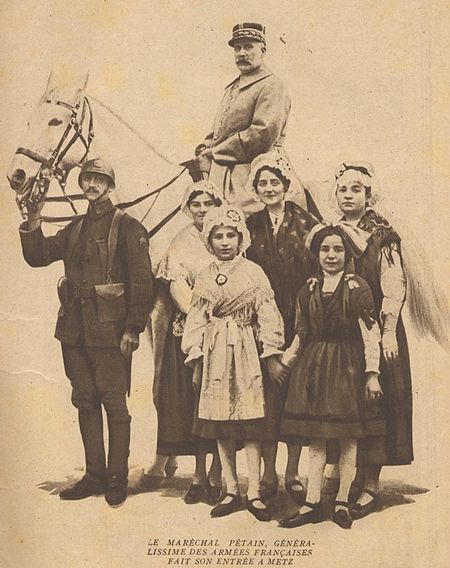

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Estienne. Jean Estienne Concours de l'Aéro Cyble à Mourmelon : Le colonel Estienne et le Général Herr en 1912 Surnom Le Père des chars Nom de naissance Jean Baptiste Eugène Estienne[1] Naissance 7 novembre 1860Condé-en-Barrois Décès 2 avril 1936 (à 75 ans)5e arrondissement de Paris Origine France Arme Artillerie Grade Général de division Années de service 1879 – 1922 Commandement 3e groupe d'aviation22e régiment...

Coppa del Mondo di sci alpino 1976 Uomini Donne Vincitori Generale Ingemar Stenmark Rosi Mittermaier Discesa libera Franz Klammer Brigitte Totschnig Slalom gigante Ingemar Stenmark Lise-Marie Morerod Slalom speciale Ingemar Stenmark Rosi Mittermaier Dati manifestazione Tappe 12 12 Gare individuali 25 26 1975 1977 La Coppa del Mondo di sci alpino 1976 fu la decima edizione della manifestazione organizzata dalla Federazione internazionale sci; ebbe inizio il 3 dicembre 1975 a Val-d'Isère, in ...

British politician (1931–1995) The neutrality of this article is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (January 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Geoffrey DickensMPMember of Parliamentfor Littleborough and SaddleworthIn office9 June 1983 – 17 May 1995Preceded byNew constituency Succeeded byChris DaviesMember of Parliamentfor Huddersfield WestIn office3 May 1979 – ...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...
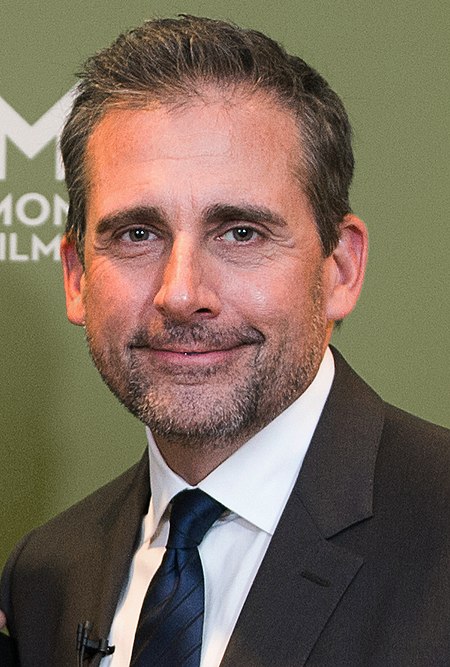

25th episode of the 5th season of The Office BrokeThe Office episodeEpisode no.Season 5Episode 25Directed bySteve CarellWritten byCharlie GrandyCinematography byRandall EinhornEditing byDavid RogersProduction code525Original air dateApril 23, 2009 (2009-04-23)Guest appearances Idris Elba as Charles Miner Andy Buckley as David Wallace Ellie Kemper as Erin Hannon Kurt Scholler as Ty Platt Episode chronology ← PreviousHeavy Competition Next →Casual Friday The O...

Boldo Ilustración de 1887 de P. boldusEstado de conservaciónPreocupación menor (UICN)[1]TaxonomíaReino: PlantaeDivisión: MagnoliophytaClase: MagnoliopsidaOrden: LauralesFamilia: MonimiaceaeGénero: PeumusEspecie: Peumus boldusMolina[2][editar datos en Wikidata] El boldo (Peumus boldus) es la única especie del género monotípico Peumus, de la familia de las monimiáceas. Este árbol es endémico de Chile. Sus hojas, de fuerte aroma, se utilizan con propós...
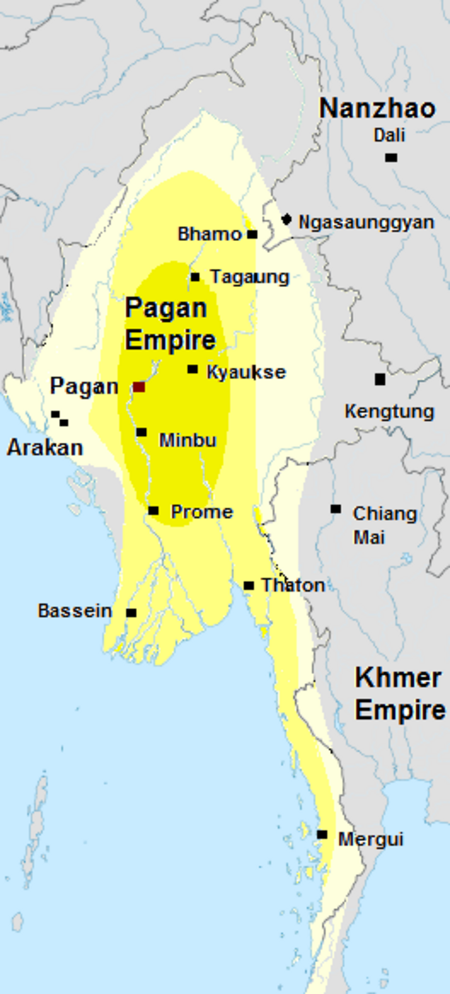
UNESCO historical city in Mandalay Region, Myanmar This article is about a city in Myanmar. For other uses, see Bagan (disambiguation). Place in Mandalay Region, MyanmarBagan ပုဂံPaganTemples and pagodas in BaganBaganLocation of Bagan, MyanmarCoordinates: 21°10′21″N 94°51′36″E / 21.17250°N 94.86000°E / 21.17250; 94.86000CountryMyanmarRegionMandalay RegionFoundedmid-to-late 9th centuryArea • Total104 km2 (40 sq mi)Populatio...
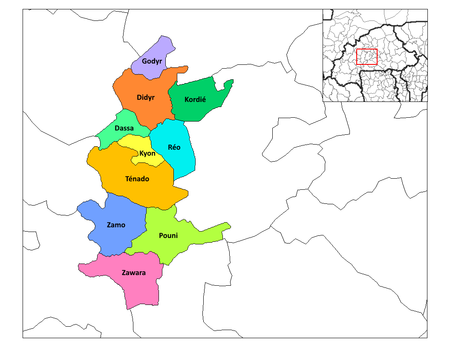
SanguieProvinsiLetak di Burkina FasoKoordinat: Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:ISO 3166/data/BF' not found.Negara Burkina FasoRegionRegion Centre-OuestIbu kotaRéoLuas • Total5,178 km2 (1,999 sq mi)Populasi (2006) • Total297.230 • Kepadatan57/km2 (150/sq mi)Zona waktuUTC+0 (GMT 0) Provinsi Sanguié adalah sebuah provinsi di Burkina Faso dan di Region Centre-Ouest. Ibu kota provinsi ini berada di Réo. Pada t...

American baseball player (born 1954) Baseball player Gary LucasLucas with the Beloit Snappers in 2008PitcherBorn: (1954-11-08) November 8, 1954 (age 69)Riverside, California, U.S.Batted: LeftThrew: LeftMLB debutApril 16, 1980, for the San Diego PadresLast MLB appearanceOctober 3, 1987, for the California AngelsMLB statisticsWin–loss record29–44Earned run average3.01Strikeouts410Saves63 Teams San Diego Padres (1980–1983) Montreal Expos (1984–1985) Cal...

2005 studio album by ZOEgirlRoom to BreatheStudio album by ZOEgirlReleasedMarch 15, 2005[1]Studio Sweetbriar Studios, The Loft, Pentavarit, Fireside Studios, Sound Stage Studios and The Lealand House (Nashville, Tennessee) Bridge Street Studios, Dark Horse Studios, Sound Kitchen, Fun Attic Studios and The Bennett House (Franklin, Tennessee) GenrePop rockCCMLength40:16LabelSparrowProducer Doubledutch (Josiah Bell & Robert Marvin) Tedd T Mark Heimmerman Shaun Shankel ZOEgir...